Page History
| HTML |
|---|
<!-- Template Revision 1.663 (HTML comments will be not displayed in the document, no need to remove them. For Template/Skeleton changes, increase Template Revision number. So we can check faster, if the TRM style is up to date). --> |
...
- Xilinx Virtex-7 FPGA module XC7VX330T-2FFG1157C (commercial temperature range)
- PCI Express 2.0 x8 card with maximum throughput of 4 GB/s
- FMC High Pin Count (HPC) connector
- 8 FPGA MGT lanes available on PCIe interface
- DDR3 SO-DIMM SDRAM socket
- 256-Mbit (32-MByte) Quad SPI Flash memory (for configuration and operation) accessible through:
- FPGA
- JTAG port (SPI indirect, bus width x4)
- External clock input via SMA coaxial connector
- 28 GTH transceivers, each with up to 13.1 Gbit/s data transmission rate
- FPGA configuration through:
- JTAG connector
- Quad SPI Flash memory
- Programmable quad clock generator
- TI LMK04828B ultra low-noise JESD204B compliant clock jitter cleaner
- On-board high-efficiency DC-DC converters
- Up to 202 FPGA I/O pins available on FMC connector (up to 101 LVDS pairs possible)
- System management and power sequencing
- AES bit-stream encryption
- eFUSE bit-stream encryption
...
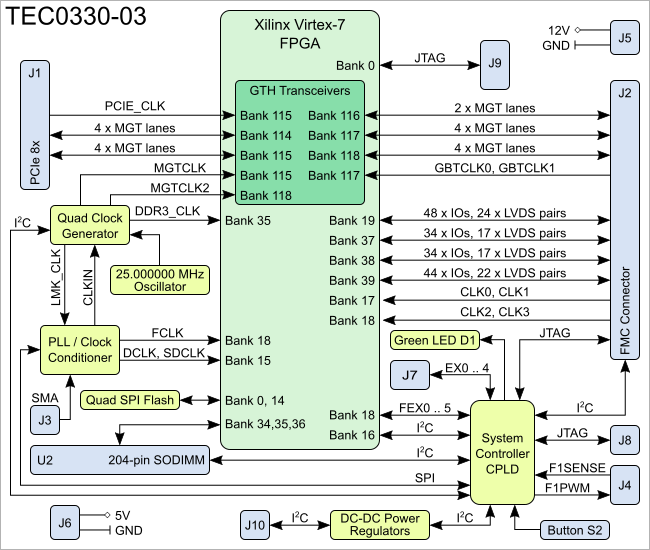
Block Diagram
Figure 1: TEC0330-03 Block Diagramblock diagram.
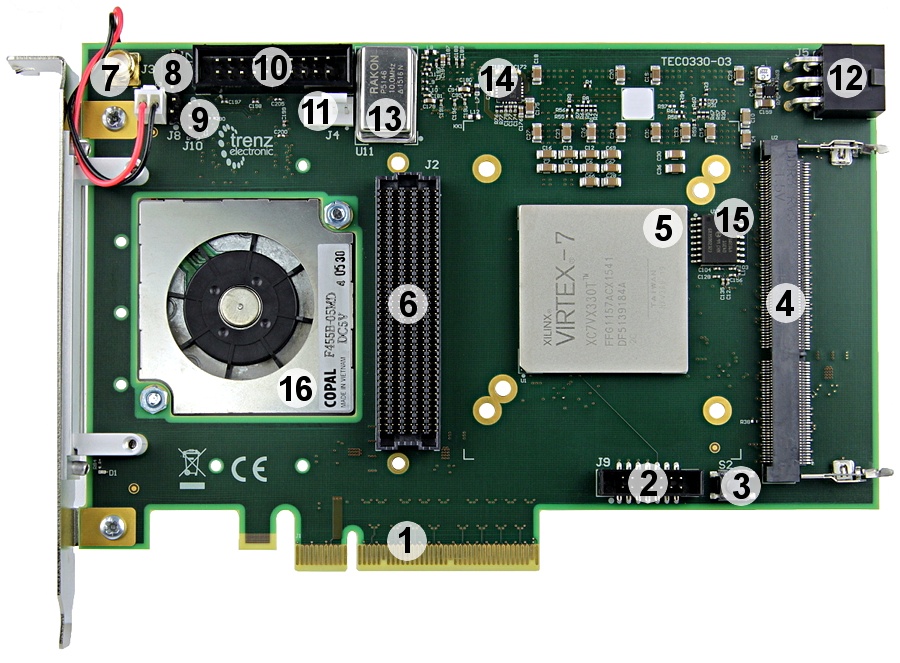
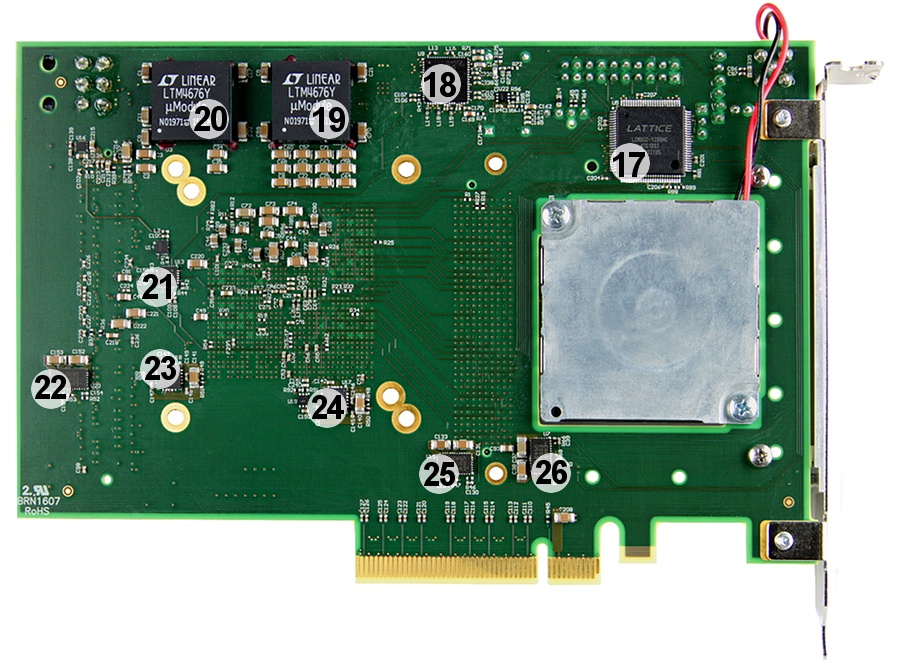
Main Components
Figure 2: FPGA board TEC0330-03.
...
The I/O signals are routed from the FPGA I/O banks to the FMC connector as LVDS pairs:
| FPGA Bank | I/O Signals | LVDS pairs |
|---|
