Template Revision 2.8 - on construction Design Name always "TE Series Name" + Design name, for example "TE0720 Test Board" |
<!-- tables have all same width (web max 1200px and pdf full page(640px), flexible width or fix width on menu for single column can be used as before) -->
<style>
.wrapped{
width: 100% !important;
max-width: 1200px !important;
}
</style> |
Important General Note: Export PDF to download, if vivado revision is changed! Designate all graphics and pictures with a number and a description, Use "Scroll Title" macro - Use "Scroll Title" macro for pictures and table labels. Figure number must be set manually at the moment (automatically enumeration is planned by scrollPDF)
- ...
|
Table of contents
|
Overview
Design example with Linux and MGT-CLK frequency monitoring over VIO.
Refer to http://trenz.org/teb0911-info for the current online version of this manual and other available documentation.
Key Features
Notes : - Add basic key futures, which can be tested with the design
|
- Vitis/Vivado 2019.2
- PetaLinux
- SD
- ETH
- MAC from EEPROM
- USB
- I2C
- PCIe
- DP
- FMeter
- LED
- Modified FSBL for SI5338 and SI5345 programming
- Special FSBL for QSPI programming
|
Revision History
Notes : - add every update file on the download
- add design changes on description
|

| Date | Vivado | Project Built | Authors | Description |
|---|
| 2020-06-03 | 2019.2 | TEB0911-test_board-vivado_2019.2-build_12_20200603131549.zip
TEB0911-test_board_noprebuilt-vivado_2019.2-build_12_20200603131603.zip | John Hartfiel | - bugfix usb3
- add nvme driver
| | 2020-03-25 | 2019.2 | TEB0911-test_board_noprebuilt-vivado_2019.2-build_8_20200325084706.zip
TEB0911-test_board-vivado_2019.2-build_8_20200325084633.zip | John Hartfiel | | | 2020-02-24 | 2019.2 | TEB0911-test_board_noprebuilt-vivado_2019.2-build_6_20200224080741.zip
TEB0911-test_board-vivado_2019.2-build_6_20200224080728.zip | John Hartfiel | - bugfix PL Design (all MGT buffer enabled)
| | 2020-02-13 | 2019.2 | TEB0911-test_board_noprebuilt-vivado_2019.2-build_5_20200213114513.zip
TEB0911-test_board-vivado_2019.2-build_5_20200213112730.zip | John Hartfiel | - 2019.2 update
- new assembly variants
- Vitis support
- FSBL SI programming procedure update
- petalinux device tree and u-boot update
- reduced DDR speed (see Xilinx Datasheet)
| | 2018-11-26 | 2018.2 | TEB0911-test_board_noprebuilt-vivado_2018.2-build_03_20181126132622.zip
TEB0911-test_board-vivado_2018.2-build_03_20181126132607.zip | John Hartfiel | - new assembly variant
- add init.sh
| | 2018-07-20 | 2018.2 | TEB0911-test_board_noprebuilt-vivado_2018.2-build_02_20180719153443.zip
TEB0911-test_board-vivado_2018.2-build_02_20180719153429.zip | John Hartfiel | |
|
Release Notes and Know Issues
Notes :- add known Design issues and general notes for the current revision
- do not delete known issue, add fixed version time stamp if issue fixed
|

| Issues | Description | Workaround | To be fixed version |
|---|
| No known issues | --- | --- | --- |
|
Requirements
Software
Notes : - list of software which was used to generate the design
|

| Software | Version | Note |
|---|
| Vitis | 2019.2 | needed, Vivado is included into Vitis installation | | PetaLinux | 2019.2 | needed | | SI ClockBuilder Pro | --- | optional |
|
Hardware
Notes : - list of software which was used to generate the design
|
Basic description of TE Board Part Files is available on TE Board Part Files.
