Page History
...
| Date | Vivado | Project Built | Authors | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018-0405-1615 | 2017.4 | TE0741-test_board-vivado_2017.4-build_07_20180416142156.zip TE0741-test_board_noprebuilt-vivado_2017.4-build_07_20180416142217.zip | John Hartfiel |
|
...
| Module Model | Board Part Short Name | PCB Revision Support | DDR | QSPI Flash | Others | Notes | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TE0741TE0841-0301-070035-2IF 1C | 070_2if | 01_35_1c | REV01 | 2x 512MB DDR4 | 32MBREV02, REV03 | --- | 32MB | MGT LR: 6,6 Gb/s | TE0741-03-160-2IF | 160_2if | |||||||||||||||
| TE0841-01-035-1I | 01_35_1i | REV01 | 2x 512MB DDR4 | 32MBREV02, REV03 | --- | ||||||||||||||||||||
| TE0841-01-035-2I | 01_35_2i | REV01 | 2x 512MB DDR4 | 32MB | 32MB | MGT LR: 6,6 Gb/s | TE0741-03-325-2IF | 325_2if | REV02, REV03 | --- | 32MB | MGT LR: 6,6 Gb/s | TE0741-03-410-2IF | 410_2if | |||||||||||
| TE0841-01-040-1C | 01_40_1c | REV01 | 2x 512MB DDR4 | 32MBREV02, REV03 | --- | 32MB | MGT LR: 6,6 Gb/s | ||||||||||||||||||
| TE0841-01-040-1I | 01_40_1i | REV01 | 2x 512MB DDR4 | 32MB | TE0741-03-070-2CF | 070_2cf | REV02, REV03 | --- | 32MB | MGT LR: 6,6 Gb/s | TE0741-03-160-2CF | 160_2cf | |||||||||||||
| TE0841-01-040-2I | 01_40_2i | REV01 | 2x 512MB DDR4 | 32MBREV02, REV03 | --- | 32MB | MGT LR: 6,6 Gb/s | TE0741-03-325-2CF | 325_2cf | REV02, REV03 | --- | 32MB | MGT LR: 6,6 Gb/s | TE0741-03-410-2CF | 410_2cf | REV02, REV03 | --- | 32MB | MGT LR: 6,6 Gb/s | TE0741-03-160-2C1 | 160_2c1 | REV02, REV03 | --- | 32MB | MGT LR: 10,3125 Gb/s |
Design supports following carriers:
...
Additional HW Requirements:
...
Content
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Remove unused content
--> |
For general structure and of the reference design, see Project Delivery
Design Sources
...
Design supports following carriers:
| Carrier Model | Notes |
|---|---|
| TE0701 | |
| TE0703 | |
| TE0705 | |
| TE0706 | |
| TEBA0841 | used as reference carrier |
Additional HW Requirements:
| Additional Hardware | Notes |
|---|---|
| USB Cable for JTAG/UART | Check Carrier Board and Programmer for correct type |
| XMOD Programmer | Carrier Board dependent, only if carrier has no own FTDI |
Content
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Remove unused content
--> |
For general structure and of the reference design, see Project Delivery
Design Sources
| Type | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Vivado | <design name>/block_design <design name>/constraints <design name>/ip_lib <design name>/firmware | Vivado Project will be generated by TE Scripts |
| SDK/HSI | <design name>/sw_lib | Additional Software Template for SDK/HSI and apps_list.csv with settings for HSI |
Additional Sources
| Type | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| SI5338 Project | \misc\SI5338 |
Prebuilt
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
<table width="100%">
<tr> <th>File </th> <th>File-Extension</th> <th>Description </th> </tr>
<tr> <td>BIF-File </td> <td>*.bif </td> <td>File with description to generate Bin-File |
Additional Sources
...
