Table of contents
Overview
Refer to http://trenz.org/te0xyz-info for the current online version of this manual and other available documentation.
Key Features
- Vitis/Vivado 2019.2
- PetaLinux
- RF Analyzer 1.6
- PCIe (endpoint)
- SD
- ETH
- USB
- I2C
- RTC
- FMeter
- Modified FSBL for SI5395 programming
- Special FSBL for QSPI programming
Revision History
| Date | Vivado | Project Built | Authors | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020-10-27 | 2019.2 | TE0835-test_board_noprebuilt-vivado_2019.2-build_15_20201027100145.zip | Mohsen Chamanbaz |
|
Release Notes and Know Issues
| Issues | Description | Workaround | To be fixed version |
|---|---|---|---|
| Updating the signal property failed, while the generation of the signal is already in progress | It is difficult to update the property of the generated signal while the generation of the signal by DACs is already running. The Generation button must be clicked several times to make the change in the output. |
| --- |
Requirements
Software
| Software | Version | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Vitis | 2019.2 | needed, Vivado is included into Vitis installation |
| PetaLinux | 2019.2 | needed |
| RF Analyzer | 1.6 | needed |
| SI ClockBuilder Pro | --- | optional |
Hardware
Basic description of TE Board Part Files is available on TE Board Part Files.
Complete List is available on <design name>/board_files/*_board_files.csv
Design supports following modules:
| Module Model | Board Part Short Name | PCB Revision Support | DDR | QSPI Flash | EMMC | Others | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TE0835-02-MXE21-A | 25dr_1e_4gb | REV2 | 4GB | 128MB | NA | NA | NA |
Design supports following carriers:
| Carrier Model | Notes |
|---|---|
| TEB0835-02 |
Additional HW Requirements:
| Additional Hardware | Notes |
|---|---|
| Micro USB Cable for JTAG/UART | |
| Cooler | It is strongly recommended that the RFSoC should not be used without heat sink. |
| SMA male connector cable | Some ADC inputs/DAC outouts have the SMA connector |
| UFL female connector cable | Some ADC inputs/DAC outouts have the UFL connector |
| Ethernet cable | |
| SD card | 16GB |
| Signal generator (optional) | To feed a desired signal to the input of ADC |
| Oscilloscope (optional) | To monitor the output signal of DACs. |
| PC | With ATX Power supply and PCIe X8 slot |
Content
For general structure and of the reference design, see Project Delivery - Xilinx devices
Design Sources
| Type | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Vivado | <design name>/block_design <design name>/constraints <design name>/ip_lib | Vivado Project will be generated by TE Scripts |
| Vitis | <design name>/sw_lib | Additional Software Template for Vitis and apps_list.csv with settings automatically for Vitis app generation |
| PetaLinux | <design name>/os/petalinux | PetaLinux template with current configuration |
Additional Sources
| Type | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| SI5395 (PLL of the RFSoc Module) | <design name>/misc/Si5395 | SI5395 Project with current PLL Configuration |
| SI5395 (PLL of the carrier board) | <design name>/misc/Si5395 | SI5395 Project with current PLL Configuration |
Prebuilt
File | File-Extension | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIF-File | *.bif | File with description to generate Bin-File |
| BIN-File | *.bin | Flash Configuration File with Boot-Image (Zynqmp RFSoC-FPGAs) |
| BIT-File | *.bit | FPGA (PL Part) Configuration File |
| DebugProbes-File | *.ltx | Definition File for Vivado/Vivado Labtools Debugging Interface |
| Diverse Reports | --- | Report files in different formats |
| Hardware-Platform-Specification-Files | *.xsa | Exported Vivado Hardware Specification for Vitis and PetaLinux |
| LabTools Project-File | *.lpr | Vivado Labtools Project File |
| OS-Image | *.ub | Image with Linux Kernel (On Petalinux optional with Devicetree and RAM-Disk) |
| Software-Application-File | *.elf | Software Application for Zynqmp RFSoC or MicroBlaze Processor Systems |
| Clock Builder Pro project file | *.slabtimeproj | Defines the necessary clock frequencies for the PLLs on the RFSoC module and carrier board |
Download
Reference Design is only usable with the specified Vivado/Vitis/PetaLinux version. Do never use different Versions of Xilinx Software for the same Project.
Reference Design is available on:
Software Setup
Download RF Analyzer GUI from the following link and install it.
Design Flow
Reference Design is available with and without prebuilt files. It's recommended to use TE prebuilt files for first lunch.
Trenz Electronic provides a tcl based built environment based on Xilinx Design Flow.
See also:
The Trenz Electronic FPGA Reference Designs are TCL-script based project. Command files for execution will be generated with "_create_win_setup.cmd" on Windows OS and "_create_linux_setup.sh" on Linux OS.
TE Scripts are only needed to generate the vivado project, all other additional steps are optional and can also executed by Xilinx Vivado/SDK GUI. For currently Scripts limitations on Win and Linux OS see: Project Delivery - Xilinx devices
- _create_win_setup.cmd/_create_linux_setup.sh and follow instructions on shell:
- Press 0 and enter to start "Module Selection Guide"
- (optional Win OS) Generate Virtual Drive or use short directory for the reference design (for example x:\<design name>)
- Create Project (follow instruction of the product selection guide), settings file will be configured automatically during this process)
- (optional for manual changes) Select correct device and Xilinx install path on "design_basic_settings.cmd" and create Vivado project with "vivado_create_project_guimode.cmd"
Note: Select correct one, see also TE Board Part Files
- (optional for manual changes) Select correct device and Xilinx install path on "design_basic_settings.cmd" and create Vivado project with "vivado_create_project_guimode.cmd"
- Create XSA and export to prebuilt folder
- Run on Vivado TCL: TE::hw_build_design -export_prebuilt
Note: Script generate design and export files into \prebuilt\hardware\<short dir>. Use GUI is the same, except file export to prebuilt folder
- Run on Vivado TCL: TE::hw_build_design -export_prebuilt
- Create Linux (bl31.elf, uboot.elf and image.ub) with exported XSA
- XSA is exported to "prebuilt\hardware\<short name>"
Note: HW Export from Vivado GUI create another path as default workspace. - Create Linux images on VM, see PetaLinux KICKstart
- Use TE Template from /os/petalinux
- XSA is exported to "prebuilt\hardware\<short name>"
- Add Linux files (bl31.elf, uboot.elf and image.ub) to prebuilt folder
- "prebuilt\os\petalinux\<ddr size>" or "prebuilt\os\petalinux\<short name>"
- Generate Programming Files with Vitis
- Run on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_vitis -all
Note: Scripts generate applications and bootable files, which are defined in "sw_lib\apps_list.csv" - (alternative) Start SDK with Vivado GUI or start with TE Scripts on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_vitis
Note: TCL scripts generate also platform project, this must be done manuelly in case GUI is used. See Vitis
- Run on Vivado TCL: TE::sw_run_vitis -all
Launch
Programming
Check Module and Carrier TRMs for proper HW configuration before you try any design.
