Template Revision 3.0Design Name always "TE Series Name" + Design name, for example "TE0720 Test Board"
|
Important General Note:
|
Overview
Notes :
|
Refer to http://trenz.org/te0xyz-info for the current online version of this manual and other available documentation.
Key Features
Notes :
|
|
Revision History
Notes :
|
|
Release Notes and Know Issues
Notes :
|
|
Requirements
Software
Notes :
|
|
Hardware
Notes :
|
Basic description of TE Board Part Files is available on TE Board Part Files.
Complete List is available on <design name>/board_files/*_board_files.csv
Design supports following modules:
|
Design supports following carriers:
|
Additional HW Requirements:
|
Content
Notes :
|
For general structure and of the reference design, see Project Delivery - Xilinx devices
Design Sources
|
Additional Sources
|
Prebuilt
Notes :
|
|
Download
Reference Design is only usable with the specified Vivado/Vitis/PetaLinux version. Do never use different Versions of Xilinx Software for the same Project.
|
Reference Design is available on:
Software Setup
Download RF Analyzer GUI from the following link and install it.
Design Flow
Notes :
|
Reference Design is available with and without prebuilt files. It's recommended to use TE prebuilt files for first lunch. |
Trenz Electronic provides a tcl based built environment based on Xilinx Design Flow.
See also:
The Trenz Electronic FPGA Reference Designs are TCL-script based project. Command files for execution will be generated with "_create_win_setup.cmd" on Windows OS and "_create_linux_setup.sh" on Linux OS.
TE Scripts are only needed to generate the vivado project, all other additional steps are optional and can also executed by Xilinx Vivado/SDK GUI. For currently Scripts limitations on Win and Linux OS see: Project Delivery - Xilinx devices
_create_win_setup.cmd/_create_linux_setup.sh and follow instructions on shell:
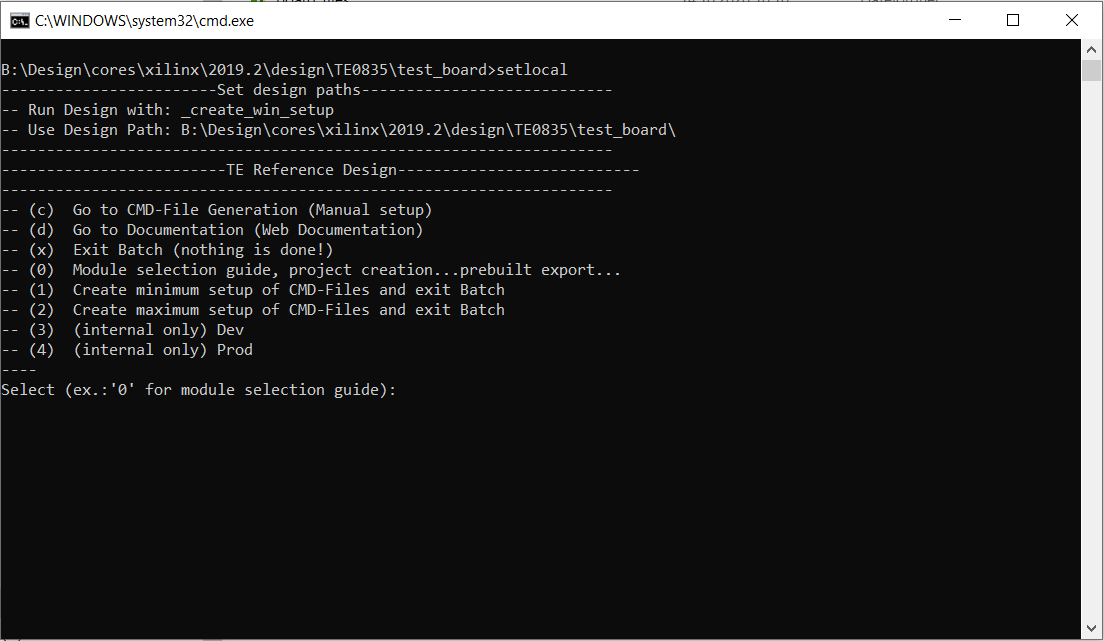
Press 0 and enter to start "Module Selection Guide"
(optional Win OS) Generate Virtual Drive or use short directory for the reference design (for example x:\<design name>)
Create Project (follow instruction of the product selection guide), settings file will be configured automatically during this process)
(optional for manual changes) Select correct device and Xilinx install path on "design_basic_settings.cmd" and create Vivado project with "vivado_create_project_guimode.cmd"
Note: Select correct one, see also TE Board Part Files
Create XSA and export to prebuilt folder
Run on Vivado TCL: TE::hw_build_design -export_prebuilt
Note: Script generate design and export files into \prebuilt\hardware\<short dir>. Use GUI is the same, except file export to prebuilt folder
Create Linux (bl31.elf, uboot.elf and image.ub) with exported XSA
XSA is exported to "prebuilt\hardware\<short name>"
Note: HW Export from Vivado GUI create another path as default workspace.
