Page History
This step chapter guides through the tasks which have to be done inside the Intel SoC Embedded Development Suite. As mentioned in page "Board bring-up overview for TEI0022" this step is for preloader and bootloader generation which should be done in the following next three stepssections:
- Preparation
- Preloader/Bootloader Generationgeneration
- Device Tree Generationgeneration
The section "Preparation" describes preparing steps which are necessary for the generation of the preloader and the bootloader which is described in section "Preloader/Bootloader Generationgeneration". After that in section "Device Tree Generationgeneration" the steps to create the device tree blob is explained.
/////
Requirements - EIGENTLICH ÜBERFLÜSSIG, da auf Seite 0 geschrieben... . ?!?
All steps to format / setup a bootable SD card can only be performed within a Linux,
(Windows Subsystem for Linux is not capable to format a SD card) the Linux tool fdisk / sfdisk depend on it.
The tools bsp-editor, alt-boot-disc-util and SoC EDS Command Shell are present.
An installation of INTEL SoC FPGA EMBEDDED DEVELOPMENT SUITE along with Intel Quartus Prime Lite, so the tools
bsp-editor, alt-boot-disc-util and SoC EDS Command Shell are present.
Background
The boot process of the HPS consists of several stages:
...
Preparation
While Intel Quartus Prime project compilation
...
DIE GRAFIK GEHÖRT INTEL; DARF DIE HIER ÜBERHAUPT SEIN?---------------------------------------------------------
...
Preparation
After compilation of the Intel Quartus project, described on page Intel Quartus Prime Project, the folder "hps_isw_handoff" is existing inside the project folder. Therefore, if this folder does not exist fix the issue and return to this point.
BSP Editor
The BSP-Editor takes the handoff folder and generates further source and configuration files to be able to compile
the U-Boot Preloader and U-Boot Bootloader for the HPS.
...
created which is now needed to generate via the bsp-editor further output for preloader and bootloader generation. To do the preparation, follow the following guide:
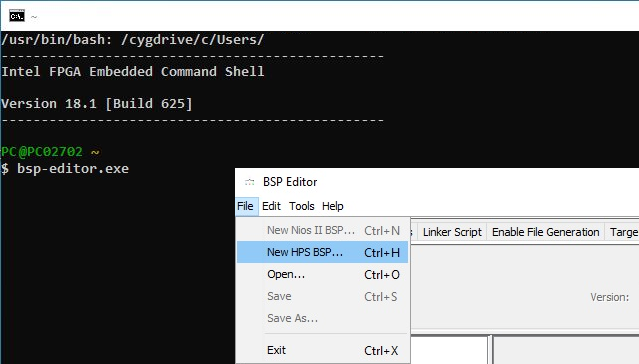
- Start the SoC EDS Shell as administrator. To do that navigate to C:\intelFPGA\18.1\embedded\
...
- , right click on the file "Embedded_Command_Shell.
...
- bat", and select "Run as administrator
...
- ". Click Yes in the
...
- window
...
- "User Account Control".
...
- In the opened shell start the bsp-editor, as visible in the next figure, via: bsp-editor.exe
...
- In the opened bsp-editor select File → New HPS BSP...
...
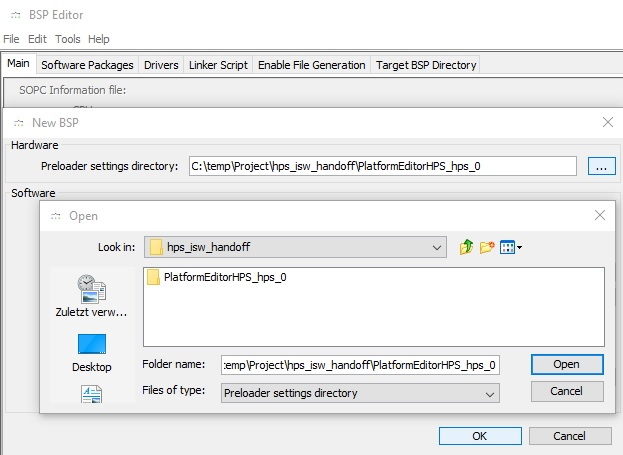
- In the opened New BSP
...
- dialogue click onto
...
- ... and select the PlatformEditorHPS_hps_0 folder inside
...
- the hps_isw_handoff folder
...