Complete List is available on <design name>/board_files/*_board_files.csv
Design supports following modules:

| Module Model | Board Part Short Name | PCB Revision Support | DDR | QSPI Flash | EMMC | Others | Notes |
|---|
TEB0911-02-ES1 | es1_4gb | REV02|REV01 | 4GB | 64MB | 4GB | SODIMM_KVR24S17S8/8 | Not longer supported by vivado | | TEB0911-04-09EG1E | 9eg_1e_8gb | REV04|REV03|REV02 | 8GB | 64MB | 8GB | SODIMM_CT8G4SFS824A |
| | TEB0911-04-15EG1E | 15eg_1e_8gb | REV04 | 8GB | 128MB | 8GB | SODIMM_CT8G4SFS824A |
| | TEB0911-04-ZU9EG1A | 9eg_1e_8gb | REV04 | 8GB | 128MB | 8GB | SODIMM_CT8G4SFS824A |
| | TEB0911-04-ZU15EGA | 15eg_1e_8gb | REV04 | 8GB | 128MB | 8GB | SODIMM_CT8G4SFS824A |
| | TEB0911-04-9BEX1FA | 9eg_1e_8gb | REV04 | 8GB | 128MB | 8GB | SODIMM_CT8G4SFS824A |
| | TEB0911-04-BBEX1FA | 15eg_1e_8gb | REV04 | 8GB | 128MB | 8GB | SODIMM_CT8G4SFS824A |
|
|
Additional HW Requirements:

| Additional Hardware | Notes |
|---|
| DDR4 | example configured for CT8G4SFS824A |
|
Content
For general structure and of the reference design, see Project Delivery - AMD devices
Design Sources

| Type | Location | Notes |
|---|
| Vivado | <design name>/block_design
<design name>/constraints
<design name>/ip_lib | Vivado Project will be generated by TE Scripts | | Vitis | <design name>/sw_lib | Additional Software Template for Vitis and apps_list.csv with settings automatically for Vitis app generation | | PetaLinux | <design name>/os/petalinux | PetaLinux template with current configuration |
|
Additional Sources

| Type | Location | Notes |
|---|
| SI5338 | <design name>/misc/Si5338 | SI5338 Project with current PLL Configuration | | SI5345 | <design name>/misc/Si5345 | SI5345 Project with current PLL Configuration | | init.sh | <design name>/misc/init_script | Additional Initialization Script for Linux |
|
Prebuilt
Notes : - prebuilt files
- Template Table:

File | File-Extension | Description |
|---|
| BIF-File | *.bif | File with description to generate Bin-File | | BIN-File | *.bin | Flash Configuration File with Boot-Image (Zynq-FPGAs) | | BIT-File | *.bit | FPGA (PL Part) Configuration File | | DebugProbes-File | *.ltx | Definition File for Vivado/Vivado Labtools Debugging Interface | Debian SD-Image | *.img | Debian Image for SD-Card | | Diverse Reports | --- | Report files in different formats | | Hardware-Platform-Specification-Files | *.xsa | Exported Vivado Hardware Specification for Vitis and PetaLinux | | LabTools Project-File | *.lpr | Vivado Labtools Project File | MCS-File | *.mcs | Flash Configuration File with Boot-Image (MicroBlaze or FPGA part only) | MMI-File | *.mmi | File with BRAM-Location to generate MCS or BIT-File with *.elf content (MicroBlaze only) | | OS-Image | *.ub | Image with Linux Kernel (On Petalinux optional with Devicetree and RAM-Disk) | | Software-Application-File | *.elf | Software Application for Zynq or MicroBlaze Processor Systems | SREC-File | *.srec | Converted Software Application for MicroBlaze Processor Systems |
|
|

File | File-Extension | Description |
|---|
| BIF-File | *.bif | File with description to generate Bin-File | | BIN-File | *.bin | Flash Configuration File with Boot-Image (Zynq-FPGAs) | | BIT-File | *.bit | FPGA (PL Part) Configuration File | | DebugProbes-File | *.ltx | Definition File for Vivado/Vivado Labtools Debugging Interface | | Diverse Reports | --- | Report files in different formats | | Hardware-Platform-Specification-Files | *.xsa | Exported Vivado Hardware Specification for Vitis and PetaLinux | | LabTools Project-File | *.lpr | Vivado Labtools Project File | | OS-Image | *.ub | Image with Linux Kernel (On Petalinux optional with Devicetree and RAM-Disk) | | Software-Application-File | *.elf | Software Application for Zynq or MicroBlaze Processor Systems |
|
Download
Reference Design is only usable with the specified Vivado/SDK/PetaLinux/SDx version. Do never use different Versions of Xilinx Software for the same Project.