Create Linux images on VM, see PetaLinux KICKstart
Use TE Template from /os/petalinux
Add Linux files (bl31.elf, uboot.elf and image.ub) to prebuilt folder
"prebuilt\os\petalinux\<ddr size>" or "prebuilt\os\petalinux\<short name>"
Generate Programming Files with Vitis
Run on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_vitis -all
Note: Scripts generate applications and bootable files, which are defined in "sw_lib\apps_list.csv"
(alternative) Start SDK with Vivado GUI or start with TE Scripts on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_vitis
Note: TCL scripts generate also platform project, this must be done manuelly in case GUI is used. See Vitis
Launch
Note:
|
Programming
Check Module and Carrier TRMs for proper HW configuration before you try any design. |
Xilinx documentation for programming and debugging: Xilinx Development Tools
Get prebuilt boot binaries
_create_win_setup.cmd/_create_linux_setup.sh and follow instructions on shell
Press 0 and enter to start "Module Selection Guide"
Select assembly version
Validate selection
Select Create and open delivery binary folder
Note: Folder (<project foler>/_binaries_<Artikel Name>) with subfolder (boot_<app name>) for different applications will be generated
QSPI
Optional for Boot.bin on QSPI Flash and image.ub on SD.
Connect JTAG and power on carrier with module
Open Vivado Project with "vivado_open_existing_project_guimode.cmd" or if not created, create with "vivado_create_project_guimode.cmd"
Type on Vivado TCL Console: TE::pr_program_flash -swapp u-boot
Note: To program with SDK/Vivado GUI, use special FSBL (zynqmp_fsbl_flash) on setup
optional "TE::pr_program_flash -swapp hello_te0835" possible
Copy image.ub on SD-Card
use files from (<project foler>/_binaries_<Articel Name>)/boot_linux from generated binary folder,see: Get prebuilt boot binaries
or use prebuilt file location, see <design_name>/prebuilt/readme_file_location.txt
Insert SD-Card
SD
Copy image.ub and Boot.bin on SD-Card
use files from (<project foler>/_binaries_<Articel Name>)/boot_linux from generated binary folder,see: Get prebuilt boot binaries
or use prebuilt file location, see <design_name>/prebuilt/readme_file_location.txt
Set Boot Mode to SD-Boot.
Depends on Carrier, see carrier TRM.
Insert SD-Card in SD-Slot.
JTAG
Not used on this Example.
Hardware Setup
The Hardware contains of a TE0835 module and TEB0835 carrier board and has 8 ADC inputs and 8 DAC outputs.
Plug the TE0835 module on the TEB0835 carrier board
Install the cooler on the RFSoC chip
Attention: It is strongly recommended that the RFSoC should not be used without heat sink.
Connect the micro USB cable to the J29 connector
Plug the board on the PCIe port of the PC
Plug the prepared SD card on the SD card socket (J28)
Connect a cable with SMA or UFL connector to one of the DAC connector( for example DAC0 J9) and feed it back to the related ADC input (for example ADC0 J1)
(optional) A signal generator can be used to feed desired sinal to ADC input.
(optional) An oscilloscope can be used to monitor the output signal of DAC.
Usage
Prepare HW like described on section TE0835 Test Board#Hardware Setup
Connect UART USB (most cases same as JTAG)
Select SD Card as Boot Mode (or QSPI - depending on step 1)
Note: See TRM of the Carrier, which is used.
Power On PCB
Note: 1. Zynqmp RFSoC Boot ROM loads FSBL from SD into OCM, 2. FSBL loads U-boot from SD into DDR, 3. U-boot load Linux from SD into DDR
Linux
Open Serial Console (e.g. putty)
Speed: 115200
COM Port: Win OS, see device manager, Linux OS see dmesg |grep tty (UART is *USB1)
Linux Console:
Note: Wait until Linux boot finished For Linux Login use:User Name: root
Password: root
You can use Linux shell now.