Prebuilt
| HTML |
|---|
<!-- <table width="100%"> <tr> <th>File </td> </th>tr> <tr> <th>File<td>BIN-Extension</th>File <th>Description </td> <td>*.bin </td> <td>Flash Configuration File with Boot-Image (Zynq-FPGAs) </th>td> </tr> <tr> <td>BIF<td>BIT-File </td> <td>*.bifbit </td> <td>File with description to generate Bin-File <td>FPGA Configuration File </td> </tr> <tr> <td>BIN<td>DebugProbes-File </td> <td>*.ltx </td> <td>*.bin <td>Definition File for Vivado/Vivado Labtools Debugging Interface </td> </tr> <tr> <td>Debian SD-Image <td>Flash Configuration File with Boot-Image (Zynq-FPGAs) </td> <td>*.img </td> <td>Debian Image for SD-Card </td> </tr> <tr> <td>BIT-File </td> <td>*.bit </td> <td>FPGA Configuration File </td> </tr> <tr> <td>Diverse Reports </td> <td> --- </td> <td>Report files in different formats </td> </tr> <tr> <td>DebugProbes-File </td> <td>*.ltx </td> <td>Definition File for Vivado/Vivado Labtools Debugging Interface </td> </tr> <tr> <td>Hardware-Platform-Specification-Files</td> <td>*.hdf </td> <td>Exported Vivado Hardware Specification for SDK/HSI </td> </tr> <tr> <td>Debian SD-Image </td> <td>*.img </td> <td>Debian Image for SD-Card</tr> <tr> <td>LabTools Project-File </td> <td>*.lpr </td> <td>Vivado Labtools Project File </td> </tr> <tr> <td>Diverse Reports </td> <td> ---</tr> <tr> <td>MCS-File </td> <td>Report files in different formats </td> <td>*.mcs </td> <td>Flash Configuration File with Boot-Image (MicroBlaze or FPGA part only) </td> </tr> <tr> <td>Hardware-Platform-Specification-Files</td> <td>*.hdf<td>MMI-File </td> <td>Exported Vivado Hardware Specification for SDK/HSI </td> <td>*.mmi </td> <td>File with BRAM-Location to generate MCS </td> </tr> <tr> <td>LabTools Projector BIT-File with *.elf content (MicroBlaze only) </td> </tr> <tr> <td>OS-Image </td> <td>*.lpr </td> <td>Vivado Labtools Project File </td> <td>*.ub </td> <td>Image with Linux Kernel (On Petalinux optional with Devicetree and RAM-Disk) </td> </tr> <tr> <td>Software-Application-File </td> <td>*.elf </td> </tr> <tr> <td>MCS-File </td> <td>Software Application for Zynq or MicroBlaze Processor Systems </td> <td>*.mcs </td> <td>Flash Configuration File with Boot-Image (MicroBlaze or FPGA part only)</tr> <tr> <td>SREC-File </td> </tr> <tr> <td>MMI-File<td>*.srec </td> <td>Converted Software Application for MicroBlaze Processor Systems </td> <td>*.mmi </td> </tr> <td>File with BRAM-Location to generate MCS or BIT-File with *.elf content (MicroBlaze only) </td> </tr> <tr> <td>OS-Image </td> <td>*.ub </td> <td>Image with Linux Kernel (On Petalinux optional with Devicetree and RAM-Disk) </td> </tr> <tr> <td>Software-Application-File </td> <td>*.elf </td> <td>Software Application for Zynq or MicroBlaze Processor Systems </td> </tr> <tr> <td>SREC-File </td> <td>*.srec </td> <td>Converted Software Application for MicroBlaze Processor Systems </td> </tr> </table> --> |
...
File
...
File-Extension
...
Description
...
MCS-File
...
*.mcs
...
Flash Configuration File with Boot-Image (MicroBlaze or FPGA part only)
...
MMI-File
...
*.mmi
...
File with BRAM-Location to generate MCS or BIT-File with *.elf content (MicroBlaze only)
...
</table>
-->
|
File | File-Extension | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIT-File | *.bit | FPGA (PL Part) Configuration File |
| DebugProbes-File | *.ltx | Definition File for Vivado/Vivado Labtools Debugging Interface |
| Diverse Reports | --- | Report files in different formats |
| Hardware-Platform-Specification-Files | *.hdf | Exported Vivado Hardware Specification for SDK/HSI and PetaLinux |
| LabTools Project-File | *.lpr | Vivado Labtools Project File |
MCS-File | *.mcs | Flash Configuration File with Boot-Image (MicroBlaze or FPGA part only) |
MMI-File | *.mmi | File with BRAM-Location to generate MCS or BIT-File with *.elf content (MicroBlaze only) |
| Software-Application-File | *.elf | Software Application for Zynq or MicroBlaze Processor Systems |
| SREC-File | *.srec | Converted Software Application for MicroBlaze Processor Systems |
Download
Reference Design is only usable with the specified Vivado/SDK/PetaLinux/SDx version. Do never use different Versions of Xilinx Software for the same Project.
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Add correct path:https://shop.trenz-electronic.de/en/Download/?path=Trenz_Electronic/TE0803/Reference_Design/2017.1/Starterkit
--> |
Reference Design is available on:
Design Flow
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Basic Design Steps
Add/ Remove project specific
--> |
| Note |
|---|
Reference Design is available with and without prebuilt files. It's recommended to use TE prebuilt files for first lunch. |
Trenz Electronic provides a tcl based built environment based on Xilinx Design Flow.
See also:Vivado/SDK/SDSoC
The Trenz Electronic FPGA Reference Designs are TCL-script based project. Command files for execution will be generated with "_create_win_setup.cmd" on Windows OS and "_create_linux_setup.sh" on Linux OS.