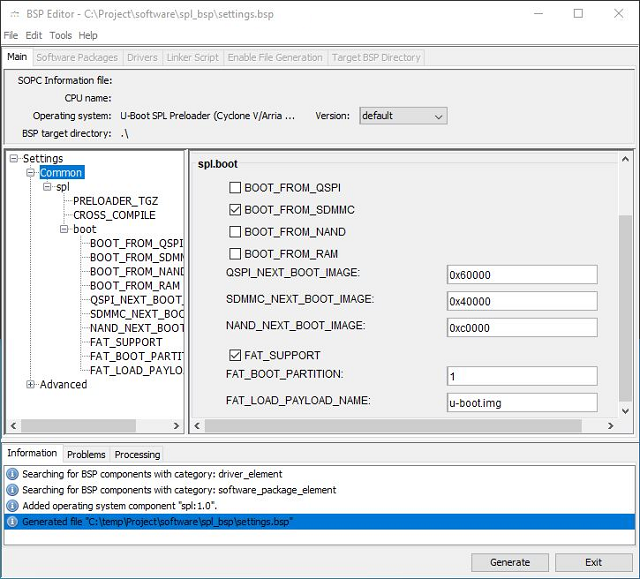
Back in the BSP-Editor, the U-Boot preloader must be configured. In the right column, under spl.boot are four Checkboxes,
each beginning with BOOT_FROM_... check only BOOT_FROM_SDMMC , the following three lines are of no interest.
...
- After that, click Open in this dialogue and OK in the previous dialogue.
- Now, in the bsp-editor, the preloader should be configured. Select only BOOT_FROM_SDMMC as BOOT_FROM_-parameter in the right window under the spl.boot header.
- Select FAT_SUPPORT.
- Select 1 as FAT_BOOT_PARTITION.
- Select u-boot.img as FAT_LOAD_PAYLOAD_NAME
...
- .
- Then, generate the output via clicking the Generate button.
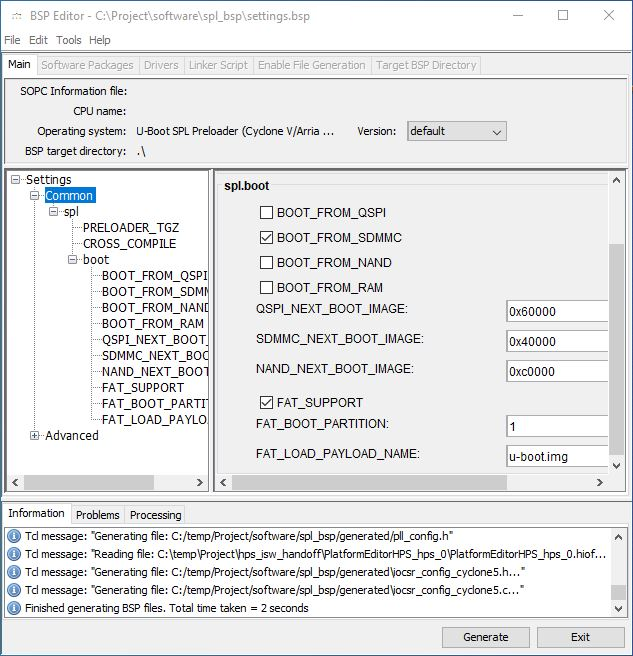
- After generation, an information like Finished generation BSP files. Total time taken =
...
In your project folder, the folder - software - appears.
U-Boot - Make preloader and main bootloader
The handoff folder contains now after the previous steps all the sources to compile the booot loaders.
On Windows 10 - Version 1909 - and cygwin - Version 2.0 - all commands which require decompressing of source archives, have to be
pointed into the right folder to be executed from, these commands beginn with /usr/bin/ . All commands are in italic and bold,
comments to commands are in brackets.
...
- ... seconds is displayed in the information tab. The folder software in the project path should now be available.
- Close the bsp-editor.
Preloader/Bootloader generation
After this preparation, it is possible to generate the preloader and the bootloader inside the shell while following the guide:
...
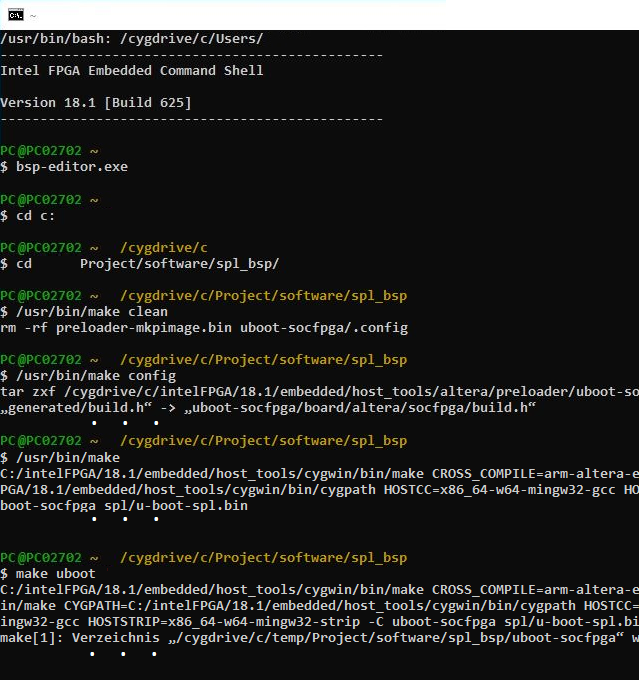
- Change into folder .../software/spl_bsp inside the project folder with the change directory command cd. For example:
...