Xilinx documentation for programming and debugging: Xilinx Development Tools
Get prebuilt boot binaries
- _create_win_setup.cmd/_create_linux_setup.sh and follow instructions on shell
- Press 0 and enter to start "Module Selection Guide"
- Select assembly version
- Validate selection
- Select Create and open delivery binary folder
Note: Folder (<project foler>/_binaries_<Artikel Name>) with subfolder (boot_<app name>) for different applications will be generated
QSPI
Optional for Boot.bin on QSPI Flash and image.ub on SD.
- Connect JTAG and power on carrier with module
- Open Vivado Project with "vivado_open_existing_project_guimode.cmd" or if not created, create with "vivado_create_project_guimode.cmd"
- Type on Vivado TCL Console: TE::pr_program_flash -swapp u-boot
Note: To program with SDK/Vivado GUI, use special FSBL (zynqmp_fsbl_flash) on setup
optional "TE::pr_program_flash -swapp hello_te0835" possible - Copy image.ub on SD-Card
- use files from (<project foler>/_binaries_<Articel Name>)/boot_linux from generated binary folder,see: Get prebuilt boot binaries
- or use prebuilt file location, see <design_name>/prebuilt/readme_file_location.txt
- Insert SD-Card
SD
- Copy image.ub and Boot.bin on SD-Card
- use files from (<project foler>/_binaries_<Articel Name>)/boot_linux from generated binary folder,see: Get prebuilt boot binaries
- or use prebuilt file location, see <design_name>/prebuilt/readme_file_location.txt
- Set Boot Mode to SD-Boot.
- Depends on Carrier, see carrier TRM.
- Insert SD-Card in SD-Slot.
JTAG
Not used on this Example.
Hardware Setup
The Hardware contains of a TE0835 module and TEB0835 carrier board and has 8 ADC inputs and 8 DAC outputs.
- Plug the TE0835 module on the TEB0835 carrier board
- Install the cooler on the RFSoC chip
- Attention: It is strongly recommended that the RFSoC should not be used without heat sink.