Reference Design is available on:
Design Flow
Reference Design is available with and without prebuilt files. It's recommended to use TE prebuilt files for first lunch. |
Trenz Electronic provides a tcl based built environment based on Xilinx Design Flow.
See also:
The Trenz Electronic FPGA Reference Designs are TCL-script based project. Command files for execution will be generated with "_create_win_setup.cmd" on Windows OS and "_create_linux_setup.sh" on Linux OS.
TE Scripts are only needed to generate the vivado project, all other additional steps are optional and can also executed by Xilinx Vivado/SDK GUI. For currently Scripts limitations on Win and Linux OS see: Project Delivery Currently limitations of functionality
- _create_win_setup.cmd/_create_linux_setup.sh and follow instructions on shell:
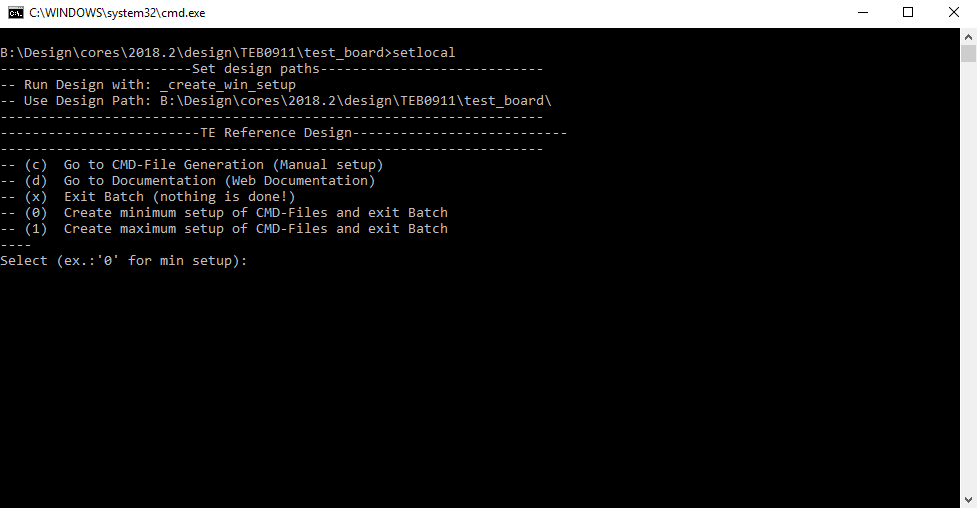
- Press 0 and enter to start "Module Selection Guide"
- (optional Win OS) Generate Virtual Drive or use short directory for the reference design (for example x:\<design name>)
- Create Project (follow instruction of the product selection guide), settings file will be configured automatically during this process
- (optional for manual changes) Select correct device and Xilinx install path on "design_basic_settings.cmd" and create Vivado project with "vivado_create_project_guimode.cmd"
Note: Select correct one, see alsoTE Board Part Files
- Create HDF and export to prebuilt folder
- Run on Vivado TCL: TE::hw_build_design -export_prebuilt
Note: Script generate design and export files into \prebuilt\hardware\<short dir>. Use GUI is the same, except file export to prebuilt folder
- Create Linux (uboot.elf and image.ub) with exported XSA
- XSAis exported to "prebuilt\hardware\<short name>"
Note: HW Export from Vivado GUI create another path as default workspace. - Create Linux images on VM, see PetaLinux KICKstart
- Use TE Template from /os/petalinux
- Add Linux files (uboot.elf and image.ub) to prebuilt folder
- "prebuilt\os\petalinux\<ddr size>" or "prebuilt\os\petalinux\<short name>"
- Generate Programming Files with Vitis
- Run on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_vitis -all
Note: Scripts generate applications and bootable files, which are defined in "sw_lib\apps_list.csv" - (alternative) Start SDK with Vivado GUI or start with TE Scripts on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_vitis
Note: TCL scripts generate also platform project, this must be done manuelly in case GUI is used. See Vitis
Launch
Note: - Programming and Startup procedure
|
Programming
Check Module and Carrier TRMs for proper HW configuration before you try any design. |
Xilinx documentation for programming and debugging: Vivado/SDK/SDSoC-Xilinx Software Programming and Debugging
Get prebuilt boot binaries
- _create_win_setup.cmd/_create_linux_setup.sh and follow instructions on shell
- Press 0 and enter to start "Module Selection Guide"
- Select assembly version
- Validate selection
- Select Create and open delivery binary folder
Note: Folder (<project foler>/_binaries_<Artikel Name>) with subfolder (boot_<app name>) for different applications will be generated
QSPI
Optional for Boot.bin on QSPI Flash and image.ub on SD.