| Bank Voltage (VCCO) | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bank 19 | 92 | 46 | 1.8V | - |
| Bank 39 | 42 | 21 | VIO_B_FMC | Bank voltage VIO_B_FMC must be supplied by FMC connector pins J2-J39, J2-K40. Bank's VREF_B_M2C signal is routed to the FMC connector pin J2-K1 (external reference voltage). |
| Bank 37 | 34 | 17 | 1.8V | Bank's VREF_A_M2C signal is routed to the FMC connector pin J2-H1 (external reference voltage). |
| Bank 38 | 34 | 17 | 1.8V | Bank's VREF_A_M2C signal is routed to the FMC connector pin J2-H1 (external reference voltage). |
Table 2: Overview of the FPGA I/O bank signals routed to the FMC.
...
There are also 10 high-speed MGT lanes (Xilinx GTH transceivers) from different FPGA MGT banks routed to the FMC connector.The MGT banks have also clock input pins which are exposed to the FMC connector. Following MGT lanes are available on the FMC connector:
| FPGA Bank | I/O signalsSignals | LVDS pairsPairs | MGT lanesLanes | MGT Bank's reference clock (LVDS pair)Reference Clock |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 116 | 108 | 54 | 2 | 1 clock-signal from clock synthesizer U9 to bank's pins T6/T5. |
| 117 | 2016 | 108 | 4 | 2 clock-signals from clock FMC connector GBTCLK0_M2C and GBTCLK1_M2C (pins J2-D4/J2-D5 and J2-B20/J2-B21) to bank's pins M6/M5 and P6/P5. |
| 118 | 2016 | 108 | 4 | 1 reference clock from clock synthesizer U9 to bank's pins F6/F5 1 reference clock from programmable quad clock generator U13 to bank's pins H6/H5. |
Table 3: Overview of MGT banks lanes routed to the FMC connector.