- Connect the micro USB cable to the J29 connector
- Plug the board on the PCIe port of the PC
- Plug the prepared SD card on the SD card socket (J28)
- Connect a cable with SMA or UFL connector to one of the DAC connector( for example DAC0 J9) and feed it back to the related ADC input (for example ADC0 J1)
- (optional) A signal generator can be used to feed desired sinal to ADC input.
- (optional) An oscilloscope can be used to monitor the output signal of DAC.
Usage
- Prepare HW like described on section TE0835 Test Board#Hardware Setup
- Connect UART USB (most cases same as JTAG)
- Select SD Card as Boot Mode (or QSPI - depending on step 1)
Note: See TRM of the Carrier, which is used. - Power On PCB
Note: 1. Zynqmp RFSoC Boot ROM loads FSBL from SD into OCM, 2. FSBL loads U-boot from SD into DDR, 3. U-boot load Linux from SD into DDR
Linux
- Open Serial Console (e.g. putty)
- Speed: 115200
- COM Port: Win OS, see device manager, Linux OS see dmesg |grep tty (UART is *USB1)
- Linux Console:
Note: Wait until Linux boot finished For Linux Login use:- User Name: root
- Password: root
- You can use Linux shell now.
- I2C Bus type: i2cdetect -y -r 0
- Bus 0 up to 5 possible
- RTC check: dmesg | grep rtc
- ETH0 works with udhcpc
- USB type "lsusb" or connect USB2.0 device
- PCIe Bus type: "lspci"
- PCIe device should be seen in the console
- I2C Bus type: i2cdetect -y -r 0
- Option Features
- Webserver to get access to Zynqmp RFSoC
- insert IP on web browser to start web interface
- init.sh scripts
- add init.sh script on SD, content will be load automatically on startup (template included in ./misc/SD)
- add init.sh script on SD, content will be load automatically on startup (template included in ./misc/SD)
- Webserver to get access to Zynqmp RFSoC
Vivado HW Manager
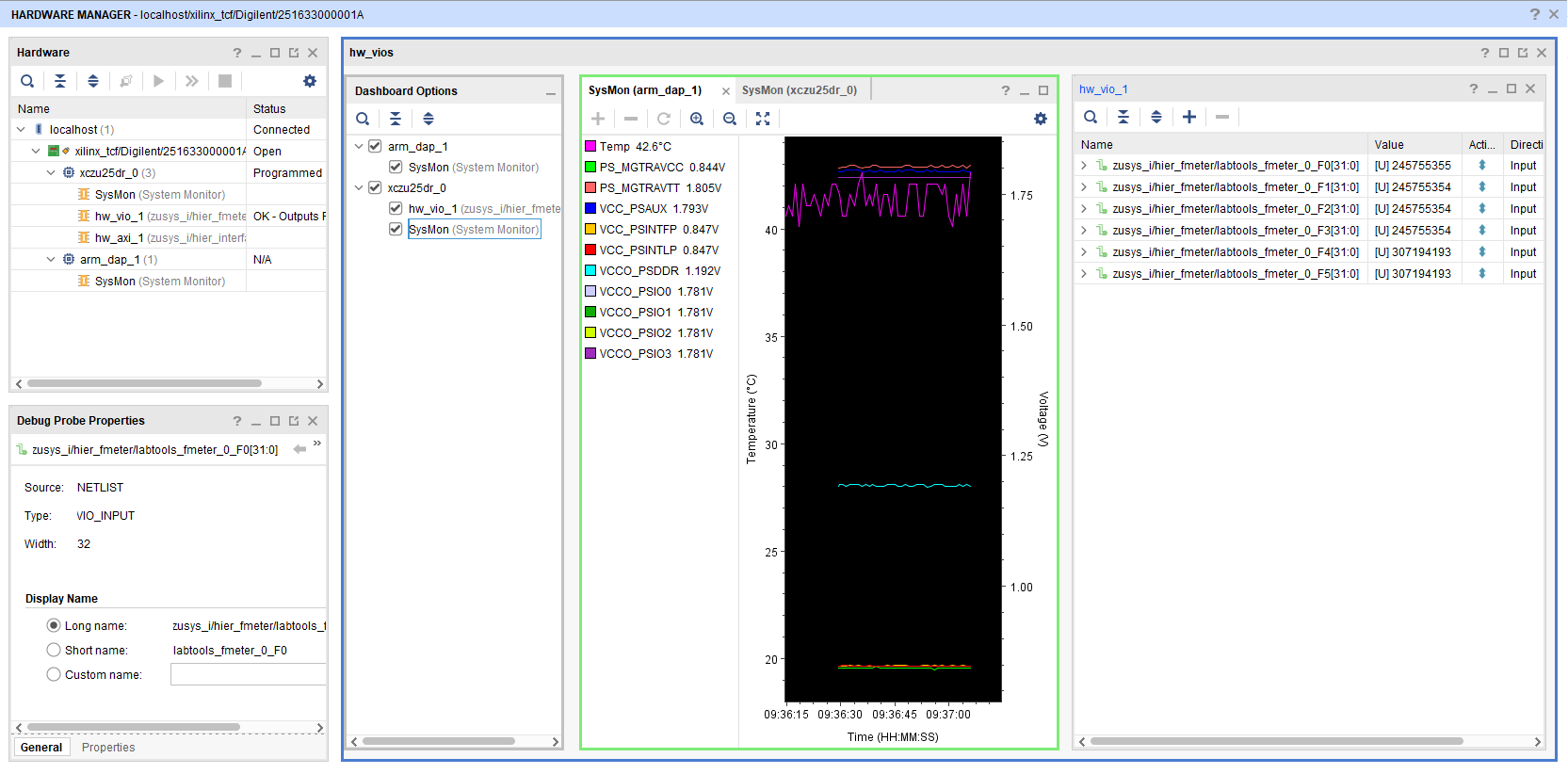