- Connect JTAG and power on carrier with module
- Open Vivado Project with "vivado_open_existing_project_guimode.cmd" or if not created, create with "vivado_create_project_guimode.cmd"
- Type on Vivado TCL Console: TE::pr_program_flash_binfile -swapp u-boot
Note: To program with SDK/Vivado GUI, use special FSBL (zynqmp_fsbl_flash) on setup
Optional "TE::pr_program_flash_binfile -swapp hello_teb0911" possible - Copy image.ub and optional misc/sd/init.sh on SD-Card
- use files from (<project foler>/_binaries_<Articel Name>)/boot_linux from generated binary folder,see: Get prebuilt boot binaries
- or use prebuilt file location, see <design_name>/prebuilt/readme_file_location.txt
- Insert SD-Card
SD
- Copy image.ub, Boot.bin and misc/sd/init.sh on SD-Card.
- use files from (<project foler>/_binaries_<Articel Name>)/boot_linux from generated binary folder,see: Get prebuilt boot binaries
- or use prebuilt file location, see <design_name>/prebuilt/readme_file_location.txt
- Set Boot Mode to SD-Boot.
- Insert SD-Card in SD-Slot.
JTAG
Not used on this Example.
Usage
- Prepare HW like described on section Programming
- Connect UART USB (same as FPGA JTAG)
- Select SD Card as Boot Mode (or QSPI - depending on step 1)
- (Optional) Insert PCIe Card (detection depends on Linux driver. Only some basic drivers are installed)
- (Optional) Connect DisplayPort Monitor (List of usable Monitors: https://www.xilinx.com/support/answers/68671.html)
- (Optional) Connect Network Cable
- Power On PCB
Note: 1. ZynqMP Boot ROM loads PMU Firmware and FSBL from SD into OCM, 2. FSBL loads ATF(bl31.elf) and U-boot from SD/QSPI into DDR, 3. U-boot load Linux from SD into DDR.
Linux
- Open Serial Console (e.g. putty)
- Speed: 115200
- COM Port: Win OS, see device manager, Linux OS see dmesg |grep tty (UART is *USB1)
- Linux Console:
Note: Wait until Linux boot finished For Linux Login use:
- User Name: root
- Password: root
- You can use Linux shell now.
