Table of Contents
<!-- Template Revision 1.66 (HTML comments will be not displayed in the document, no need to remove them. For Template/Skeleton changes, increase Template Revision number. So we can check faster, if the TRM style is up to date). --> |
<!-- General Notes: If some section is CPLD firmware dependent, make a note and if available link to the CPLD firmware description. It's in the TE shop download area in the corresponding module -> revision -> firmware folder. --> |
<!-- General Notes: Designate all graphics and pictures with a number and a description. For example "Figure 1: TE07xx-xx Block Diagram" or "Table 1: Initial delivery state". "Figure x" and "Table x" have to be formatted to bold. --> |
Table of Contents |
<!-- Wiki Link: Go to Base Folder of the Module or Carrier, for example : https://wiki.trenz-electronic.de/display/PD/TE0712 --> |
The Trenz Electronic TEF0008 is a FPGA to Mezzanine Card (FMC) based on VITA 57.1 FMC HPC Standard, with four SFP+ 10Gb fiber optical (850nm) ports. It is inteded for use on a FMC HPC carrier and can not be used stand-alone.

Figure 1: TEF0008-01 block diagram.
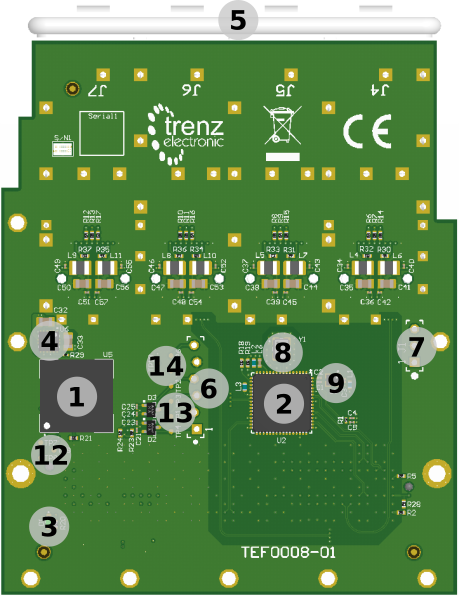

Figure 2: TEF0008-01 FMC overview.
Table 1: TEF0008-01 main components.
Storage device name | Content | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Max10 FPGA 10M08SAU169C8G | Programmed | U5. Level shifter and controlller functions. |
Clock generator Si5345A-B-GM | Programmed | U2, Only OUT7 (GBTCLK0) and OUT2 (GBTCLK1) enabeld. |
EEPROM 24LC128-I/ST | Programmed | U4, IPMI and VITA57.1 compatible. |
Table 2: Initial delivery state of programmable devices on the module.
The MAX10 FPGA boots form its internal configuration flash memory, which is programmable via JTAG.
<!-- Connections and Interfaces or B2B Pin's which are accessible by User --> |
I/O signals connected to the FPGA I/O bank and B2B connector:
| Bank | Type | B2B Connector | I/O Signal Count | Bank Voltage | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | GPI/Os | J2 | 20 I/Os | VADJ | Supplied by the carrier board. |
Table 3: General overview of I/O signals connected to the B2B connectors.
<!-- TO-DO (future): If Vivado board part files are available for this module, the standard configuration of the MIO pins by using this board part files should be mentioned here. This standard configuration of those pins are also apparent of the on-board peripherals of base-boards related to the module. --> |
<!-- MGT lanes should be listed separately, as they are more specific than just general I/Os. --> |
MGT (Multi Gigabit Transceiver) lane consists of one transmit and one receive (TD/RD) differential pairs, two signals each or four signals total per one MGT lane. Following table lists lane number, MGT bank number, transceiver type, signal schematic name, and HPC FMC Pin:
| Lane | SFP+ | Signal Name | HPC FMC Pin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | J4 |
|
|
| 1 | J5 |
|
|
| 2 | J6 |
|
|
| 3 | J7 |
|
|
Table 4: MGT lanes.
Below are listed MGT banks reference clock sources.
| Clock signal | Source | HPC FMC Pin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| GBTCLK0_P | U2-51 | J2-D4, GBTCLK0_M2C_P | On-board Si5345A. |
| GBTCLK0_N | U2-50 | J2-D5, GBTCLK0_M2C_N | On-board Si5345A. |
| GBTCLK1_P | U2-31 | J2-B20, GBTCLK1_M2C_P | On-board Si5345A. |
| GBTCLK1_N | U2-30 | J2-B21, GBTCLK1_M2C_N | On-board Si5345A. |
Table 5: MGT reference clock sources.