Open Vivado HW-Manager and add VIO signal to dashboard (*.ltx located on prebuilt folder)
- Monitoring:
- The output frequency of MMCM blocks can be monitored.
- Set radix from VIO signals to unsigned integer.
- The tempreature of ARM processor and FPGA can be measured too.
- The output frequency of MMCM blocks can be monitored.
RF Analyzer
- Open the RF Analyzer GUI
- Click on Connect button
- Adjust the desired JTAG frequency (for example 30MHZ)
- Give the generated bitstream file path
- Click on Download Bitstream button to load the Bitstream file on the FPGA
- When downloading is finished, click on Select Target button
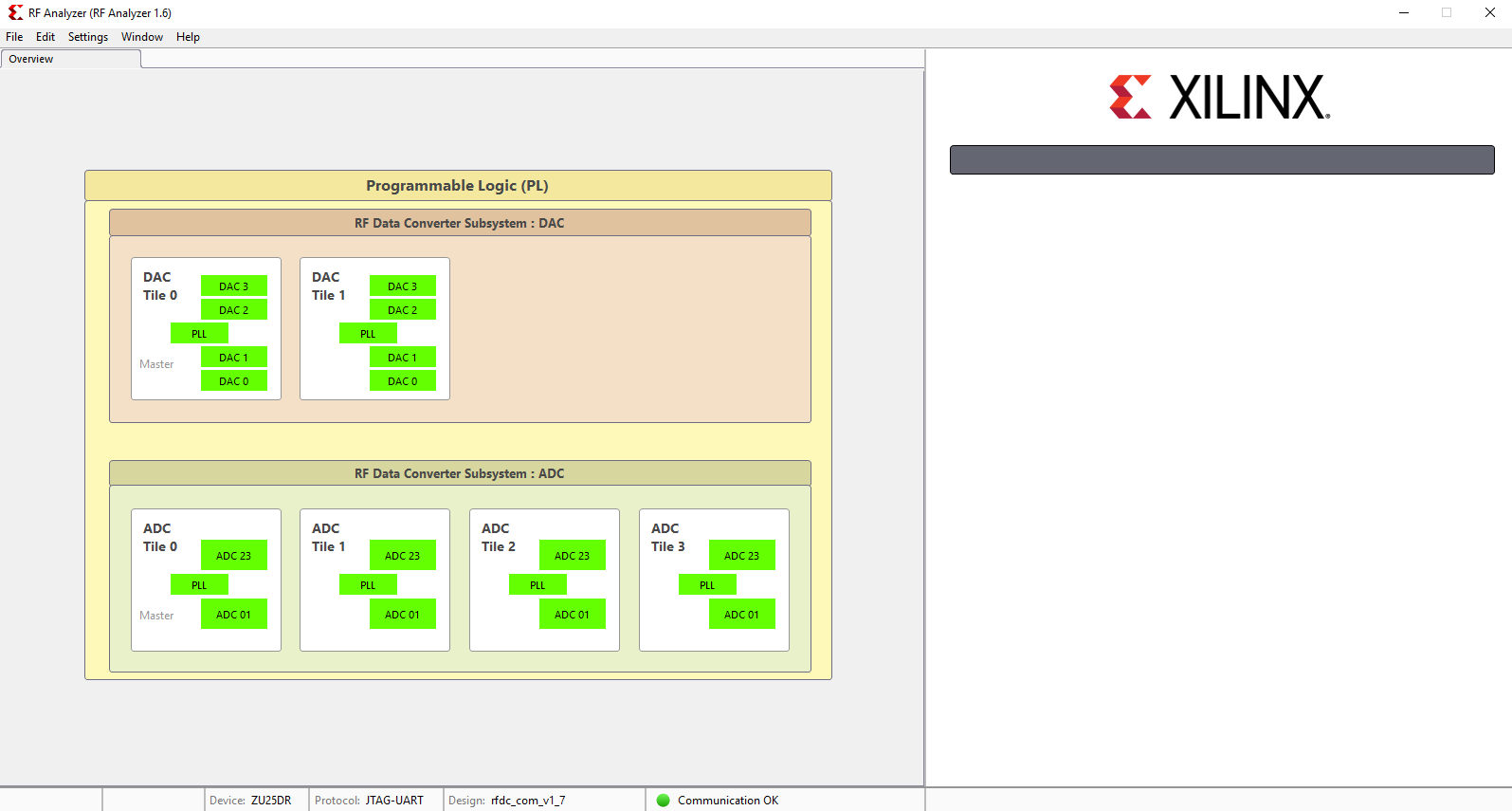
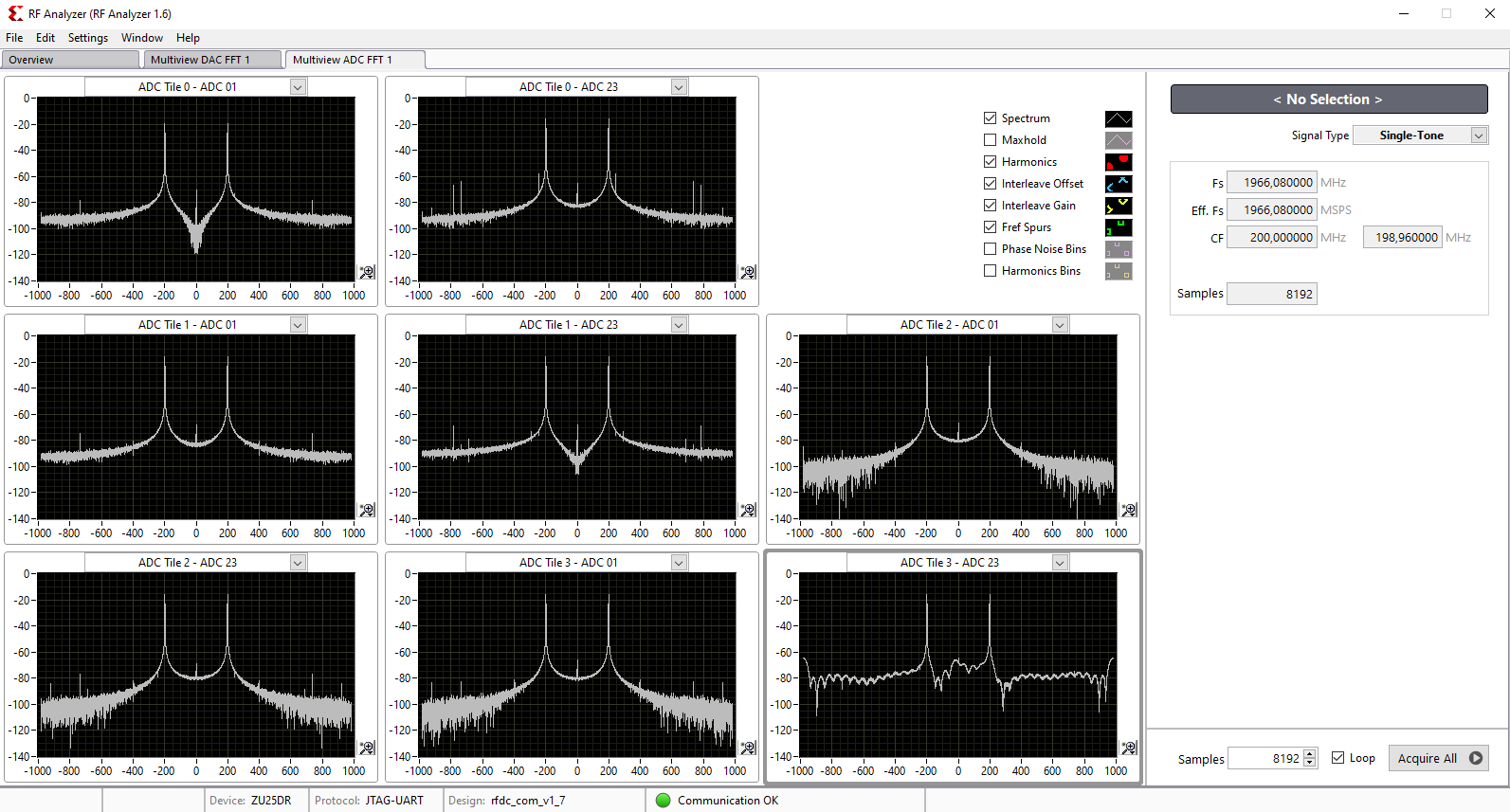
- After initilalisation, all ADCs/DACs tiles are visible
- Click on desired DAC tile and choose a DAC (for example DAC0)
- Adjust desired DAC properties (for example output frequency)
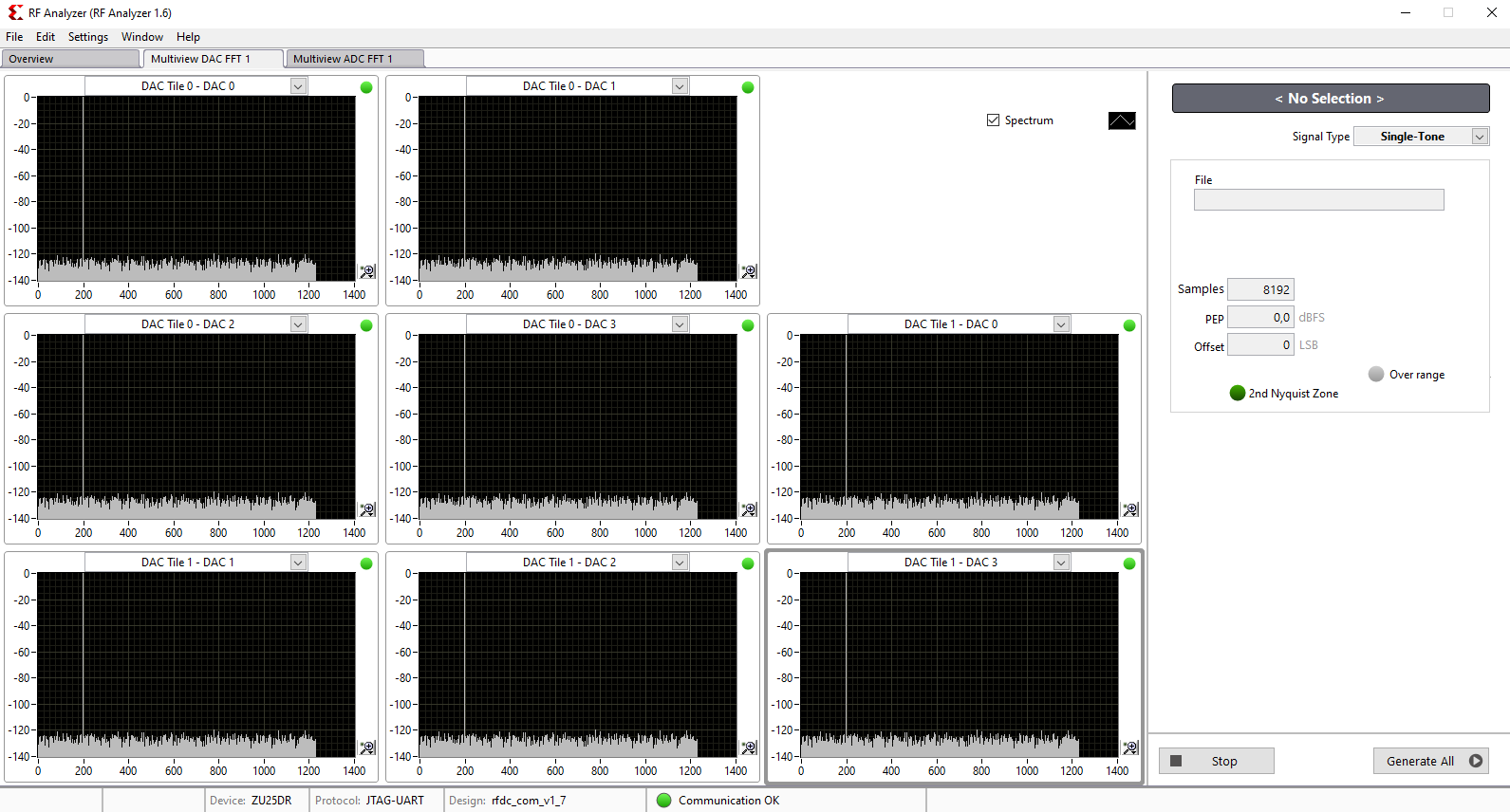
- Click on Generate button to generate the signal in output of DAC
- Click on the related ADC tile and choose the related ADC (for example ADC0)
- Click on Acquire button to aqcuire the input signal
- The spectum of the DAC output signal can be seen now. The signal can be visible in time domain too.
- Tip: In menu Window click on Multiview to see all of DACs and ADCs simultaneously.
| RF Analyzer GUI | Board TE0835 ( RFSoC U1) | TEB0835 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tile /Converter | SoC Pin Name | SoC Pin Number | B2B | Signal Name | Connector Designator | Connector Type |
| ADC Tile 0-ADC 01 | ADC0_P/ADC0_N | AK2/AK1 | 31/29 | ADC0_P/ADC0_N | J1 | SMA |
| ADC Tile 0-ADC 23 | ADC1_P/ADC1_N | AH2/AH1 | 43/41 | ADC1_P/ADC1_N | J2 | UFL |
| ADC Tile 1-ADC 01 | ADC2_P/ADC2_N | AF2/AF1 | 49/47 | ADC2_P/ADC2_N | J3 | SMA |
| ADC Tile 1-ADC 23 | ADC3_P/ADC3_N | AD2/AD1 | 59/61 | ADC3_P/ADC3_N | J4 | UFL |