I2C Bus type: i2cdetect -y -r 0
Bus 0 up to 5 possible
RTC check: dmesg | grep rtc
ETH0 works with udhcpc
USB type "lsusb" or connect USB2.0 device
PCIe Bus type: "lspci"
PCIe device should be seen in the console
Option Features
Webserver to get access to Zynqmp RFSoC
insert IP on web browser to start web interface
init.sh scripts
add init.sh script on SD, content will be load automatically on startup (template included in ./misc/SD)
Vivado HW Manager
Note:
|
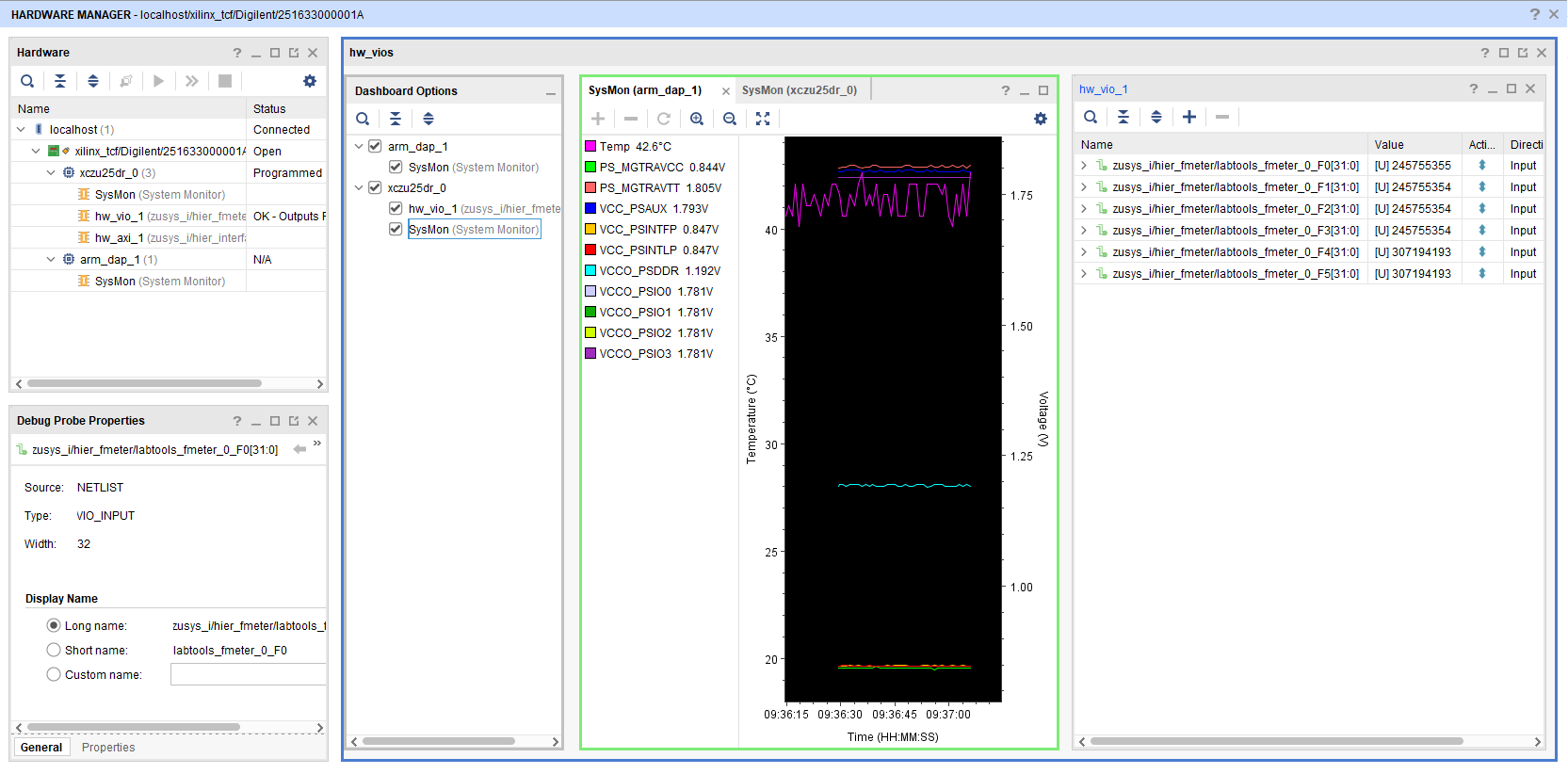
Open Vivado HW-Manager and add VIO signal to dashboard (*.ltx located on prebuilt folder)
Monitoring:
The output frequency of MMCM blocks can be monitored.
Set radix from VIO signals to unsigned integer.
The tempreature of ARM processor and FPGA can be measured too.