Follwowing table contains a brief description of the control and status signals of the SFP+ connectors:
| Signal Schematic Name | FPGA Direction | Description | Logic |
|---|---|---|---|
| SFPx_TX_DISABLE | Output | SFP Enabled / Disabled | Low active |
| SFPx_LOS | Input | Loss of receiver signal | High active |
| SFPx_RS0 | Output | Full RX bandwidth | Low active |
| SFPx_RS1 | Output | Reduced RX bandwidth | Low active |
| SFPx_M-DEF0 | Input | Module present / not present | Low active |
| SFPx_TX_FAULT | Input | Fault / Normal Operation | High active |
| SFPx_SDA | BiDir | 2-wire Serial Interface Data | - |
| SFPx_SCL | Output (BiDir) | 2-wire Serial Interface Clock | - |
Up to 100kHz the modules operate without clock streching. Therfore SCL can be implemented as driven by Master only. |
JTAG access to the MAX10 FPGA is provided through HPC FMC Connector and an additional pin header connector as well as testpoints.
JTAG Signal | HPC FMC Pin | Pin Header | Testpoints |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCK | J2-D29 | J3-4 | TP2 |
| TDI | J2-D33 | J3-2 | TP1 |
| TDO | J2-D30 | J3-3 | TP3 |
| TMS | J2-D31 | J3-1 | TP4 |
Table 6: JTAG interface signals.
<!-- For the detailed function of the pins and signals, the internal signal assignment and implemented logic, look to the Wiki reference page SC CPLD of this module or into the bitstream file of the SC CPLD. Add link to the Wiki reference page of the SC CPLD, if available. --> |
On-board I2C devices are connected to the HPC FMC Pin C30 SCL and pin C31 SDA which are reserved for I2C. Level shift and for PLL and SFP+ I²C is done by the FPGA as well as MUX for SFP+. Addresses for on-board devices are listed in the table below:
| I2C Device | I2C Address | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| J4, SFP+ | 1100001 / 1100000 | Conventional SFP Memory / Enhanced Feature Set Memory, SFP Device select via MAX10 FPGA implementation. |
| J5, SFP+ | 1100001 / 1100000 | Conventional SFP Memory / Enhanced Feature Set Memory, SFP Device select via MAX10 FPGA implementation. |
| J6, SFP+ | 1100001 / 1100000 | Conventional SFP Memory / Enhanced Feature Set Memory, SFP Device select via MAX10 FPGA implementation. |
| J7, SFP+ | 1100001 / 1100000 | Conventional SFP Memory / Enhanced Feature Set Memory, SFP Device select via MAX10 FPGA implementation. |
| U2, Si5345A | 1101001 | Level shifted via MAX10 FPGA |
| U4, EEPROM | 10100xx | Last digits determined by carrier board via HPC FMC (C34 GA0, C35 GA1). |
Table 7: I2C slave device addresses.
<!-- Components on the Module, like Flash, PLL, PHY... --> |
There is a Silicon Labs I2C programmable clock generator on-board (Si5345A, U2) to generate reference clocks for the module.
Not connected.
| Si5345A Pin | Signal Name / Description | Connected To | Direction | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
IN0 | Reference input clock. | U1 | Input | 25.000000 MHz oscillator, Si8208AI |
| IN1 | - | Not connected. | Input | Not used. |
IN2 | - | Not connected. | Input | Not used. |
IN3 | CLK2 | J2-K4/K5 | Input | HPC FMC configured as C2M clock. |
A1 | - | GND | Input | I2C slave device address LSB. |
| XAXB | - | Y1 | Input | 54.0000 MHz XTAL CX3225SB |
OUT0 | CLKPLL2F | U5-H6/G5 | Output | FPGA bank 2. |
| OUT1 | - | Not connected. | Output | Not used. |
| OUT2 | GBTCLK1 | J2-B20/B21 | Output | M2C via HPC FMC. |
| OUT3 | - | Not connected. | Output | Not used. |
| OUT4 | - | Not connected. | Output | Not used. |
| OUT5 | - | Not connected. | Output | Not used. |
| OUT6 | - | Not connected. | Output | Not used. |
| OUT7 | GBTCLK0 | J2-D4/D5 | Output | M2C via HPC FMC. |
| OUT8 | CLK0 | J2-H4/H5 | Output | M2C via HPC FMC. |
| OUT9 | CLK1 | J2-G2/G3 | Output | M2C via HPC FMC. |
Table 8: Programmable clock generator inputs and outputs.