| ADC Tile 2-ADC 01 | ADC4_P/ADC4_N | AB2/AB1 | 67/65 | ADC4_P/ADC4_N | J5 | SMA |
| ADC Tile 2-ADC 23 | ADC5_P/ADC5_N | Y2/Y1 | 79/77 | ADC5_P/ADC5_N | J6 | UFL |
| ADC Tile 3-ADC 01 | ADC6_P/ADC6_N | V2/V1 | 85/83 | ADC6_P/ADC6_N | J7 | SMA |
| ADC Tile 3-ADC 23 | ADC7_P/ADC7_N | T2/T1 | 97/95 | ADC7_P/ADC7_N | J8 | UFL |
| DAC Tile 0-DAC 0 | DAC0_P/DAC0_N | N2/N1 | 103/101 | DAC0_P/DAC0_N | J9 | SMA |
| DAC Tile 0-DAC 1 | DAC1_P/DAC1_N | L2/L1 | 109/107 | DAC1_P/DAC1_N | J10 | UFL |
| DAC Tile 0-DAC 2 | DAC2_P/DAC2_N | J2/J1 | 121/119 | DAC2_P/DAC2_N | J11 | SMA |
| DAC Tile 0-DAC 3 | DAC3_P/DAC3_N | G2/G1 | 127/125 | DAC3_P/DAC3_N | J12 | UFL |
| DAC Tile 1-DAC 0 | DAC4_P/DAC4_N | E2/E1 | 133/131 | DAC4_P/DAC4_N | J13 | UFL |
| DAC Tile 1-DAC 1 | DAC5_P/DAC5_N | C2/C1 | 139/137 | DAC5_P/DAC5_N | J14 | UFL |
| DAC Tile 1-DAC 2 | DAC6_P/DAC6_N | B4/A4 | 151/149 | DAC6_P/DAC6_N | J15 | UFL |
| DAC Tile 1-DAC 3 | DAC7_P/DAC7_N | B6/A6 | 157/155 | DAC7_P/DAC7_N | J16 | UFL |
As an example the GUi should be seen after initialization as below:
For example, when all DACs are in operation, the GUI can be seen as below:
For example, when all ADCs are in operation, the GUI can be seen as below:
System Design - Vivado
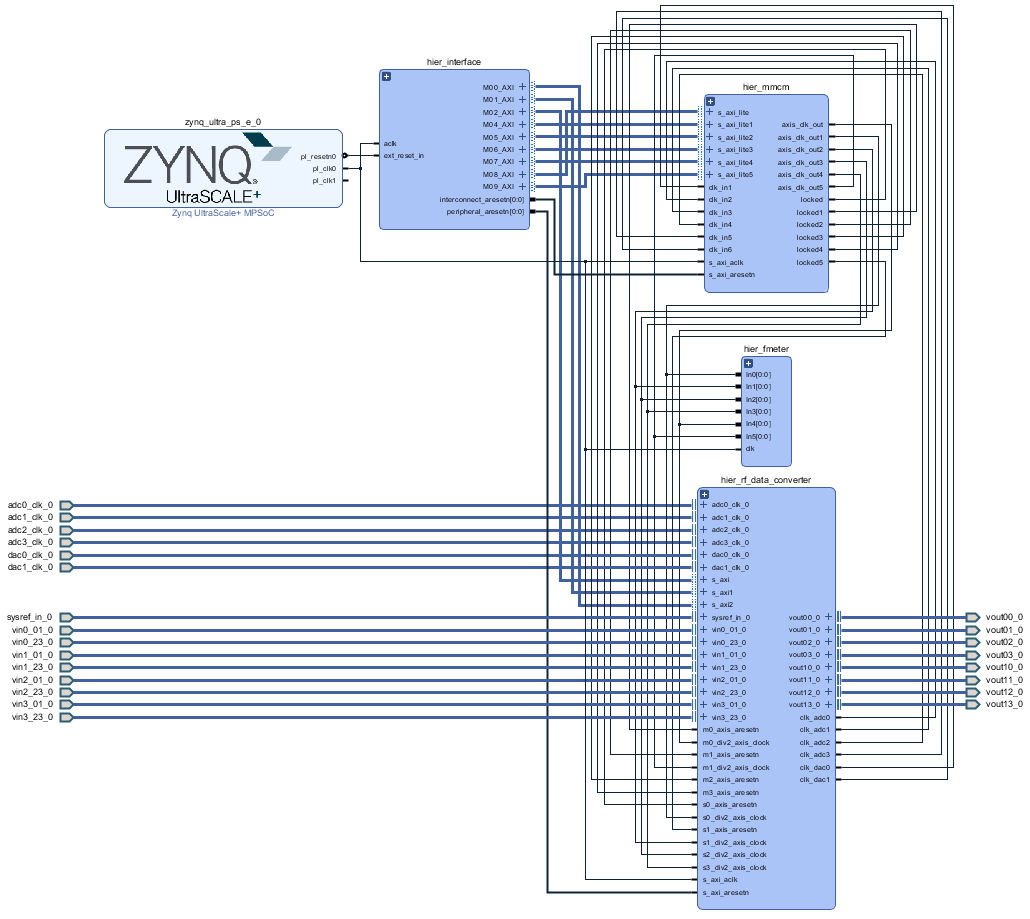
Block Design
PS Interfaces
Activated interfaces:
| Type | Note |
|---|---|
| DDR | |
| QSPI | MIO |
| SD1 | MIO |
| I2C0 | MIO |
| I2C1 | MIO |
| UART0 | MIO |
| GPIO0 | MIO |
| GPIO1 | MIO |
| GPIO2 | MIO |
| SWDT0..1 | |
| TTC0..3 | |
| GEM3 | MIO |
| USB0 | MIO |
| PCIe | MIO |
Constrains
Basic module constrains
set_property BITSTREAM.GENERAL.COMPRESS TRUE [current_design] set_property BITSTREAM.CONFIG.UNUSEDPIN PULLNONE [current_design]
Design specific constrain