RF Analyzer
Open the RF Analyzer GUI
Click on Connect button
Adjust the desired JTAG frequency (for example 30MHZ)
Give the generated bitstream file path
Click on Download Bitstream button to load the Bitstream file on the FPGA
When downloading is finished, click on Select Target button
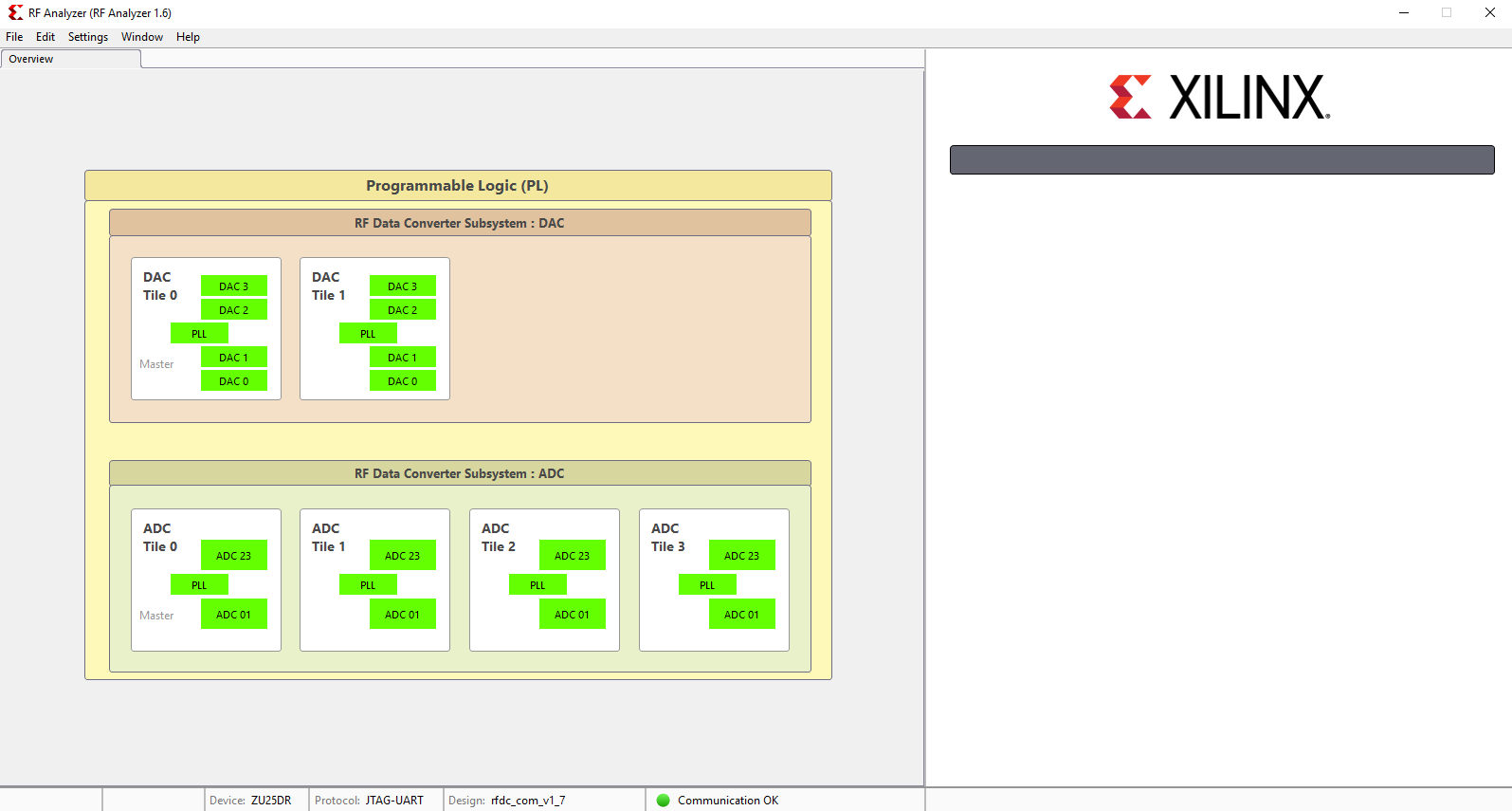
After initilalisation, all ADCs/DACs tiles are visible
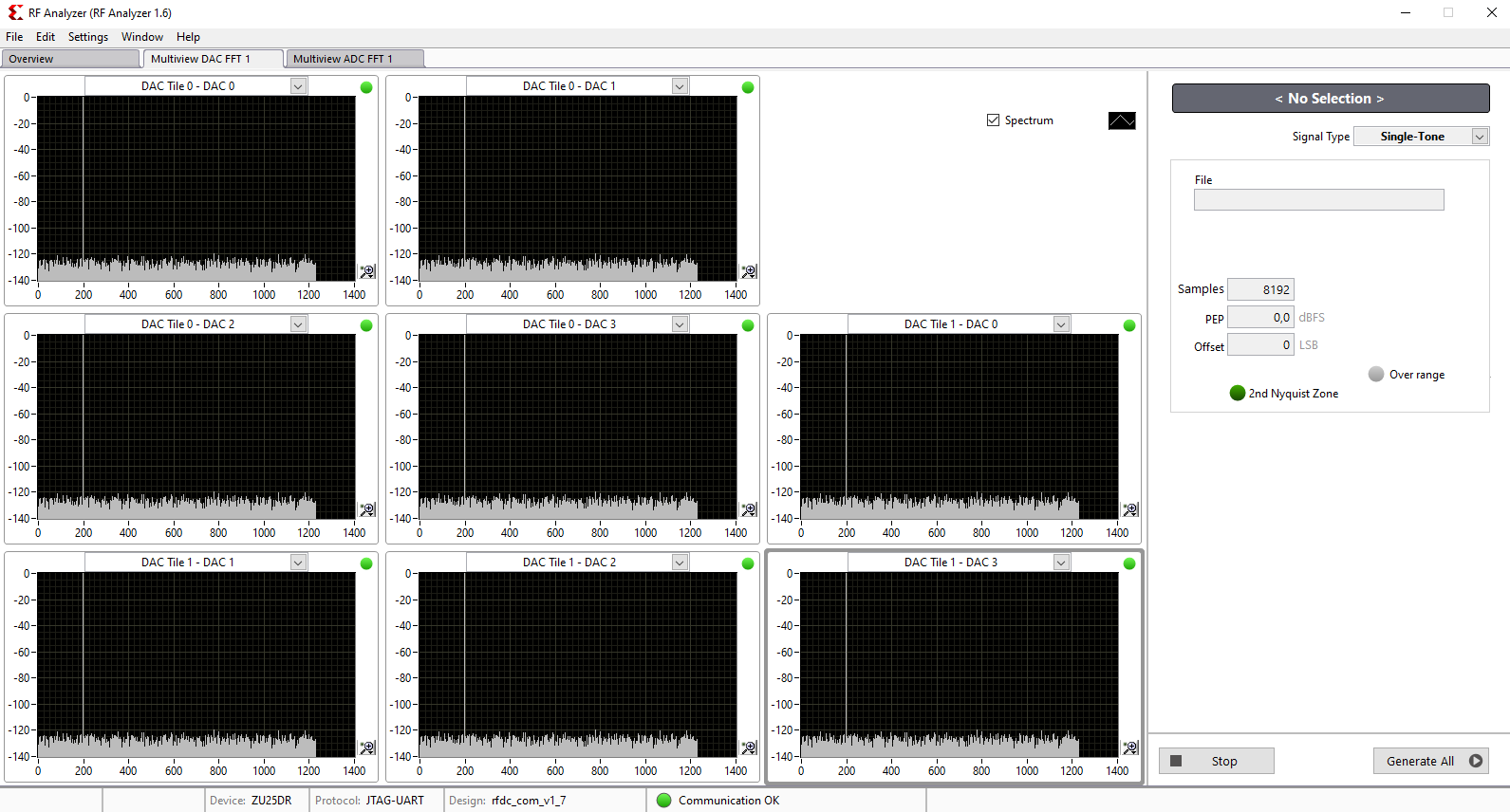
Click on desired DAC tile and choose a DAC (for example DAC0)
Adjust desired DAC properties (for example output frequency)
Click on Generate button to generate the signal in output of DAC
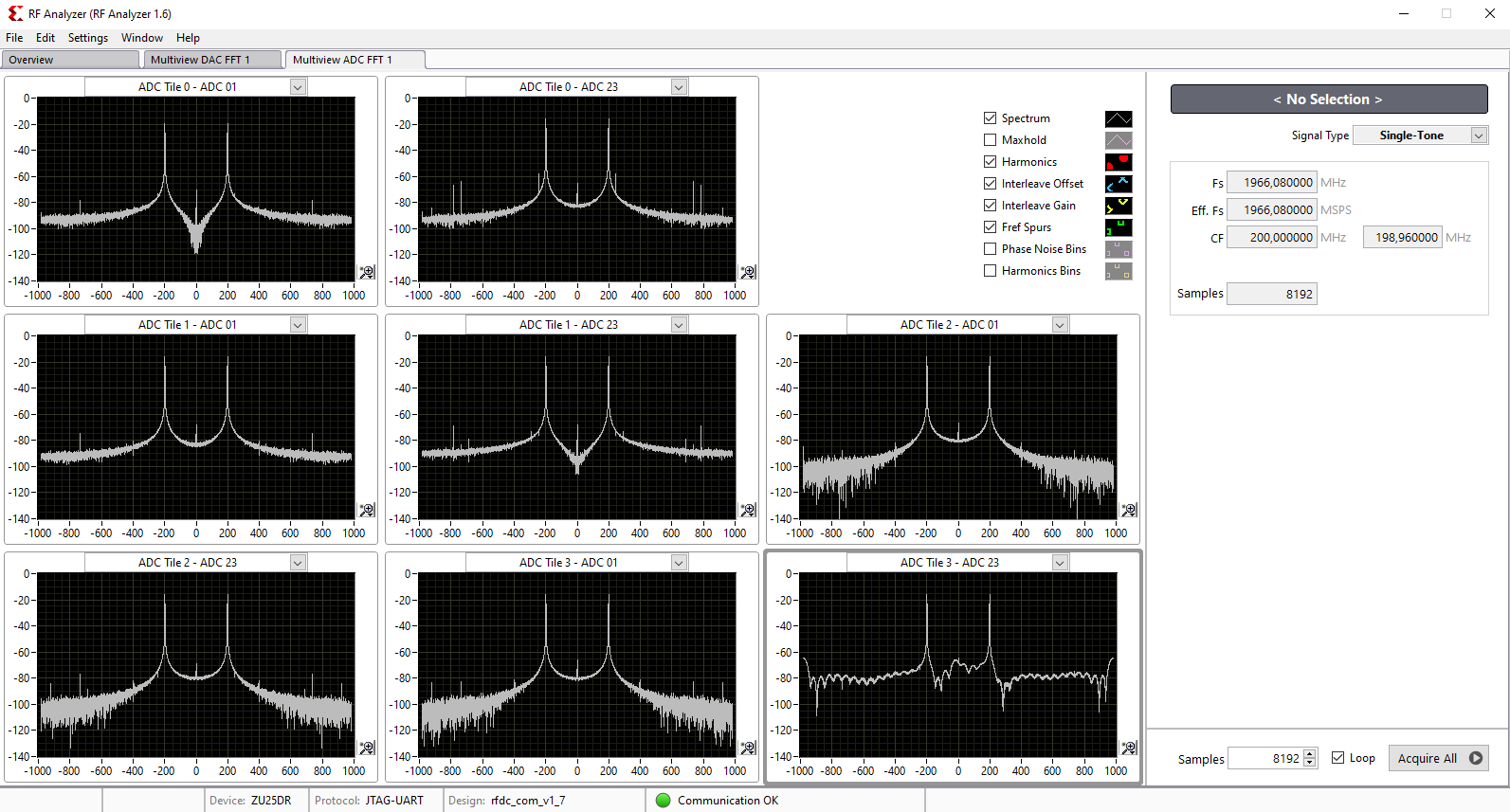
Click on the related ADC tile and choose the related ADC (for example ADC0)
Click on Acquire button to aqcuire the input signal
The spectum of the DAC output signal can be seen now. The signal can be visible in time domain too.
Tip: In menu Window click on Multiview to see all of DACs and ADCs simultaneously.
RF Analyzer GUI | Board TE0835 ( RFSoC U1) | TEB0835 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Tile /Converter | SoC Pin Name | SoC Pin Number | B2B | Signal Name | Connector Designator | Connector Type |
ADC Tile 0-ADC 01 | ADC0_P/ADC0_N | AK2/AK1 | 31/29 | ADC0_P/ADC0_N | J1 | SMA |
ADC Tile 0-ADC 23 | ADC1_P/ADC1_N | AH2/AH1 | 43/41 | ADC1_P/ADC1_N | J2 | UFL |