TE Scripts are only needed to generate the vivado project, all other additional steps are optional and can also executed by Xilinx Vivado/SDK GUI. For currently Scripts limitations on Win and Linux OS see: Project Delivery Currently limitations of functionality
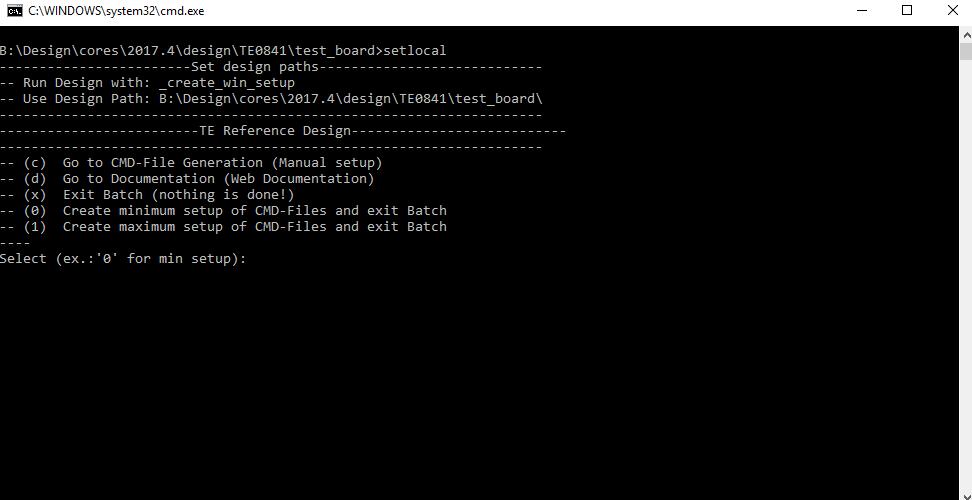
- _create_win_setup.cmd/_create_linux_setup.sh and follow instructions on shell:
- Press 0 and enter for minimum setup
- (optional Win OS) Generate Virtual Drive or use short directory for the reference design (for example x:\<design name>)
- Create Project
- Select correct device and Xilinx install path on "design_basic_settings.cmd" and create Vivado project with "vivado_create_project_guimode.cmd"
Note: Select correct one, see TE Board Part Files
- Select correct device and Xilinx install path on "design_basic_settings.cmd" and create Vivado project with "vivado_create_project_guimode.cmd"
- Create HDF and export to prebuilt folder
- Run on Vivado TCL: TE::hw_build_design -export_prebuilt
Note: Script generate design and export files into \prebuilt\hardware\<short dir>. Use GUI is the same, except file export to prebuilt folder
- Run on Vivado TCL: TE::hw_build_design -export_prebuilt
- Generate MCS Firmware (optional):
- Create SDK Project with TE Scripts on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_sdk
- Create "SCU" application
Note: Select MCS Microblaze and SCU Application - Select Release Built
- Regenerate App
- Generate Programming Files with HSI/SDK
- Run on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_hsi
Note: Scripts generate applications and bootable files, which are defined in "sw_lib\apps_list.csv" - (alternative) Start SDK with Vivado GUI or start with TE Scripts on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_sdk
Note: See SDK Projects
- Run on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_hsi
- Copy "\prebuilt\software\<short name>\srec_spi_bootloader.elf" into "\firmware\microblaze_0\"
- (optional) Copy "\\workspace\sdk\scu\Release\scu.elf" into "\firmware\microblaze_mcs_0\"
- Regenerate Vivado Project or Update Bitfile only with "srec_spi_bootloader.elf" and "scu.elf"
- Generate MCS file with Bitfile and application for SREC Bootloader
- Create SDK Project with TE Scripts on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_hsi
Note: SREC convertion from *.elf to *.srec will be done by scripts, alternative use SDK, see SDK Projects
- Create SDK Project with TE Scripts on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_hsi
Launch
Programming
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Description of Block Design, Constrains...
BD Pictures from Export...
--> |
| Note |
|---|
Check Module and Carrier TRMs for proper HW configuration before you try any design. |
Xilinx documentation for programming and debugging: Vivado/SDK/SDSoC-Xilinx Software Programming and Debugging
QSPI
- Connect JTAG and power on PCB
- (if not done)
Download
Reference Design is only usable with the specified Vivado/SDK/PetaLinux/SDx version. Do never use different Versions of Xilinx Software for the same Project.
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Add correct path:https://shop.trenz-electronic.de/en/Download/?path=Trenz_Electronic/TE0803/Reference_Design/2017.1/Starterkit
--> |
Reference Design is available on:
Design Flow
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Basic Design Steps
Add/ Remove project specific
--> |
| Note |
|---|
Reference Design is available with and without prebuilt files. It's recommended to use TE prebuilt files for first lunch. |
Trenz Electronic provides a tcl based built environment based on Xilinx Design Flow.
See also:Vivado/SDK/SDSoC
The Trenz Electronic FPGA Reference Designs are TCL-script based project. Command files for execution will be generated with "_create_win_setup.cmd" on Windows OS and "_create_linux_setup.sh" on Linux OS.
TE Scripts are only needed to generate the vivado project, all other additional steps are optional and can also executed by Xilinx Vivado/SDK GUI. For currently Scripts limitations on Win and Linux OS see: Project Delivery Currently limitations of functionality
- _create_win_setup.cmd/_create_linux_setup.sh and follow instructions on shell:
- Press 0 and enter for minimum setup
- (optional Win OS) Generate Virtual Drive or use short directory for the reference design (for example x:\<design name>)
- Create Project
Select correct device and Xilinx install path on "design_basic_settings.cmd" and create Vivado project with "vivado_create_project_guimode.cmd"
Note: Select correct one, see TE Board Part Filesor open with "vivado_open_project_guimode.cmd", if generated. - Type on Vivado ConsoleCreate HDF and export to prebuilt folder
Run on Vivado TCL: TE::hwpr_program_buildflash_design mcsfile -exportswapp hello_prebuiltte0841
Note: Script generate design and export files into \Alternative use SDK or setup Flash on Vivado manually - Reboot (if not done automatically)
SD
Not used on this Example.