set_false_path -from [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/*/CLK}] -to [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/F_reg[*]/D}]
set_false_path -from [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/toggle_reg/C}] -to [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/*/bl.DSP48E_2/*}]
set_false_path -from [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/toggle_reg/C}] -to [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/*/bl.DSP48E_2/DSP_A_B_DATA_INST/*}]
set_false_path -from [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/toggle_reg/C}] -to [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/*/bl.DSP48E_2/DSP_ALU_INST/*}]
set_false_path -from [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/toggle_reg/C}] -to [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/*/bl.DSP48E_2/DSP_OUTPUT_INST/*}]
set_false_path -from [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/toggle_reg/C}] -to [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/*/bl.DSP48E_2/DSP_C_DATA_INST/*}]
set_false_path -from [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/FMETER_gen[4].COUNTER_F_inst/bl.DSP48E_2/DSP_ALU_INST/CLK}] -to [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/FMETER_gen[4].COUNTER_F_inst/bl.DSP48E_2/DSP_OUTPUT_INST/*}]
set_false_path -from [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/FMETER_gen[5].COUNTER_F_inst/bl.DSP48E_2/DSP_ALU_INST/CLK}] -to [get_pins -hier -filter {name=~*labtools_fmeter_0/U0/FMETER_gen[5].COUNTER_F_inst/bl.DSP48E_2/DSP_OUTPUT_INST/*}]
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Title : Example top level constraints for UltraScale+ RF Data Converter
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# File : usp_rf_data_converter_0_example_design.xdc
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Description: Xilinx Constraint file for the example design for