ADC Tile 1-ADC 01 | ADC2_P/ADC2_N | AF2/AF1 | 49/47 | ADC2_P/ADC2_N | J3 | SMA |
ADC Tile 1-ADC 23 | ADC3_P/ADC3_N | AD2/AD1 | 59/61 | ADC3_P/ADC3_N | J4 | UFL |
ADC Tile 2-ADC 01 | ADC4_P/ADC4_N | AB2/AB1 | 67/65 | ADC4_P/ADC4_N | J5 | SMA |
ADC Tile 2-ADC 23 | ADC5_P/ADC5_N | Y2/Y1 | 79/77 | ADC5_P/ADC5_N | J6 | UFL |
ADC Tile 3-ADC 01 | ADC6_P/ADC6_N | V2/V1 | 85/83 | ADC6_P/ADC6_N | J7 | SMA |
ADC Tile 3-ADC 23 | ADC7_P/ADC7_N | T2/T1 | 97/95 | ADC7_P/ADC7_N | J8 | UFL |
DAC Tile 0-DAC 0 | DAC0_P/DAC0_N | N2/N1 | 103/101 | DAC0_P/DAC0_N | J9 | SMA |
DAC Tile 0-DAC 1 | DAC1_P/DAC1_N | L2/L1 | 109/107 | DAC1_P/DAC1_N | J10 | UFL |
DAC Tile 0-DAC 2 | DAC2_P/DAC2_N | J2/J1 | 121/119 | DAC2_P/DAC2_N | J11 | SMA |
DAC Tile 0-DAC 3 | DAC3_P/DAC3_N | G2/G1 | 127/125 | DAC3_P/DAC3_N | J12 | UFL |
DAC Tile 1-DAC 0 | DAC4_P/DAC4_N | E2/E1 | 133/131 | DAC4_P/DAC4_N | J13 | UFL |
DAC Tile 1-DAC 1 | DAC5_P/DAC5_N | C2/C1 | 139/137 | DAC5_P/DAC5_N | J14 | UFL |
DAC Tile 1-DAC 2 | DAC6_P/DAC6_N | B4/A4 | 151/149 | DAC6_P/DAC6_N | J15 | UFL |
DAC Tile 1-DAC 3 | DAC7_P/DAC7_N | B6/A6 | 157/155 | DAC7_P/DAC7_N | J16 | UFL |
As an example the GUi should be seen after initialization as below:
For example, when all DACs are in operation, the GUI can be seen as below:
For example, when all ADCs are in operation, the GUI can be seen as below:
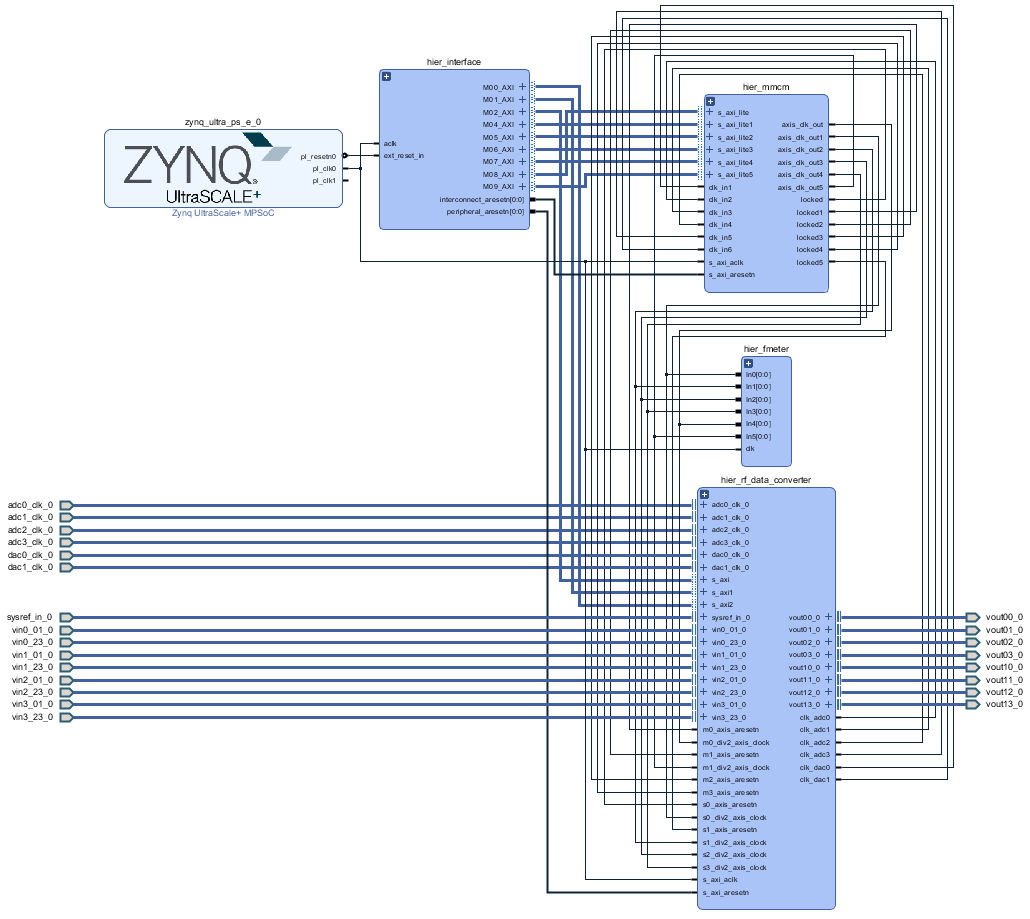