The module has following reference clock signals provided by on-board oscillators and external source from carrier board:
| Clock Source | Schematic Name | Frequency | Clock Destination |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiTime SiT8008AI oscillator, U1 | - | 25.000000 MHz | U2-63/64 |
| Carrier board via HPC FMC J2-K4/K5 | CLK2 | Defined by carrier. | U2-61/62 |
Table 9: Reference clock signals.
A Microchip 24AA025E48 serial EEPROM (U23) contains a globally unique 48-bit node address, which is compatible with EUI-48(TM) specification. The device is organized as two blocks of 128 x 8-bit memory. One of the blocks stores the 48-bit node address and is write protected, the other block is available for application use. It is accessible over I2C bus with slave device address 0x53.
| LED | Color | Connected to | Description and Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | Green | U5-C2 (bank 1A) | Status LED: ... |
Table 10: On-board LEDs.
<!-- If power sequencing and distribution is not so much, you can join both sub sections together --> |
The maximum power consumption of a module depends on the design running on the FPGA.
| 3P3V | TBD* |
| VADJ (at 1.8V) | TBD* |
3P3VAUX | TBD* |
Table 11: Typical power consumption.
* TBD - To Be Determined with reference design setup.
Regulator dependencies and max. current.
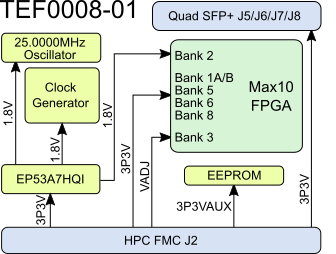
Figure 3: Module power distribution diagram.
Power Rail Name | HPC FMC Connector (J2) | Direction | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3P3V | D36, D38, D40, C39 | Input | Supply voltage from carrier board. |
| 1.8V | - | Output | Module on-board 1.8V voltage supply (Max 1A). |
| 3P3VAUX | D32 | Input | Supply voltage from carrier board. |
VADJ | H40, G39, F40, E39 | Input | Supply voltage from carrier board. |
| 12V | C35, C37 | Input | Not used supply voltage from carrier board. |
Table 12: Module power rails.
Bank | Schematic Name | Voltage | Voltage Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | 3P3V | 3.3V | - |
| 1B | 3P3V | 3.3V | - |
| 2 | 1.8V | 1.8V | - |
| 3 | VADJ | Carrier supplied | 1.2V - 3.3V |
| 5 | 3P3V | 3.3V | - |
| 6 | 3P3V | 3.3V | - |
| 8 | 3P3V | 3.3V | - |
Table 13: Module PL I/O bank voltages.
| Module Variant | FPGA | Operating Temperature | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| TE0008-01 | 10M08SAU169C8G | 0°C to +70°C | Commercial |
Table 14: Module variants.
Parameter | Min | Max | Units | Reference Document |
|---|---|---|---|---|
VIN supply voltage | V | - | ||
Storage temperature | °C | - |
Table 15: Module absolute maximum ratings.
| Parameter | Min | Max | Units | Reference Document |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN supply voltage | ||||
| Operating temperature |
Table 16: Module recommended operating conditions.
Commercial grade: 0°C to +70°C.
Module size: 69 mm × 84 mm, SFP+ conector excluded (+ 5.5 mm). See Vita 57.1 standard.
PCB thickness: 1.6 mm.
Highest part on PCB top is 9.5 mm (SFP+ cage, excluded front plate), bottom 1.4 mm (MAX10 FPGA). Please download the step model for exact numbers.
All dimensions are given in millimeters.
Figure 4: Module physical dimensions drawing
Mounting holes near the front pannel are not implemented due to physical restrictions caused by the SFP cage. The dimensions exceed in some area the by Vita 57.1 standard defined dimensions. In the middle region of the card the cage is higher than the specified max high for this area. The bottom side is at the high limit. |
| Date | Revision | Notes | PCN | Documentation Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 01 |
Table 17: Module hardware revision history.
Hardware revision number can be found on the PCB board together with the module model number separated by the dash.
Figure 5: Module hardware revision number.
<!-- Generate new entry: 1.add new row below first 2.Copy "Page Information Macro(date)" Macro-Preview, Metadata Version number, Author Name and description to the empty row. Important Revision number must be the same as the Wiki document revision number 3.Update Metadata = "Page Information Macro (current-version)" Preview+1 and add Author and change description. --> |
Date | Revision | Contributors | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Author Name | What changed? | ||
Martin Rohrmüller | Initial document. | ||
all | Jan Kumann, John Hartfiel |
Table 18: Document change history.