- cd Project/software/spl_bsp
...
- Clean the folder via running /usr/bin/make clean
...
- Configure the build process via
- /usr/bin/make
...
- config which generates
...
- the folder .../software/spl_bsp
...
- /uboot-socfpga.
- Generate the preloader via /usr/bin/make which generates the file .../software/spl_bsp/
...
- preloader-mkpimage.bin
...
- .
...
- Generate the bootloader via /usr/bin/
...
- make uboot which generates the image .../software/spl_bsp/uboot-socfpga/u-boot.img.
- If the make process ends with an error, try to rerun /usr/bin/make uboot until there is no error and the output is generated.
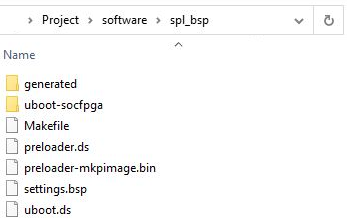
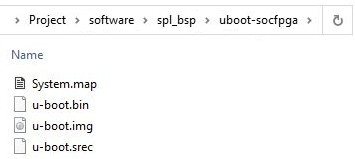
After that, the folder .../software/spl_bsp/ should look like the following figure.
The folder .../software)To generate the main U-Boot boot loader, type:
make uboot (Places the image u-boot.img into softwae/spl_bsp/uboot-socfpga ) should contain the files shown in the next figure.
Device Tree
...
Lastly, the Device Tree Blob must be generated, whereby Linux can start automated without user interaction.
It acts as an Interface from the board hardware to the Linux Kernel. The .dtb file informs the Linux Kernel about the existing Hardware,
its Configuration and which driver to use for controlling it.
Generate - .dtb or .dts file from .sopcinfo file
...
generation
The device tree generation is a crucial part to tell the linux kernel which hardware has to be handled. To generate the device tree blob follow this guide:
- For device tree generation the Golden Hardware Reference Design file .../intelFPGA/18.1/embedded/examples/hardware/cv_soc_devkit_ghrd
...
- /hps_common_board_info.xml is needed. Therefore, copy this file into the project folder where the software folder, the output_files folder, ... are. This file contains information regarding the board which can be adapted, if necessary.
- Generate the device tree via the shell command: sopc2dts --input <Project Name>.sopcinfo --output socfpga
To generate the .dtb file, a folder containing the Golden Hardware Reference Design for Cyclone 5 FPGA's is required. A copy of it is
part of Intels SoC FPGA Embedded Development Suite. To be on the safe side, copy the file
soc_system_18_1_09132018_94307.tar.gz
inside the folder
c:\intelFPGA\18.1\embedded\examples\hardware\cv_soc_devkit_ghrd\tgz\
to new folder inside your project directory, for example,
c:\Project\ghrd_cyc5
via a file browser.
Use a SoC EDS SHell with administrative privileges to navigate to your newly folder
cd c:/Project/ghrd_cyc5
and extract the .tar.gz archieve .
tar xvf soc_system_18_1_09132018_94307.tar.gz (Decompress the archieve)
...
- .dtb --type dtb --board hps_common_board_info.xml --bridge-removal all --clocks
...
- The output in the following listing can be ignored.
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
$ sopc2dts.exe --input PlatformEditorHPS.sopcinfo --output DTBsocfpga.dts --type dts --board |
Kurzform:
sopc2dts -i HPS.sopcinfo -o DTBsocfpga.dtb -t dtb --board hps_common_board_info.xml --bridge-removal all --clocks
In case a .dts file is desired, use this command:
sopc2dts -i HPS.sopcinfo -o DTBsocfpga.dts -t dts --board hps_common_board_info.xml --bridge-removal all --clocks
--------------
...
hps_common_board_info.xml |
...
--bridge-removal all --clocks |
...
MasterIF sopc2dts.lib.components.Interface@76fb509a slaveIF null |
...
MasterIF sopc2dts.lib.components.Interface@76fb509a slaveIF null |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for #address-cells. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for #size-cells. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for reg. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for spi-max-frequency. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for m25p,fast-read. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for page-size. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for block-size. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for tshsl-ns. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for tsd2d-ns. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for tchsh-ns. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for tslch-ns. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for cdns,page-size. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for cdns,block-size. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for cdns,read-delay. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for cdns,tshsl-ns. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for cdns,tsd2d-ns. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for cdns,tchsh-ns. Adding to root |
...
DTAppend: Unable to find parent, null, for cdns,tslch-ns. Adding to |
...
--------------
Decompile - .dtb file to .dts file
C:\intelFPGA\18.1\embedded\host_tools\gnu\dtc\ dtc.exe
cd /cygdrive/c/intelFPGA/18.1/embedded/host_tools/gnu/dtc
dtc -I dts -O dtb -o device-tree.dtb devicetree.dts
Generate - .dts file to .dtb file
cd /cygdrive/c/intelFPGA/18.1/embedded/host_tools/gnu/dtc
...
root |