JTAG
- Connect JTAG and power on PCB
- Open Vivado HW Manager
- Program FPGA with Bitfile from "prebuilt\hardware\<short dir>. Use GUI is the same, except file export to prebuilt folder
- Generate MCS Firmware (optional):
- Create SDK Project with TE Scripts on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_sdk
- Create "SCU" application
Note: Select MCS Microblaze and SCU Application - Select Release Built
- Regenerate App
- Generate Programming Files with HSI/SDK
- Run on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_hsi
Note: Scripts generate applications and bootable files, which are defined in "sw_lib\apps_list.csv" - (alternative) Start SDK with Vivado GUI or start with TE Scripts on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_sdk
Note: See SDK Projects
- Run on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_hsi
- Copy "\prebuilt\software\<short name>\hello_te0741.elf" into "\firmware\microblaze_0\"
- (optional) Copy "\\workspace\sdk\scu\Release\scu.elf" into "\firmware\microblaze_mcs_0\"
- Regenerate Vivado Project or Update Bitfile only with "hello_te0741.elf" and "scu.elf"
Launch
Programming
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Description of Block Design, Constrains...
BD Pictures from Export...
--> |
| Note |
|---|
Check Module and Carrier TRMs for proper HW configuration before you try any design. |
Xilinx documentation for programming and debugging: Vivado/SDK/SDSoC-Xilinx Software Programming and Debugging
QSPI
- Connect JTAG and power on PCB
- (if not done) Select correct device and Xilinx install path on "design_basic_settings.cmd" and create Vivado project with "vivado_create_project_guimode.cmd" or open with "vivado_open_project_guimode.cmd", if generated.