page-break
The FMC connector has also two reference clock input pairs (LVDS) routed to the FPGA MGT bank 117, see also section MGT lanes.
| Page break |
|---|
There are also JTAG, I2C interface and power good control signals routed between FMC connector and System Controller CPLD provides JTAG and I2C interfaces to the System Controller CPLD:
| Interface | I/O |
|---|
| Signals | Schematic |
|---|
| Name / FMC |
|---|
| Pin | Connected to | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JTAG | 5 | FMC_TRST, pin D34 FMC_TCK, pin D29 FMC_TMS, pin D33 FMC_TDI, pin D30 FMC_TDO, pin D31 | SC CPLD, bank 2 | VCCIO: 3V3PCI. |
| I2C | 2 | FMC_SCL, pin C30 FMC_SDA, pin C31 | SC CPLD, bank 2 | VCCIO: 3V3PCI. I2C-lines 3V3PCI pulled-up. |
| Control lines | 3 | FMC_PRSNT_M2C_L, pin H2 FMC_PG_C2M, pin D1 (3V3FMC pull-up) FMC_PG_M2C, pin F1 (3V3FMC pull-up) | SC CPLD, bank 1 | PG - Power Good signal. C2M - carrier to mezzanine module. M2C - mezzanine module to carrier. Internal System Controller CPLD signal assignment: FEX_0_N <= FMC_PG_M2C FMC_PG_C2M <= FMC_PRSNT_M2C_L |
Table 4: FMC connector pin-outs of available interfaces to the System Controller CPLD.
...
FPGA bank 17 and 18 clock inputs from FMC connector:
| Schematic nameName | FMC connector pinsConnector Pins | FPGA bankBank | FPGA pinsPins |
|---|---|---|---|
| CLK0_P, CLK0_N | H4, H5 | 17 | R28, R29 |
| CLK1_P, CLK1_N | G2, G3 | 17 | P29, P30 |
| CLK2_P, CLK2_N | K4, K5 | 18 | G31, G31 |
| CLK3_P, CLK3_N | J2, J3 | 18 | H29, H30 |
...
Several VCCIO voltages are available on the FMC connector for FPGA I/O banks:
| Schematic nameName | Max currentCurrent | FMC connector pinsConnector Pins | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 1A | C35/, C37 | Externally supplied 12V |
| 3V3PCI | 20mA | D32 | Supplied by the PCIe interface |
| 3V3FMC | 3A | D36/, D38/, D40/, C39 | Supplied by DC-DC converter U15 |
| VIO_B_FMC | External supply | J39/, K40 | Externally supplied VCCO to HB FPGA bank 39 |
| FMC_VADJ | 4A | H40/, G39/, F40/, E39 | Fixed to 1.8V, supplied by DC-DC converter U7 |
...
The TEC0330 FPGA board is also a PCI Express card designed to fit in computing into systems with PCI Express x8 slots (PCIe 2.0 or higher) and is PCIe Gen. 2 capable. 8 MGT lanes are See next section for the overview of FPGA MGT lanes routed to the PCIe interface composed of .
MGT Lanes
MGT (Multi Gigabit Transceiver) lane consists of one receive and one transmit (RX/TX LVDS pairs for each lane:
...
MGT lanes
...
1 reference clock from programmable quad clock generator
U13 to bank's pins AB6/AB5
1 reference clock from PCIe interface J1 to bank's pins AD6/AD5
) differential pairs, four signals total per one MGT lane. Following table lists lane number, MGT bank number, transceiver type, signal schematic name, FMC connector pin connection and FPGA pin connection information.
FPGA to FMC Connector MGT lanes
Table 7: MGT lanes available on PCIe interface.