System Design - Vivado
Note:
|
Block Design
PS Interfaces
Note:
|
Activated interfaces:
|
Constrains
Basic module constrains
Design specific constrain
Software Design - Vitis
Note:
|
For SDK project creation, follow instructions from:
Vitis
Application
----------------------------------------------------------FPGA ExamplescuMCS Firmware to configure SI5338 and Reset System.srec_spi_bootloaderTE modified 2019.2 SRECBootloader to load app or second bootloader from flash into DDRDescriptions:
xilisf_v5_11TE modified 2019.2 xilisf_v5_11
----------------------------------------------------------Zynq Example:zynq_fsblTE modified 2019.2 FSBLGeneral:
Module Specific:
zynq_fsbl_flashTE modified 2019.2 FSBLGeneral:
ZynqMP Example:----------------------------------------------------------zynqmp_fsblTE modified 2019.2 FSBLGeneral:
Module Specific:
zynqmp_fsbl_flashTE modified 2019.2 FSBLGeneral:
zynqmp_pmufwXilinx default PMU firmware.----------------------------------------------------------General Example:hello_te0820Hello TE0820 is a Xilinx Hello World example as endless loop instead of one console output.u-bootU-Boot.elf is generated with PetaLinux. Vitis is used to generate Boot.bin. |
Template location: ./sw_lib/sw_apps/
zynqmp_fsbl
TE modified 2019.2 FSBL
General:
Modified Files: xfsbl_main.c, xfsbl_hooks.h/.c, xfsbl_board.h/.c(search for 'TE Mod' on source code)