- Type on Vivado Console: TE::pr_program_flash_mcsfile -swapp u-boot
Note: Alternative use SDK or setup Flash on Vivado manually - Reboot (if not done automatically)
SD
Not used on this Example.
JTAG
- Connect JTAG and power on PCB
- Open Vivado HW Manager
- Program FPGA with Bitfile from "prebuilt\hardware\<short dir>"
Usage
- Prepare HW like described on section Programming
- Connect UART USB (most cases same as JTAG)
- Power on PCB
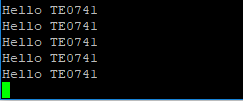
Note: FPGA Loads Bitfile from Flash,MCS Firmware configure SI5338 and starts Microblaze, Hello TE0741 from Bitfile Example will be run on UART console.
Do not reboot, if Bitfile programming over JTAG is used as programming method.
UART
Open Serial Console (e.g. putty)
- Speed: 9600
- COM Port: Win OS, see device manager, Linux OS see dmesg |grep tty (UART is *USB1)
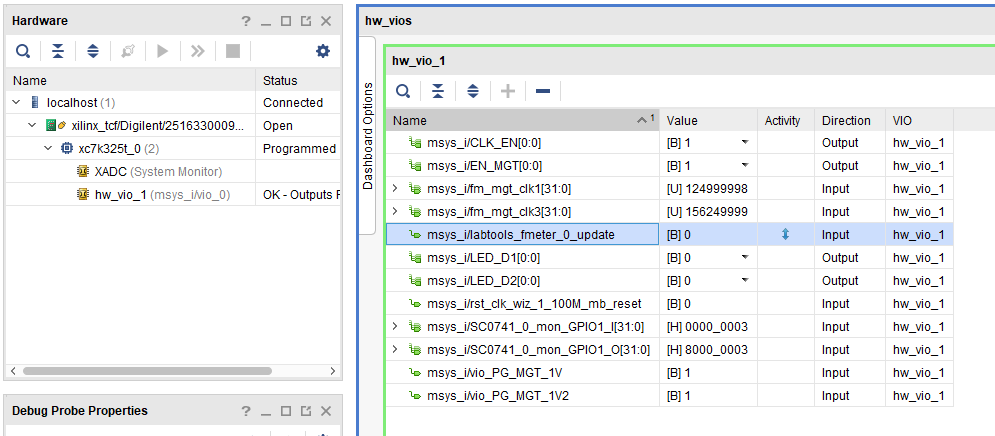
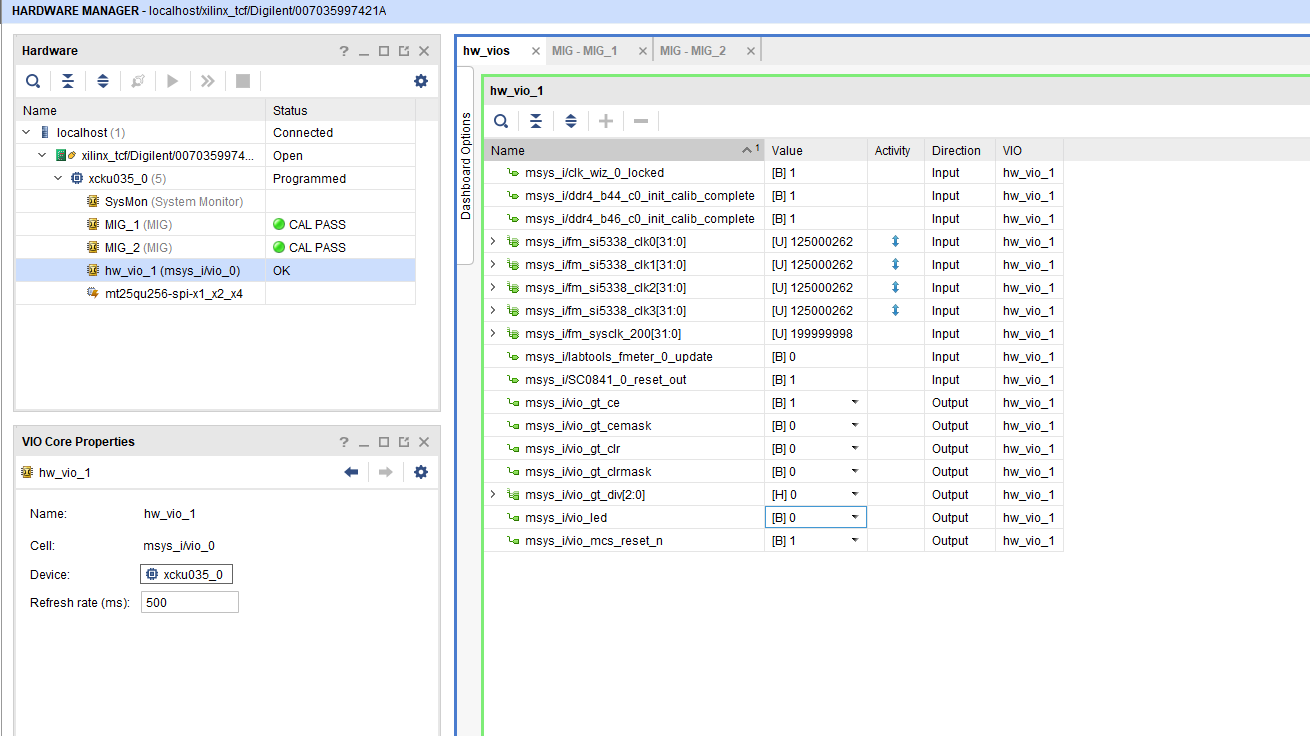
Vivado HW Manager:
- Open Vivado HW-Manager and add VIO signal to dashboard (*.ltx located on prebuilt folder).
- Set radix from VIO signals (MGT...) to unsigned integer.
Note: Frequency Counter is inaccurate and displayed unit is Hz - MGT REFCL1~125MHz, GT_REFCLK3~156,25MHz (default off, configured with MCS Firmware)
- LED_D1/D2 control
- SI5338 25MHz REF CLK Enable
- MGT Power Monitoring+MGT Enable
- Set radix from VIO signals (MGT...) to unsigned integer.
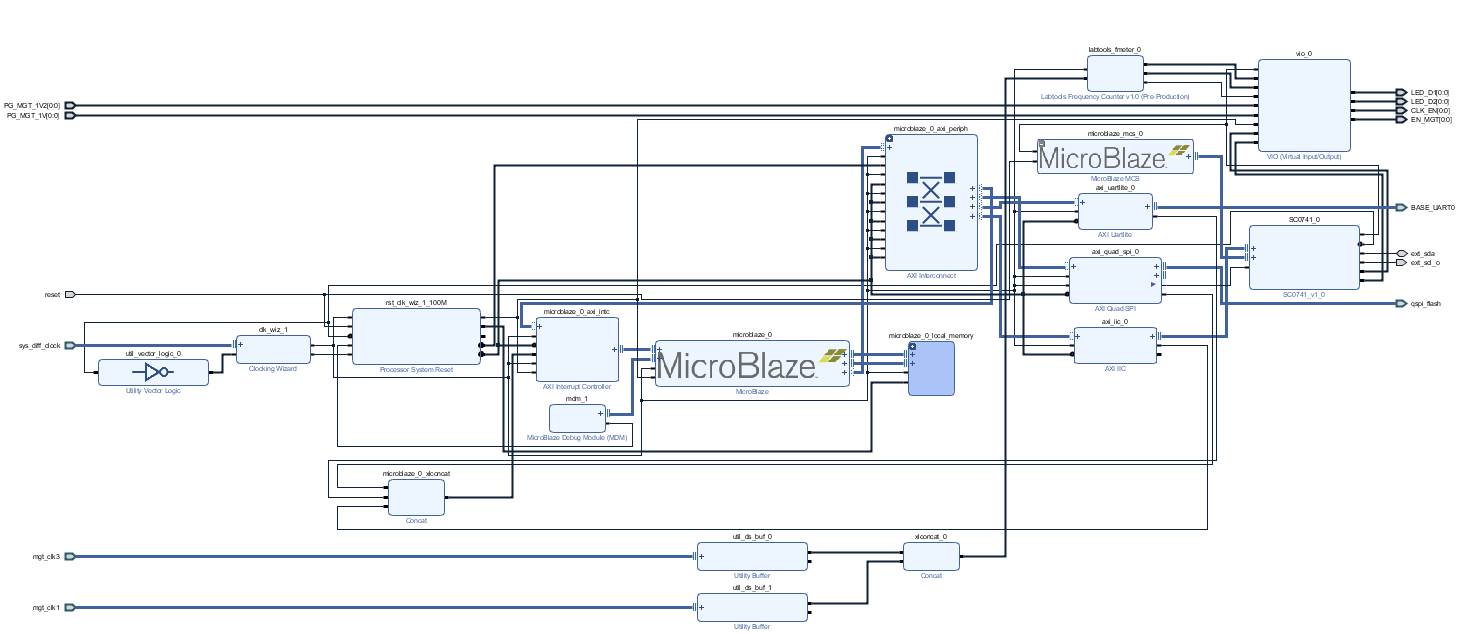
System Design - Vivado
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Description of Block Design, Constrains...