MGT Lanes
MGT (Multi Gigabit Transceiver) lane consists of one receive and one transmit (RX/TX) differential pairs, four signals total per one MGT lane. Following table lists lane number, MGT bank number, transceiver type, signal schematic name, FMC connector pin connection and FPGA pin connection information:
FPGA to FMC MGT lanes
- DP0_M2C_P
- DP0_M2C_N
- DP0_C2M_P
- DP0_C2M_N
- J2A-C6
- J2A-C7
- J2A-C2
- J2A-C3
- MGTHRXP0_117, N4
- MGTHRXN0_117, N3
- MGTHTXP0_117, M2
- MGTHTXN0_117, M1
- DP1_M2C_P
- DP1_M2C_N
- DP1_C2M_P
- DP1_C2M_N
- J2A-A2
- J2A-A3
- J2A-A22
- J2A-A23
- MGTHRXP1_117, L4
- MGTHRXN1_117, L3
- MGTHTXP1_117, K2
- MGTHTXN1_117, K1
- DP2_M2C_P
- DP2_M2C_N
- DP2_C2M_P
- DP2_C2M_N
| Lane | FPGA Bank | Type | Signal Name | FPGA Pin | FMC Pin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 117 | GTH |
|
|
|
| 1 | 117 | GTH |
|
|
|
| 2 | 117 | GTH |
|
|
|
- MGTHRXP2_117, K6
- MGTHRXN2_117, K5
- MGTHTXP2_117, H2
- MGTHTXN2_117, H1
| 3 | 117 | GTH |
|
- J2A-A10
- J2A-A11
- J2A-A30
- J2A-A31
|
|
| ||
| 4 | 118 | GTH |
|
- J2A-A14
- J2A-A15
- J2A-A34
- J2A-A35
|
- DP5_M2C_P
- DP5_M2C_N
- DP5_C2M_P
- DP5_C2M_N
|
|
|
|
|
Table 8: FPGA to FMC connector MGT lanes overview (continue on next page).
| Page break |
|---|
FPGA to FMC Connector MGT lanes (continued)
| Lane | FPGA Bank | Type | Signal Name | FPGA Pin | FMC Pin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 |
- MGTHRXP1_118, E4
- MGTHRXN1_118, E3
- MGTHTXP1_118, C4
- MGTHTXN1_118, C3
| 118 | GTH |
|
|
|
|
- J2A-B16
- J2A-B17
- J2A-B36
- J2A-B37
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| 6 | 118 | GTH |
|
|
|
|
- J2A-B12
- J2A-B13
- J2A-B32
- J2A-B33
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 7 | 118 |
| GTH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| 8 | 116 | GTH |
|
|
|
| 9 | 116 | GTH |
|
- J2A-B4
- J2A-B5
- J2A-B24
- J2A-B25
|
...
|
Table 8: FPGA to FMC connector MGT lanes overview (continue on next page).
Page break
FPGA to FMC PCIe Connector MGT lanes (continued)
| Lane | FPGA Bank | Type | Signal Name |
|---|
| FPGA Pin |
|---|
| PCIe Pin |
|---|
| 0 |
| 115 | GTH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- J2A-A18
- J2A-A19
- J2A-A38
- J2A-A39
- MGTHRXP1_118, E4
- MGTHRXN1_118, E3
- MGTHTXP1_118, C4
- MGTHTXN1_118, C3
- DP6_M2C_P
- DP6_M2C_N
- DP6_C2M_P
- DP6_C2M_N
- J2A-B16
- J2A-B17
- J2A-B36
- J2A-B37
- MGTHRXP2_118, D6
- MGTHRXN2_118, D5
- MGTHTXP2_118, B2
- MGTHTXN2_118, B1
- DP7_M2C_P
- DP7_M2C_N
- DP7_C2M_P
- DP7_C2M_N
- J2A-B12
- J2A-B13
- J2A-B32
- J2A-B33
- MGTHRXP3_118, B6
- MGTHRXN3_118, B5
- MGTHTXP3_118, A4
- MGTHTXN3_118, A3
- DP8_M2C_P
- DP8_M2C_N
- DP8_C2M_P
- DP8_C2M_N
- J2A-B8
- J2A-B9
- J2A-B28
- J2A-B29
- MGTHRXP2_116, U4
- MGTHRXN2_116, U3
- MGTHTXP2_116, T2
- MGTHTXN2_116, T1
- DP9_M2C_P
- DP9_M2C_N
- DP9_C2M_P
- DP9_C2M_N
- J2A-B4
- J2A-B5
- J2A-B24
- J2A-B25
- MGTHRXP3_116, R4
- MGTHRXN3_116, R3
- MGTHTXP3_116, P2
- MGTHTXN3_116, P1
Table 8: FPGA to FMC connector MGT lanes overview.
| Page break |
|---|
JTAG Interfaces
TEC0330 board JTAG interfaces accessing the FPGA or the System Controller CPLD:
...
