FSBL
FSBL is responsible for all system initialization and configuration.
FSBL Checklist
- Are relevant PS7 settings correct in Vivado IPI BD customization Dialog?
- If using board part files, has the automation been executed on the PS7 block with apply presets enabled?
- Has Vivado flow been executed successfully until bitgen?
- Has the hardware been exported with include bitstream option?
- Is SDK using the hardware description exported from Vivado?
- Has bsp for FSBL been regenerated from sources since last export?
- Is FSBL set to use correct bsp?
- Has FSBL been re-compiled?
- Is bootgen using the correct fsbl.elf file?
- Is the sdcard formattet as ms-dos, not gpt?
No Console Output
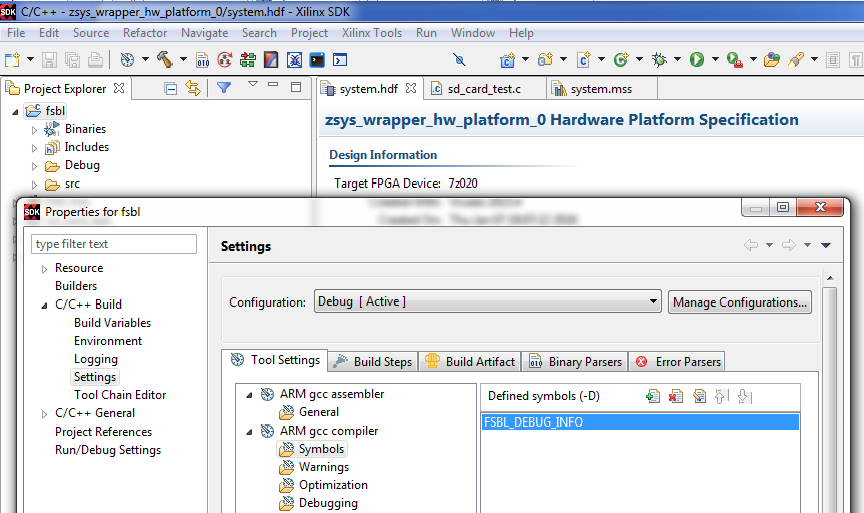
Xilinx standard FSBL when compiled with default settings is in "quiet" mode, with no console output if something goes wrong. If there is any doubt that there are problems with FSBL it is necessary to make FSBL more verbose. One possibility is to enable DEBUG logging in FSBL by defining compiler symbol.
If there is however problem with DDR memory there may not come any log messages, also when DEBUG is enabled. In such cases adding
xil_printf("FSBL before DDR");
just at the begin of main() in FSBL would help to see if at least the console UART is working.
Enabling Debug info logging in FSBL.
zynq_flash
Is a command-line tool from Xilinx to write nonvolatile memory connected to Zynq PS. With current versions of tools there is minor problem with file extensions: on windows platforms only lowercase .bin is accepted as extension. Boot bin generated with petalinux would be however generated as BOOT.BIN with uppercase extension. It is not possible to use it with Xilinx SDK Flash Programmer GUI or the commandline zynq_flash. GUI Flasher will not allow to select a file with upper case extension, and zynq_flash will also refuse to flash from it if the file is given with uppercase extension. As a workaround the image to be burned has to be renamed with lower case extension (.bin). The name of the image can be anything, just the extension has to be bin in lowercase. There is no need to convert bin to mcs for the zynq_flash, it makes little sense.
bootgen
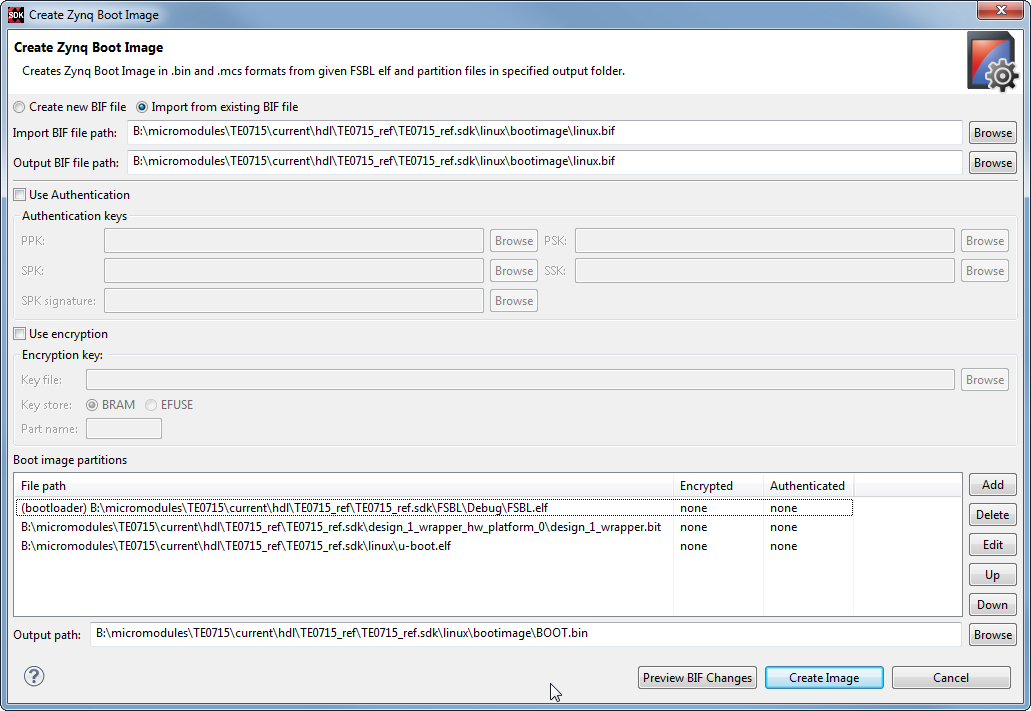
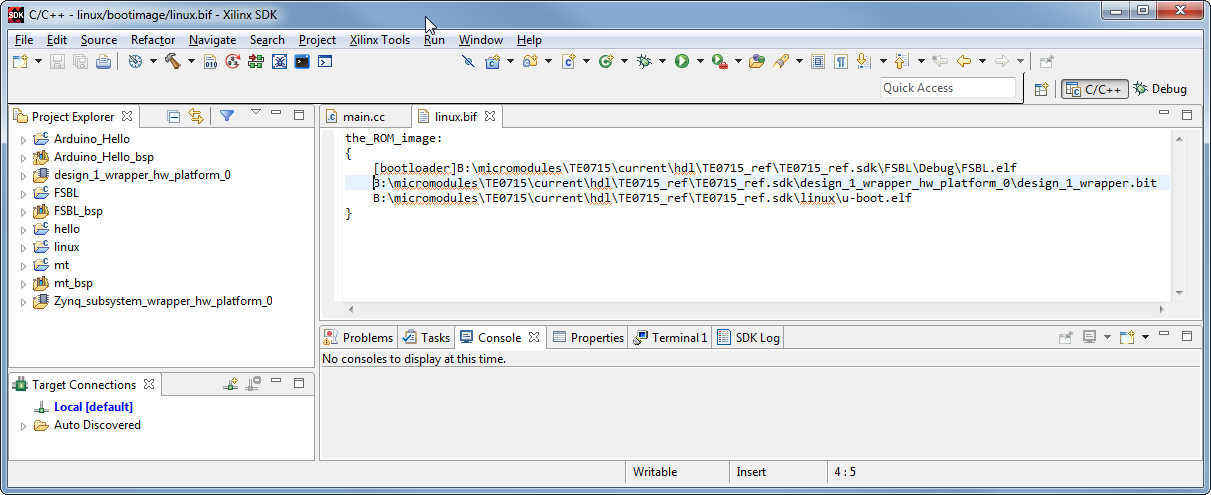