Add Files: te_*
General Changes:
Display FSBL Banner and Device Name
Module Specific:
Add Files: all TE Files start with te_*
Si5395 on the TE0835 RFSoC module configuration
Si5395 on the TEB0835 carrier board configuration
zynqmp_fsbl_flash
TE modified 2019.2 FSBL
General:
Modified Files: xfsbl_initialisation.c, xfsbl_hw.h, xfsbl_handoff.c, xfsbl_main.c
General Changes:
Display FSBL Banner
Set FSBL Boot Mode to JTAG
Disable Memory initialisation
zynqmp_pmufw
Xilinx default PMU firmware.
hello_te0835
Hello TE0835 is a Xilinx Hello World example as endless loop instead of one console output.
u-boot
U-Boot.elf is generated with PetaLinux. Vitis is used to generate Boot.bin.
Software Design - PetaLinux
Note:
|
For PetaLinux installation and project creation, follow instructions from:
Config
Start with petalinux-config or petalinux-config --get-hw-description
Changes:
CONFIG_SUBSYSTEM_ETHERNET_PSU_ETHERNET_3_MAC=""
U-Boot
Start with petalinux-config -c u-boot
Changes:
CONFIG_ENV_IS_NOWHERE=y
# CONFIG_ENV_IS_IN_SPI_FLASH is not set
CONFIG_I2C_EEPROM=y
CONFIG_ZYNQ_GEM_I2C_MAC_OFFSET=0xFA
CONFIG_SYS_I2C_EEPROM_ADDR=0
CONFIG_SYS_I2C_EEPROM_BUS=0
CONFIG_SYS_EEPROM_SIZE=256
CONFIG_SYS_EEPROM_PAGE_WRITE_BITS=0
CONFIG_SYS_EEPROM_PAGE_WRITE_DELAY_MS=0
CONFIG_SYS_I2C_EEPROM_ADDR_LEN=1
CONFIG_SYS_I2C_EEPROM_ADDR_OVERFLOW=0