- I2C 0 Bus type: i2cdetect -y -r 0
- ETH0 works with udhcpc
- USB type "lsusb" or connect USB device
- PCIe type "lspci"
Vivado HW Manager
Control:
- User LED Control (D16, D15)
Monitoring:
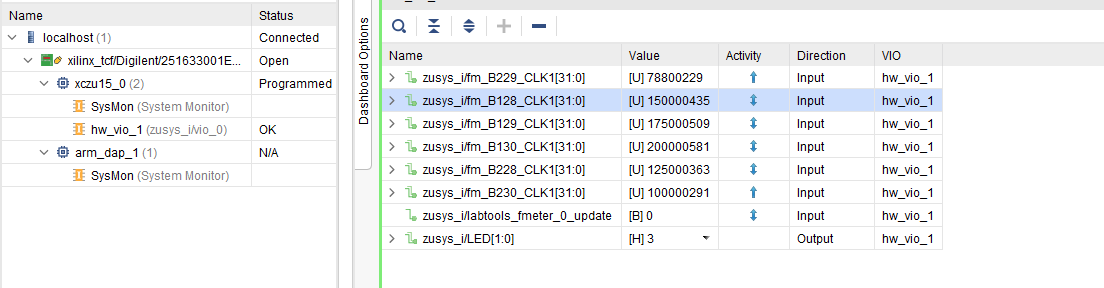
- MGT CLK Measurement:
- Open Vivado HW-Manager and add VIO signal to dashboard (*.ltx located on prebuilt folder).Set radix from VIO signals to unsigned integer.Note: Frequency Counter is inaccurate and displayed unit is Hz
- Default B229_CLK1: 78,8MHz, B128_CLK1: 150MHz, B129_CLK1: 175MHz, B130_CLK1: 200MHz, B228_CLK1: 125MHz, B23ß_CLK1: 100MHz
System Design - Vivado
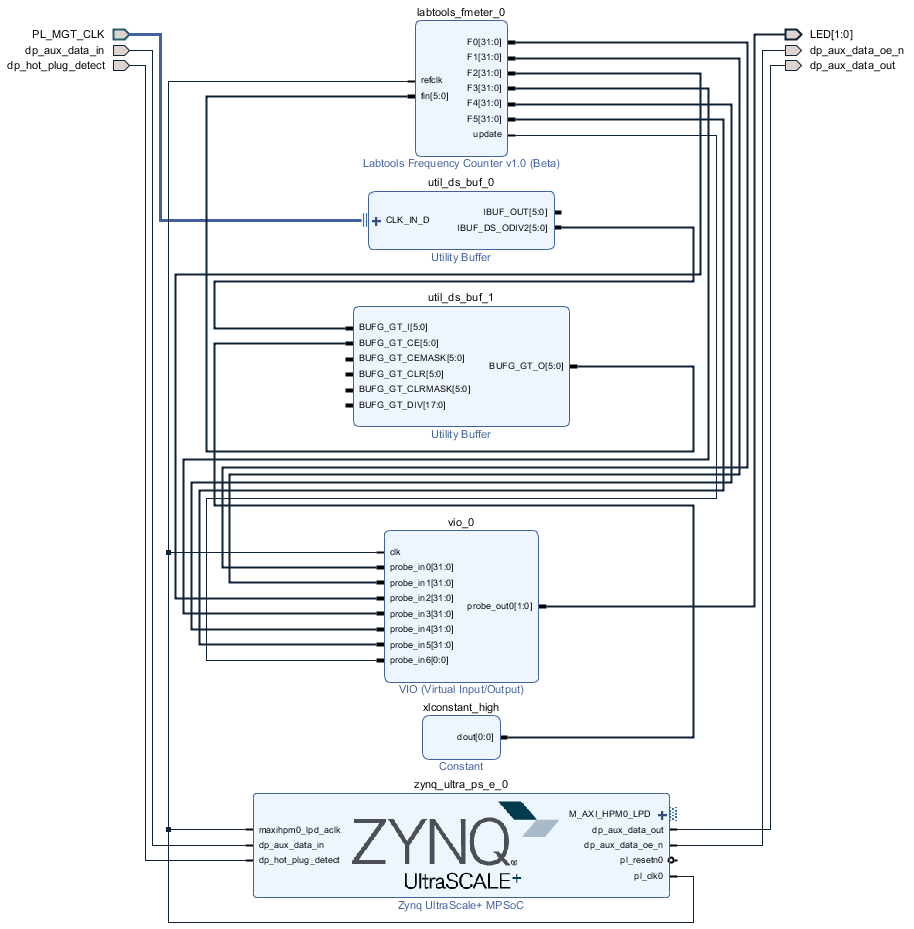
Block Design
PS Interfaces
Activated interfaces:

| Type | Note |
|---|
| DDR | SODIMM, setting depends on used memory | | QSPI | MIO | | SD0 | MIO | | SD1 | MIO | | I2C0 | MIO | | PJTAG0 | MIO | | UART0 | MIO | | GPIO0 | MIO | | SWDT0..1 |
| | TTC0..3 |
| | GEM3 | MIO | | USB0 | MIO/GTP | | PCIe | MIO/GTP | | DisplayPort | EMIO/GTP |
|
Constrains
Basic module constrains
set_property BITSTREAM.GENERAL.COMPRESS TRUE [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.UNUSEDPIN PULLNONE [current_design] |
Design specific constrain
# GT Clocks
#B128-1
set_property PACKAGE_PIN N27 [get_ports {PL_MGT_CLK_clk_p[0]}]
#B129-1
set_property PACKAGE_PIN J27 [get_ports {PL_MGT_CLK_clk_p[1]}]
#B228-1
set_property PACKAGE_PIN J8 [get_ports {PL_MGT_CLK_clk_p[2]}]
#B130-1
set_property PACKAGE_PIN E27 [get_ports {PL_MGT_CLK_clk_p[3]}]
#B229-1
set_property PACKAGE_PIN E8 [get_ports {PL_MGT_CLK_clk_p[4]}]
#B230-1
set_property PACKAGE_PIN B10 [get_ports {PL_MGT_CLK_clk_p[5]}]
## DP
set_property PACKAGE_PIN AB1 [get_ports dp_aux_data_in]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN V9 [get_ports dp_hot_plug_detect]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN AA8 [get_ports dp_aux_data_out]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN AA3 [get_ports dp_aux_data_oe_n]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS18 [get_ports dp_*]
## LED
set_property PACKAGE_PIN K14 [get_ports {LED[0]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN K10 [get_ports {LED[1]}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS18 [get_ports {LED*}]
|
Software Design - Vitis
For SDK project creation, follow instructions from:
Vitis
Application
SDK template in ./sw_lib/sw_apps/ available.