BD Pictures from Export...
--> |
Block Design
Constrains
...
- "
- Note SREC Bootloader try to find application on flash, this will stop, if Flash is empty.
Usage
- Prepare HW like described on section Programming
- Connect UART USB (most cases same as JTAG)
- Power on PCB
Note: FPGA Loads Bitfile from Flash,MCS Firmware configure SI5338 and starts MicroBlaze, MicroBlaze SREC Bootloader loads Hello TE0781 from Flash into RAM and starts application. Example will be run on UART console.
Do not reboot, if Bitfile programming over JTAG is used as programming method.
UART
Open Serial Console (e.g. putty)
- Speed: 9600
- COM Port: Win OS, see device manager, Linux OS see dmesg |grep tty (UART is *USB1)
Vivado HW Manager:
- Open Vivado HW-Manager and add VIO signal to dashboard (*.ltx located on prebuilt folder).
- Set radix from VIO signals (fm_si...) to unsigned integer.
Note: Frequency Counter is inaccurate and displayed unit is Hz - SI will be configured with MCS firmware, default all off on PCB REV01
- LED control via VIO
- MGT CLK Freq can be changed over BUFG_GT control signals divider
- MCS Reset possible via VIO
- Set radix from VIO signals (fm_si...) to unsigned integer.
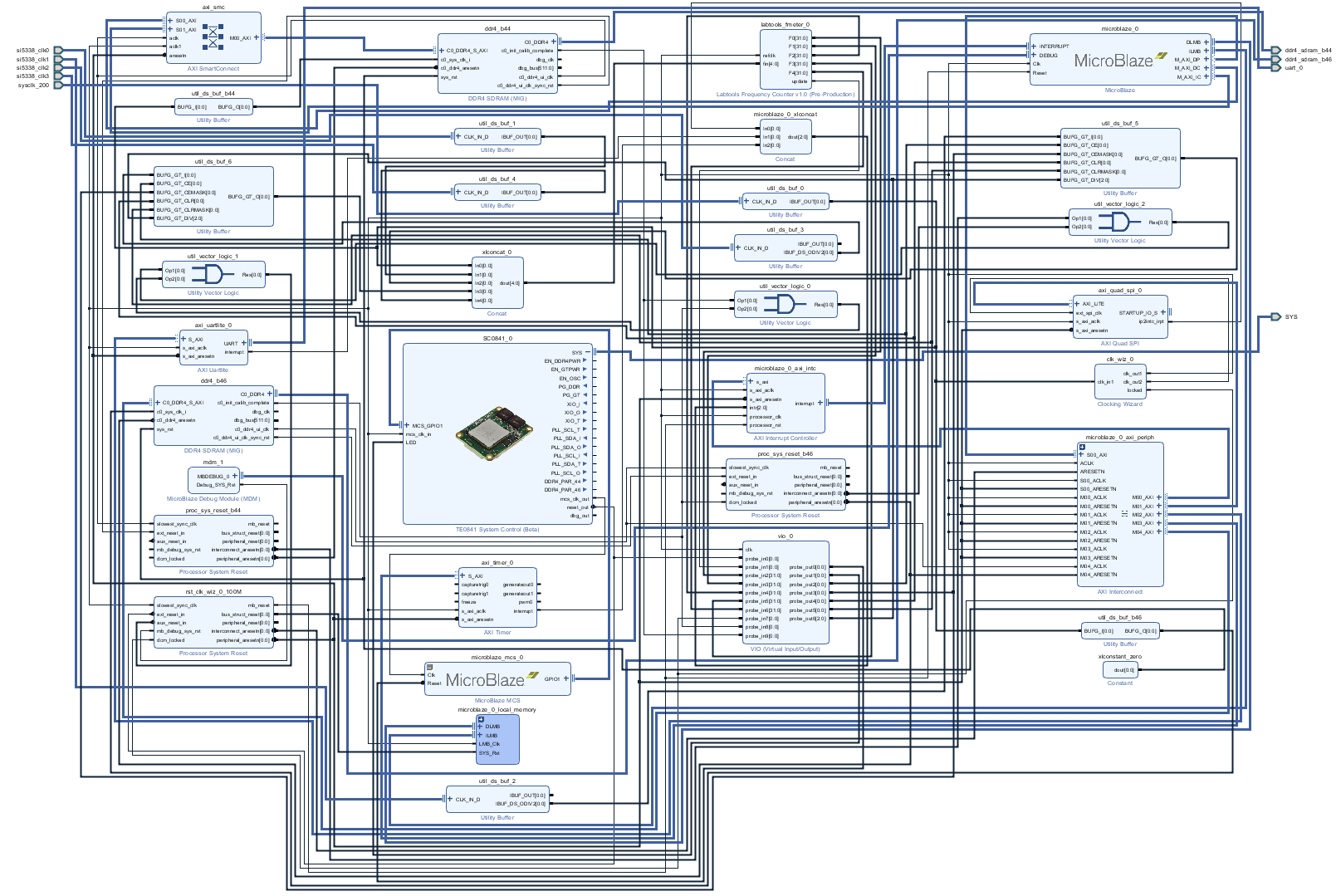
System Design - Vivado
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Description of Block Design, Constrains...