# UltraScale+ RF Data Converter core
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# DISCLAIMER
# This disclaimer is not a license and does not grant any
# rights to the materials distributed herewith. Except as
# otherwise provided in a valid license issued to you by
# Xilinx, and to the maximum extent permitted by applicable
# law: (1) THESE MATERIALS ARE MADE AVAILABLE "AS IS" AND
# WITH ALL FAULTS, AND XILINX HEREBY DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES
# AND CONDITIONS, EXPRESS, IMPLIED, OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING
# BUT NOT LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, NON-
# INFRINGEMENT, OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE; and
# (2) Xilinx shall not be liable (whether in contract or tort,
# including negligence, or under any other theory of
# liability) for any loss or damage of any kind or nature
# related to, arising under or in connection with these
# materials, including for any direct, or any indirect,
# special, incidental, or consequential loss or damage
# (including loss of data, profits, goodwill, or any type of
# loss or damage suffered as a result of any action brought
# by a third party) even if such damage or loss was
# reasonably foreseeable or Xilinx had been advised of the
# possibility of the same.
#
# CRITICAL APPLICATIONS
# Xilinx products are not designed or intended to be fail-
# safe, or for use in any application requiring fail-safe
# performance, such as life-support or safety devices or
# systems, Class III medical devices, nuclear facilities,
# applications related to the deployment of airbags, or any
# other applications that could lead to death, personal
# injury, or severe property or environmental damage
# (individually and collectively, "Critical
# Applications"). Customer assumes the sole risk and
# liability of any use of Xilinx products in Critical
# Applications, subject only to applicable laws and
# regulations governing limitations on product liability.
#
# THIS COPYRIGHT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER MUST BE RETAINED AS
# PART OF THIS FILE AT ALL TIMES.
#
#---------------------------------------------------------------------
#------------------------------------------
# TIMING CONSTRAINTS
#------------------------------------------
# Set AXI-Lite Clock to 100MHz
#create_clock -period 10.000 -name usp_rf_data_converter_0_axi_aclk [get_pins axi_aclk_i/CFGMCLK]
# ADC Reference Clock for Tile 0 running at 245.760 MHz
create_clock -period 4.069 -name usp_rf_data_converter_0_adc0_clk [get_ports adc0_clk_p]
# ADC Reference Clock for Tile 1 running at 245.760 MHz
create_clock -period 4.069 -name usp_rf_data_converter_0_adc1_clk [get_ports adc1_clk_p]
# ADC Reference Clock for Tile 2 running at 245.760 MHz
create_clock -period 4.069 -name usp_rf_data_converter_0_adc2_clk [get_ports adc2_clk_p]
# ADC Reference Clock for Tile 3 running at 245.760 MHz
create_clock -period 4.069 -name usp_rf_data_converter_0_adc3_clk [get_ports adc3_clk_p]
# DAC Reference Clock for Tile 0 running at 307.200 MHz
create_clock -period 3.255 -name usp_rf_data_converter_0_dac0_clk [get_ports dac0_clk_p]
# DAC Reference Clock for Tile 1 running at 307.200 MHz
create_clock -period 3.255 -name usp_rf_data_converter_0_dac1_clk [get_ports dac1_clk_p]
set_multicycle_path -to [get_pins -filter {REF_PIN_NAME== D} -of [get_cells -hier -filter {name =~ *usp_rf_data_converter_0_ex_i/ex_design/usp_rf_data_converter_0/inst/IP2Bus_Data_reg*}]] -setup 2
set_multicycle_path -to [get_pins -filter {REF_PIN_NAME== D} -of [get_cells -hier -filter {name =~ *usp_rf_data_converter_0_ex_i/ex_design/usp_rf_data_converter_0/inst/IP2Bus_Data_reg*}]] -hold 1
###############################################################################
# False paths
# For debug in synth use
# report_timing_summary -setup -slack_lesser_than 0
###############################################################################
# Data generator/capture constraints
set rfa_from_list [get_cells -hier -regexp .*rf(?:da|ad)c_exdes_ctrl_i\/(?:da|ad)c_exdes_cfg_i\/.+num_samples_reg.*]
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_00*addrb_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_00*addrbend_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_01*addrb_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_01*addrbend_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_02*addrb_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_02*addrbend_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_03*addrb_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_03*addrbend_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_10*addrb_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_10*addrbend_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_11*addrb_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_11*addrbend_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_12*addrb_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_12*addrbend_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_13*addrb_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_dac_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*dg_slice_13*addrbend_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_dac_signal_list
set rfa_from_list [get_cells -hier -regexp .*rf(?:da|ad)c_exdes_ctrl_i\/(?:da|ad)c_exdes_cfg_i\/.+num_samples_reg.*]
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_00*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_00*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_00*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_00*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_01*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_01*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_01*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_01*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_02*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_02*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_02*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_02*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_03*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_03*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_03*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_03*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_10*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_10*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_10*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_10*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_11*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_11*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_11*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_11*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_12*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_12*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_12*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_12*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_13*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_13*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_13*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_13*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_20*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_20*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_20*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_20*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_21*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_21*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_21*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_21*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_22*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_22*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_22*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_22*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_23*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_23*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_23*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_23*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_30*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_30*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_30*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_30*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_31*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_31*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_31*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_31*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_32*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_32*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_32*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_32*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_33*addra_reg[*]}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_33*working_i_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_33*cap_complete_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
set rfa_adc_signal_list [get_cells -hier -filter {name=~*ds_slice_33*wea_r_reg}]
set_false_path -from $rfa_from_list -to $rfa_adc_signal_list
Software Design - Vitis
For SDK project creation, follow instructions from:
Application
Template location: ./sw_lib/sw_apps/
zynqmp_fsbl
TE modified 2019.2 FSBL
General:
- Modified Files: xfsbl_main.c, xfsbl_hooks.h/.c, xfsbl_board.h/.c(search for 'TE Mod' on source code)
- Add Files: te_*
- General Changes:
- Display FSBL Banner and Device Name
Module Specific:
- Add Files: all TE Files start with te_*
- Si5395 on the TE0835 RFSoC module configuration
- Si5395 on the TEB0835 carrier board configuration
zynqmp_fsbl_flash
TE modified 2019.2 FSBL
General:
- Modified Files: xfsbl_initialisation.c, xfsbl_hw.h, xfsbl_handoff.c, xfsbl_main.c
- General Changes:
- Display FSBL Banner
- Set FSBL Boot Mode to JTAG
- Disable Memory initialisation
zynqmp_pmufw
Xilinx default PMU firmware.
hello_te0835
Hello TE0835 is a Xilinx Hello World example as endless loop instead of one console output.
u-boot
U-Boot.elf is generated with PetaLinux. Vitis is used to generate Boot.bin.
Software Design - PetaLinux
For PetaLinux installation and project creation, follow instructions from:
Config
Start with petalinux-config or petalinux-config --get-hw-description
Changes:
- CONFIG_SUBSYSTEM_ETHERNET_PSU_ETHERNET_3_MAC=""
U-Boot
Start with petalinux-config -c u-boot
Changes:
CONFIG_ENV_IS_NOWHERE=y
# CONFIG_ENV_IS_IN_SPI_FLASH is not set
CONFIG_I2C_EEPROM=y
CONFIG_ZYNQ_GEM_I2C_MAC_OFFSET=0xFA
CONFIG_SYS_I2C_EEPROM_ADDR=0
CONFIG_SYS_I2C_EEPROM_BUS=0
CONFIG_SYS_EEPROM_SIZE=256
CONFIG_SYS_EEPROM_PAGE_WRITE_BITS=0
CONFIG_SYS_EEPROM_PAGE_WRITE_DELAY_MS=0
CONFIG_SYS_I2C_EEPROM_ADDR_LEN=1
CONFIG_SYS_I2C_EEPROM_ADDR_OVERFLOW=0
Change platform-top.h:
Device Tree
/include/ "system-conf.dtsi"
/ {
chosen {
xlnx,eeprom = &eeprom;
};
};
/* SDIO */
&sdhci1 {
disable-wp;
no-1-8-v;
};
/* ETH PHY */
&gem3 {
status = "okay";
ethernet_phy0: ethernet-phy@0 {
compatible = "marvell,88e1510";
device_type = "ethernet-phy";
reg = <1>;
};
};
/* USB 2.0 */
/* USB */
&dwc3_0 {
status = "okay";
dr_mode = "host";
maximum-speed = "high-speed";
/delete-property/phy-names;
/delete-property/phys;
/delete-property/snps,usb3_lpm_capable;
snps,dis_u2_susphy_quirk;
snps,dis_u3_susphy_quirk;
};
&usb0 {
status = "okay";
/delete-property/ clocks;
/delete-property/ clock-names;
clocks = <0x3 0x20>;
clock-names = "bus_clk";
};
/* QSPI PHY */
&qspi {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
status = "okay";
flash0: flash@0 {
compatible = "jedec,spi-nor";
reg = <0x0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
};
};
// This I2C Port can be found in the RFSoC Module TE0835 to control PLL chip SI5395A-A-GM on the
// RFSoC Module.