---------------------------------------------------------- FPGA Example scuMCS Firmware to configure SI5338 and Reset System. srec_spi_bootloaderTE modified 2019.2 SREC Bootloader to load app or second bootloader from flash into DDR Descriptions: - Modified Files: blconfig.h, bootloader.c
- Changes:
- Add some console outputs and changed bootloader read address.
- Add bugfix for 2018.2 qspi flash
xilisf_v5_11TE modified 2019.2 xilisf_v5_11 - Changed default Flash type to 5.
---------------------------------------------------------- Zynq Example: zynq_fsblTE modified 2019.2 FSBL General: Module Specific: - Add Files: all TE Files start with te_*
- READ MAC from EEPROM and make Address accessible by UBOOT (need copy defines on uboot platform-top.h)
- CPLD access
- Read CPLD Firmware and SoC Type
- Configure Marvell PHY
zynq_fsbl_flashTE modified 2019.2 FSBL General: - Modified Files: main.c
- General Changes:
- Display FSBL Banner
- Set FSBL Boot Mode to JTAG
- Disable Memory initialisation
ZynqMP Example: ---------------------------------------------------------- zynqmp_fsblTE modified 2019.2 FSBL General: - Modified Files: xfsbl_main.c, xfsbl_hooks.h/.c, xfsbl_board.h/.c(search for 'TE Mod' on source code)
- Add Files: te_xfsbl_hooks.h/.c (for hooks and board)\n\
- General Changes:
- Display FSBL Banner and Device Name
Module Specific: - Add Files: all TE Files start with te_*
- Si5338 Configuration
- ETH+OTG Reset over MIO
zynqmp_fsbl_flashTE modified 2019.2 FSBL General: - Modified Files: xfsbl_initialisation.c, xfsbl_hw.h, xfsbl_handoff.c, xfsbl_main.c
- General Changes:
- Display FSBL Banner
- Set FSBL Boot Mode to JTAG
- Disable Memory initialisation
zynqmp_pmufwXilinx default PMU firmware. ---------------------------------------------------------- General Example: hello_te0820Hello TE0820 is a Xilinx Hello World example as endless loop instead of one console output. u-bootU-Boot.elf is generated with PetaLinux. Vitis is used to generate Boot.bin. |
zynqmp_fsbl
TE modified 2019.2 FSBL
General:
- Modified Files: xfsbl_main.c, xfsbl_hooks.h/.c, xfsbl_board.h/.c(search for 'TE Mod' on source code)
- Add Files: te_xfsbl_hooks.h/.c (for hooks and board)\n\
- General Changes:
- Display FSBL Banner and Device Name
Module Specific:
- Add Files: all TE Files start with te_*
- Si5338 and SI5345 Configuration
- PCIe reset
zynqmp_fsbl_flash
TE modified 2019.2 FSBL
General:
- Modified Files: xfsbl_initialisation.c, xfsbl_hw.h, xfsbl_handoff.c, xfsbl_main.c
- General Changes:
- Display FSBL Banner
- Set FSBL Boot Mode to JTAG
- Disable Memory initialisation
zynqmp_pmufw
Xilinx default PMU firmware.