File order is important when creating Zynq Boot image with Xilinx bootgen, BITSTREAM if present must be specified as second file, before application and second stage bootloader (normally u-boot). If not then Xilinx standard FSBL will give an error.
Note: Xilinx how-to "Prepare Boot Image" is incomplete and out-dated as well (rev 23 from November 2014). Xilinx how-to does not show a bitstream at all, and lists files to be included that are not needed with latest petalinux standard kernels.
Defaults by SDK, dummy "hello.elf" replaced with u-boot.elf to create BOOT.bin for Linux boot from SD Card.
Example BIF file for BOOT.bin, FPGA bitstream is clearly visible as second file. This is how SDK wizard does it by default, this order should not be changed. As 3rd file is normally the second stage bootloader (u-boot). For boot file for SD Card, this is all that goes into BOOT.bin, the remaining files will be copied to SD card. For SPI Flash images linux image should be added as well as last file, with correct offset (it must match the offset u-boot is expecting it).
Note: petalinux-package (2014.4) seems to have trouble with offset in BIF, so it would fail to create boot images for SPI Flash (SD Card images are OK). As workaround the boot images should be generated with bootgen using manually created bif files.
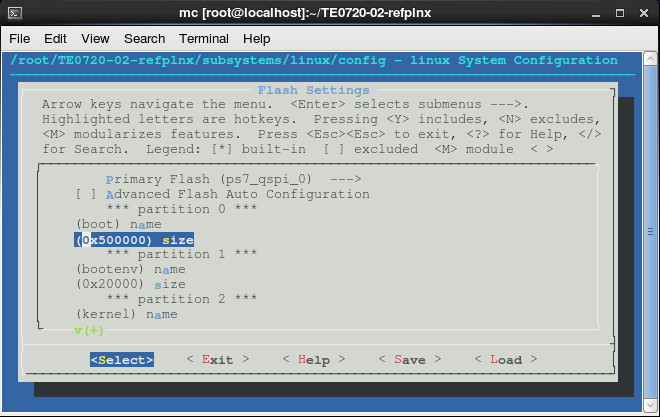
Petalinux default size for boot partition is 0x50_0000 and 0x2_0000 for Flash environment, hence the offset for image.ub in the BOOT.bin for SPI Flash should be set to 0x520000.
Boot from SD Card
If there is doubt that booting from SD card is failing, then as first step a special BOOT.bin should be used to verify the that Zynq Bootrom can load the boot code from SD Card at all. This special image does not use or initialize any PS peripherals including external DDR memory, it also does not attempt to configure the PL portion. The image simply Blinks a LED connected to some MIO pin. The same image can be used on any Zynq device, if the SD boot process succeeds at all then code in the image will be executing.
SDIO MIO Pullups
If SDIO interface is connected to SD card via special purpose level shifter IC, then it maybe desirable or even necessary to disable MIO internal pullups for SDIO pins. Some SD Cards may fail when the SDIO MIO internal pullups are enabled.