&i2c1 {
eeprom: eeprom@50 {
compatible = "atmel,24c08";
reg = <0x50>;
};
};
// This I2C Port connects RFSoC FPGA on the RFSoC Module and I2C multiplexer Chip on the carrier
// board through B2B connector.
&i2c0 {
// This I2C multiplexer chip can be found in TEB0835 carrier board.
i2c_mux@70 { /* TCA9544APWR U7 in the carrier board TEB0835 */
compatible = "nxp,pca9544";
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <0x70>;
i2c@0 { /* FireFly_B*/
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <0>;
};
i2c@1 { /* FireFly_A*/
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <1>;
};
i2c@3 { /* LM96163CISD/NOPB U9 FAN Controller in the carrier board TEB0835*/
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <3>;
temp@4c {/* lm96163 - u9*/
compatible = "national,lm96163";
reg = <0x4c>;
};
};
i2c@4 { /* SI5395A-A-GM U5 DPLL in the carrier board TEB0835*/
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <4>;
clock-generator@68{/* SI5395A-A-GM U5 DPLL in the carrier board TEB0835 */
compatible = "silabs,si5395";
reg = <0x68>;
};
};
};
};
Kernel
Start with petalinux-config -c kernel
Changes:
CONFIG_CPU_IDLE is not set (only needed to fix JTAG Debug issue)
CONFIG_CPU_FREQ is not set (only needed to fix JTAG Debug issue)
- CONFIG_EDAC_CORTEX_ARM64=y
Rootfs
Start with petalinux-config -c rootfs
Changes:
- CONFIG_i2c-tools=y
- CONFIG_busybox-httpd=y (for web server app)
- CONFIG_packagegroup-petalinux-utils(util-linux,cpufrequtils,bridge-utils,mtd-utils,usbutils,pciutils,canutils,i2c-tools,smartmontools,e2fsprogs)
Applications
See: \os\petalinux\project-spec\meta-user\recipes-apps\
startup
Script App to load init.sh from SD Card if available.
webfwu
Webserver application accemble for Zynqmp RFSoC access. Need busybox-httpd
Additional Software
No additional software is needed.
SI5395 of RFSoC module
File location <design name>/misc/Si5395/Si5395-*-835-*.slabtimeproj
General documentation how you work with these project will be available on Si5395
SI5395 of carrier board
File location <design name>/misc/Si5395/Si5395-*-B835-*.slabtimeproj
General documentation how you work with these project will be available on Si5395
Appx. A: Change History and Legal Notices
Document Change History
To get content of older revision got to "Change History" of this page and select older document revision number.
| Date | Document Revision | Authors | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| -- | all | -- |
Legal Notices
Data Privacy
Please also note our data protection declaration at https://www.trenz-electronic.de/en/Data-protection-Privacy
Document Warranty
The material contained in this document is provided “as is” and is subject to being changed at any time without notice. Trenz Electronic does not warrant the accuracy and completeness of the materials in this document. Further, to the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, Trenz Electronic disclaims all warranties, either express or implied, with regard to this document and any information contained herein, including but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose or non infringement of intellectual property. Trenz Electronic shall not be liable for errors or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, use, or performance of this document or of any information contained herein.
Limitation of Liability
In no event will Trenz Electronic, its suppliers, or other third parties mentioned in this document be liable for any damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, those resulting from lost profits, lost data or business interruption) arising out of the use, inability to use, or the results of use of this document, any documents linked to this document, or the materials or information contained at any or all such documents. If your use of the materials or information from this document results in the need for servicing, repair or correction of equipment or data, you assume all costs thereof.
Copyright Notice
No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means (including electronic storage and retrieval or translation into a foreign language) without prior agreement and written consent from Trenz Electronic.
Technology Licenses
The hardware / firmware / software described in this document are furnished under a license and may be used /modified / copied only in accordance with the terms of such license.
Environmental Protection
To confront directly with the responsibility toward the environment, the global community and eventually also oneself. Such a resolution should be integral part not only of everybody's life. Also enterprises shall be conscious of their social responsibility and contribute to the preservation of our common living space. That is why Trenz Electronic invests in the protection of our Environment.
REACH, RoHS and WEEE
REACH
Trenz Electronic is a manufacturer and a distributor of electronic products. It is therefore a so called downstream user in the sense of REACH. The products we supply to you are solely non-chemical products (goods). Moreover and under normal and reasonably foreseeable circumstances of application, the goods supplied to you shall not release any substance. For that, Trenz Electronic is obliged to neither register nor to provide safety data sheet. According to present knowledge and to best of our knowledge, no SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) on the Candidate List are contained in our products. Furthermore, we will immediately and unsolicited inform our customers in compliance with REACH - Article 33 if any substance present in our goods (above a concentration of 0,1 % weight by weight) will be classified as SVHC by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA).
RoHS
Trenz Electronic GmbH herewith declares that all its products are developed, manufactured and distributed RoHS compliant.
WEEE
Information for users within the European Union in accordance with Directive 2002/96/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 January 2003 on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE).
Users of electrical and electronic equipment in private households are required not to dispose of waste electrical and electronic equipment as unsorted municipal waste and to collect such waste electrical and electronic equipment separately. By the 13 August 2005, Member States shall have ensured that systems are set up allowing final holders and distributors to return waste electrical and electronic equipment at least free of charge. Member States shall ensure the availability and accessibility of the necessary collection facilities. Separate collection is the precondition to ensure specific treatment and recycling of waste electrical and electronic equipment and is necessary to achieve the chosen level of protection of human health and the environment in the European Union. Consumers have to actively contribute to the success of such collection and the return of waste electrical and electronic equipment. Presence of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment results in potential effects on the environment and human health. The symbol consisting of the crossed-out wheeled bin indicates separate collection for waste electrical and electronic equipment.
Trenz Electronic is registered under WEEE-Reg.-Nr. DE97922676.