hello_teb0911
Hello TEB0911 is a Xilinx Hello World example as endless loop instead of one console output.
u-boot
U-Boot.elf is generated with PetaLinux. SDK/HSI is used to generate Boot.bin.
Software Design - PetaLinux
For PetaLinux installation and project creation, follow instructions from:
Config
Start with petalinux-config or petalinux-config --get-hw-description
Changes:
- SUBSYSTEM_PRIMARY_SD_PSU_SD_1_SELECT
- CONFIG_SUBSYSTEM_ETHERNET_PSU_ETHERNET_3_MAC=""
U-Boot
Start with petalinux-config -c u-boot
Changes:
- CONFIG_ENV_IS_NOWHERE=y
- # CONFIG_ENV_IS_IN_SPI_FLASH is not set
- CONFIG_I2C_EEPROM=y
- CONFIG_ZYNQ_GEM_I2C_MAC_OFFSET=0xFA
- CONFIG_SYS_I2C_EEPROM_ADDR=0x54
- CONFIG_SYS_I2C_EEPROM_BUS=5
- CONFIG_SYS_EEPROM_SIZE=256
- CONFIG_SYS_EEPROM_PAGE_WRITE_BITS=0
- CONFIG_SYS_EEPROM_PAGE_WRITE_DELAY_MS=0
- CONFIG_SYS_I2C_EEPROM_ADDR_LEN=1
- CONFIG_SYS_I2C_EEPROM_ADDR_OVERFLOW=0
Change platform-top.h
Device Tree
/include/ "system-conf.dtsi"
/ {
chosen {
xlnx,eeprom = &eeprom;
};
};
/* USB */
&dwc3_0 {
status = "okay";
dr_mode = "host";
snps,usb3_lpm_capable;
snps,dis_u3_susphy_quirk;
snps,dis_u2_susphy_quirk;
phy-names = "usb2-phy","usb3-phy";
phys = <&lane1 4 0 1 100000000>;
maximum-speed = "super-speed";
};
/* QSPI */
&qspi {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
status = "okay";
flash0: flash@0 {
compatible = "jedec,spi-nor";
reg = <0x0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
};
};
/* ETH */
&gem3 {
phy-handle = <&phy0>;
phy0: phy0@1 {
device_type = "ethernet-phy";
reg = <1>;
};
};
/* SD1 */
&sdhci1 {
// disable-wp;
no-1-8-v;
};
&i2c0 {
i2cswitch@76 { // I2C Switch U13
compatible = "nxp,pca9548";
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <0x76>;
i2c-mux-idle-disconnect;
i2c@2 { // FMCD (/dev/i2c-3)
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <2>;
};
i2c@3 { // FMCE (/dev/i2c-4)
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <3>;
};
i2c@4 { // FMCB (/dev/i2c-5)
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <4>;
};
i2c@5 { // FMCC (/dev/i2c-6)
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <5>;
};
i2c@6 { // PLL (/dev/i2c-7)
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <6>;
si570_2: clock-generator3@5d {
#clock-cells = <0>;
compatible = "silabs,si570";
reg = <0x5d>;
temperature-stability = <50>;
factory-fout = <156250000>;
clock-frequency = <78800000>;
};
};
};
i2cswitch@77 { // I2C Switch U37
compatible = "nxp,pca9548";
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <0x77>;
i2c-mux-idle-disconnect;
i2c@0 { // SFP2 (/dev/i2c-9)
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <0>;
};
i2c@1 { // FMCA (/dev/i2c-10)
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <1>;
};
i2c@2 { // FMCF (/dev/i2c-11)
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <2>;
};
i2c@3 { // SFP0 (/dev/i2c-12)
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <3>;
};
i2c@4 { // SFP1 (/dev/i2c-13)
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <4>;
};
i2c@5 { // MEM (/dev/i2c-14)
// Low frequency to work with CPLD