BD Pictures from Export...
--> |
Block Design
Constrains
Basic module constrains
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
set_property BITSTREAM.GENERAL.COMPRESS TRUE [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.CONFIGRATE 69 [current_design]
set_property CFGBVS GND [current_design]
set_property CONFIG_VOLTAGE 1.8 [current_design]
set_property CONFIG_MODE SPIx4 [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.SPI_32BIT_ADDR YES [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.SPI_BUSWIDTH 4 [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.M1PIN PULLNONE [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.M2PIN PULLNONE [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.M0PIN PULLNONE [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.USR_ACCESS TIMESTAMP [current_design] |
Design specific constrain
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
set_property CLOCK_DEDICATED_ROUTE BACKBONE [get_pins -hier -filter {NAME =~ */u_ddr4_infrastructure/gen_mmcme*.u_mmcme_adv_inst/CLKIN1}]
create_clock -name ddr4_0_clk -period 4.95 [get_pins */ddr4_0/*/u_ddr4_infrastructure/gen_mmcme*.u_mmcme_adv_inst/CLKIN1]
create_clock -name ddr4_1_clk -period 4.95 [get_pins */ddr4_1/*/u_ddr4_infrastructure/gen_mmcme*.u_mmcme_adv_inst/CLKIN1]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.UNUSEDPIN PULLUP [current_design |
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
set_property BITSTREAM.GENERAL.COMPRESS TRUE [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.CONFIGRATE 66 [current_design]
set_property CONFIG_VOLTAGE 3.3 [current_design]
set_property CFGBVS VCCO [current_design]
set_property CONFIG_MODE SPIx4 [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.SPI_32BIT_ADDR YES [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.SPI_BUSWIDTH 4 [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.M1PIN PULLNONE [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.M2PIN PULLNONE [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.M0PIN PULLNONE [current_design]
set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.USR_ACCESS TIMESTAMP [current_design] |
Design specific constrain
| ||||||
# You must provide all the delay numbers
# CCLK delay is 0.1, 6.7 ns min/max for ultra-scale devices; refer Data sheet
# Consider the max delay for worst case analysis
set cclk_delay 6.7
create_generated_clock -name clk_sck -source [get_pins -hierarchical *axi_quad_spi_0/ext_spi_clk] -edges {3 5 7} -edge_shift [list $cclk_delay $cclk_delay $cclk_delay] [get_pins -hierarchical *USRCCLKO]
set_multicycle_path -setup -from clk_sck -to [get_clocks -of_objects [get_pins -hierarchical */ext_spi_clk]] 2
set_multicycle_path -hold -end -from clk_sck -to [get_clocks -of_objects [get_pins -hierarchical */ext_spi_clk]] 1
set_multicycle_path -setup -start -from [get_clocks -of_objects [get_pins -hierarchical */ext_spi_clk]] -to clk_sck 2
set_multicycle_path -hold -from [get_clocks -of_objects [get_pins -hierarchical */ext_spi_clk]] -to clk_sck 1