Change platform-top.h:
Device Tree
Kernel
Start with petalinux-config -c kernel
Changes:
CONFIG_CPU_IDLE is not set (only needed to fix JTAG Debug issue)
CONFIG_CPU_FREQ is not set (only needed to fix JTAG Debug issue)
CONFIG_EDAC_CORTEX_ARM64=y
Rootfs
Start with petalinux-config -c rootfs
Changes:
CONFIG_i2c-tools=y
CONFIG_busybox-httpd=y (for web server app)
CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-utils(util-linux,cpufrequtils,bridge-utils,mtd-utils,usbutils,pciutils,canutils,i2c-tools,smartmontools,e2fsprogs)
Applications
See: \os\petalinux\project-spec\meta-user\recipes-apps\
startup
Script App to load init.sh from SD Card if available.
webfwu
Webserver application accemble for Zynqmp RFSoC access. Need busybox-httpd
Additional Software
Note: |
No additional software is needed.
SI5395 of RFSoC module
File location <design name>/misc/Si5395/Si5395-*-835-*.slabtimeproj
General documentation how you work with these project will be available on Si5395
SI5395 of carrier board
File location <design name>/misc/Si5395/Si5395-*-B835-*.slabtimeproj
General documentation how you work with these project will be available on Si5395
Appx. A: Change History and Legal Notices
Document Change History
To get content of older revision got to "Change History" of this page and select older document revision number.
|
|
Legal Notices
|