clock-frequency = <100000>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <5>;
eeprom: eeprom@54 {
compatible = "atmel,24c08";
reg = <0x54>;
};
};
i2c@6 { // DDR4 (/dev/i2c-15)
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <6>;
};
i2c@7 { // USBH (/dev/i2c-16)
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <7>;
};
};
};
|
Kernel
Start with petalinux-config -c kernel
Changes:
- # CONFIG_CPU_IDLE is not set (only needed to fix JTAG Debug issue)
- # CONFIG_CPU_FREQ is not set (only needed to fix JTAG Debug issue)
- CONFIG_EDAC_CORTEX_ARM64=y (only needed to fix JTAG Debug issue)
- CONFIG_NVME_CORE=y
- CONFIG_BLK_DEV_NVME=y
- # CONFIG_NVME_MULTIPATH is not set
- CONFIG_NVME_TARGET=y
- # CONFIG_NVME_TARGET_LOOP is not set
- # CONFIG_NVME_TARGET_FC is not set
- CONFIG_NVM=y
- CONFIG_NVM_PBLK=y
- CONFIG_NVM_PBLK_DEBUG=y
Rootfs
Start with petalinux-config -c rootfs
Changes:
- CONFIG_i2c-tools=y
- CONFIG_busybox-httpd=y (for web server app)
- CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-utils(util-linux,cpufrequtils,bridge-utils,mtd-utils,usbutils,pciutils,canutils,i2c-tools,smartmontools,e2fsprogs)
Applications
See: \os\petalinux\project-spec\meta-user\recipes-apps\
startup
Script App to load init.sh from SD Card if available.
webfwu
Webserver application accemble for Zynq access. Need busybox-httpd
Additional Software
Note:
- Add description for other Software, for example SI CLK Builder ...
- SI5338 and SI5345 also Link to:
|
No additional software is needed.
SI5338
File location <design name>/misc/Si5338/Si5338-*.slabtimeproj
General documentation how you work with these project will be available on Si5338
SI5345
File location <design name>/misc/Si5345/Si5345-RevD-0911-Project.slabtimeproj
General documentation how you work with these project will be available on Si5345
Appx. A: Change History and Legal Notices
Document Change History
To get content of older revision got to "Change History" of this page and select older document revision number.
- Note this list must be only updated, if the document is online on public doc!
- It's semi automatically, so do following
Add new row below first Copy "Page Information Macro(date)" Macro-Preview, Metadata Version number, Author Name and description to the empty row. Important Revision number must be the same as the Wiki document revision number Update Metadata = "Page Information Macro (current-version)" Preview+1 and add Author and change description. --> this point is will be deleted on newer pdf export template - Metadata is only used of compatibility of older exports
|

| Date | Document Revision | Authors | Description |
|---|
| | | | | 2020-06-03 | v.10 | John Hartfiel | | | 2020-03-25 | v.9 | John Hartfiel | | | 2020-02-24 | v.8 | John Hartfiel | | | 2020-02-13 | v7 | John Hartfiel | - new assembly variants
- Release 2019.2
| | 2019-02-07 | v.6 | John Hartfiel | | | v.5 | John Hartfiel | - new assembly variant
- documentation style update
| | v.4 | John Hartfiel | | | -- | all | | -- |
|
Legal Notices