# Max delay constraints are used to instruct the tool to place IP near to STARTUPE3 primitive.
# If needed adjust the delays appropriately
set_max_delay -datapath_only -from [get_pins -hier {*STARTUP*_inst/DI[*]}] 1.000
set_max_delay -datapath_only -from [get_clocks clk_out2_msys_clk_wiz_0_0] -to [get_pins -hier *STARTUP*_inst/USRCCLKO] 1.000
#set_max_delay -datapath_only -from [get_clocks clk_out2_msys_clk_wiz_0_0] -to [get_pins -hier *STARTUP*_inst/DO[*] {*STARTUP*_inst/DTS[*]}] 1.000
set_max_delay -datapath_only -from [get_clocks clk_out2_msys_clk_wiz_0_0] -to [get_pins -hier *STARTUP*_inst/DO[*]] 1.000
set_max_delay -datapath_only -from [get_clocks clk_out2_msys_clk_wiz_0_0] -to [get_pins -hier *STARTUP*_inst/DTS[*]] 1.000
| ||||||
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
#LED
set_property PACKAGE_PIN D26 [get_ports {LED_D1[0]}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports {LED_D1[0]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN E26 [get_ports {LED_D2[0]}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports {LED_D2[0]}]
#MGT Power
set_property PACKAGE_PIN G25 [get_ports {PG_MGT_1V2[0]}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports {PG_MGT_1V2[0]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN K23 [get_ports {PG_MGT_1V[0]}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports {PG_MGT_1V[0]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN H22 [get_ports {EN_MGT[0]}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports {EN_MGT[0]}]
#SI5338 CLK
set_property PACKAGE_PIN C26 [get_ports {CLK_EN[0]}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports {CLK_EN[0]}]
#I2C PLL SI5338
set_property PACKAGE_PIN A20 [get_ports ext_scl_o]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports ext_scl_o]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN B21 [get_ports ext_sda]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports ext_sda] |
| Code Block | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
#Fmeter can be ignored, it's only simple measurement set_false_path -from [get_pinsclocks {msys_i/labtoolsutil_ds_fmeterbuf_05/U0/FMETERBUFG_GT_genO[*].COUNTER_F_inst/bl.DSP48E_2/CLK0]}] -to [get_clocks -of_objects [get_pins {msys_i/labtoolsclk_fmeterwiz_0/U0inst/F_reg[*]/D}] mmcme3_adv_inst/CLKOUT0]] set_false_path -from [get_pinsclocks {msys_i/labtoolsutil_ds_fmeterbuf_06/U0/toggle_reg/CBUFG_GT_O[0]}] -to [get_clocks -of_objects [get_pins {msys_i/labtoolsclk_fmeterwiz_0/U0inst/FMETER_gen[*].COUNTER_F_inst/bl.DSP48E_2/RSTC}mmcme3_adv_inst/CLKOUT0]] set_false_path -from [get_clocks -of_objects [get_pins msys_i/labtoolsclk_fmeterwiz_0/U0inst/togglemmcme3_adv_reginst/CCLKOUT0]] -to [get_pinsclocks {msys_i/labtoolsutil_ds_fmeterbuf_06/U0/FMETERBUFG_GT_genO[*].COUNTER_F_inst/bl.DSP48E_2/RSTA0]}] set_false_path -from [get_clocks -of_objects [get_pins msys_i/labtoolsclk_fmeterwiz_0/U0inst/togglemmcme3_adv_reginst/CCLKOUT0]] -to [get_pinsclocks {msys_i/labtoolsutil_ds_fmeterbuf_05/U0/FMETERBUFG_GT_genO[*].COUNTER_F_inst/bl.DSP48E_2/RSTB0]}] set_false_path -from [get_clocks -of_objects [get_pins msys_i/labtoolsclk_fmeterwiz_0/U0inst/togglemmcme3_adv_reginst/CCLKOUT0]] -to [get_pinsclocks {msys_i/labtoolsutil_ds_fmeterbuf_01/U0/FMETERIBUF_gen[*].COUNTER_F_inst/bl.DSP48E_2/CEALUMODEOUT[0]}] set_false_path -from [get_clocks -of_objects [get_pins msys_i/labtoolsclk_fmeterwiz_0/U0inst/togglemmcme3_adv_reginst/CCLKOUT0]] -to [get_pinsclocks {msys_i/labtoolsutil_ds_fmeterbuf_04/U0/FMETERIBUF_genOUT[*].COUNTER_F_inst/bl.DSP48E_2/RSTCTRL}] set_false_path -from0]}] set_false_path -from [get_clocks {msys_i/util_ds_buf_1/U0/IBUF_OUT[0]}] -to [get_clocks -of_objects [get_pins msys_i/clk_wiz_10/inst/mmcmmmcme3_adv_inst/CLKOUT0]] set_false_path -tofrom [get_clocks {msys_i/util_ds_buf_04/U0/IBUF_OUT[0]}] set_false_path -fromto [get_clocks -of_objects [get_pins msys_i/clk_wiz_10/inst/mmcm_adv_inst/CLKOUT0]] -to [get_clocks {msys_i/util_ds_buf_1/U0/IBUF_OUT[0]}mmcme3_adv_inst/CLKOUT0]] |
Software Design - SDK/HSI
...
Template location: \sw_lib\sw_apps\scu
Hello
...
TE0841
Xilinx Hello World example as andless endless loop
Template location: \sw_lib\sw_apps\hello_te0741te0841
SREC SPI Bootloader
Modified Xilinx SREC Bootloader. Changes: Correct flash typ and SRec Start address, some additional console outputs, see source code
Template location: \sw_lib\sw_apps\srec_spi_bootloader
\sw_lib\sw_services\xilisf_v5_9
Additional Software
| HTML |
|---|
<!-- Add Description for other Software, for example SI CLK Builder ... --> |
...