CPLD JTAG
VCCIO: 3V3PCI
Connector: J8
...
J8-4
...
FPGA JTAG
VCCIO: 1V8
Connector: J9
...
FMC JTAG
VCCIO: 3.3VPCI
Connector: J2
...
Table 9: JTAG Interface on TEC0330 board.
SO-DIMM Socket for DDR3 SDRAM
The TEC0330 board supports additional DDR3 SO-DIMM (204-pin) via 204-pin SO-DIMM socked U2. The DDR3 memory interface is routed to the FPGA banks 34, 35 and 36.
The reference clock signal for the DDR3 interface is generated by the quad programmable reference clock U13 and is applied to bank 35.
There is also a I2C interface between the System Controller CPLD and the DDR3 SDRAM memory:
...
Table 10: I2C-interface between SC CPLD and DDR3 SDRAM memory.
System Controller CPLD
The System Controller CPLD is the central system management unit that provides numerous interfaces between the on-board peripherals and to the FPGA module. The signals routed to the CPLD will be linked by the logic implemented in the CPLD firmware, which generates output signals to control the system, the on-board peripherals and the interfaces. So some interfaces between the on-board peripherals and to the FPGA module are by-passed, forwarded and controlled by the System Controller CPLD.
Other tasks of the System Controller CPLD are the monitoring of the power-on sequence, the proper programing of the FPGA module and to display its programming state.
...
Table 11: VCCIO voltages of CPLD banks.
Following table describes the interfaces and functionalities of the System Controller CPLD, which are not described elsewhere in this TRM:
...
FPGA_IIC_SDA, pin 24
FPGA_IIC_SCL, pin 25
FPGA_IIC_OE, pin 19
...
FPGA bank 16, pin V29
FPGA bank 16, pin W29
FPGA bank 16, pin W26
...
VCCIO: 1V8, all with pull-up to 1V8.
Following devices and connectors are linked to the FPGA_IIC I2C interface:
- DC-DC converter U3 and U4 (LT LTM4676)
- Programmable quad clock generator U13
- FMC connector J2
- PCIe connector J1
Note: FPGA_IIC_OE must kept high for I2C operation.
For I2C slave device addresses refer to the component datasheets.
...
User I/Os
External LVDS pairs
...
10 I/Os
5 x differential signaling pairs
...
EX0_P ... EX4_P
EX0_N ... EX4_N
...
Can also be used for single-ended signaling.
...
User I/Os
Internal LVDS pairs
...
13 I/Os
6 x differential signaling pairs
...
FEX0_P ... FEX5_P
FEX0_N ... FEX5_N
FEX_DIR (single-ended I/O)
...
VCCIO: 1V8
Can also be used for single-ended signaling.
FPGA bank 18 has also reference clock input from FMC connector (CLK2, CLK3) and clock synthesizer U9 (FCLK).
Internal signal assignment:
FEX_DIR <= FMC_PRSNT_M2C_L
...
DONE, pin 7
PROGRAM_B, pin 8
...
FPGA bank 0, pin V8
FPGA bank 0, pin U8
...
PLL_SCL, pin 14
PLL_SDA, pin 15
...
U13, pin 12
U13, pin 19
...
VCCIO: 1V8
Only PLL_SDA has 1V8 pull-up.
...
F1SENSE, pin 99
F1PWM, pin 98
...
J4-3 (active low)
J4-4
...
Internal signal assignment:
FEX_5_P <= F1SENSE
FEX_5_N => F1PWM
...
Fast blinking, when FPGA is not programmed.
Internal signal assignment:
LED1 <= Button S2 or FEX0_P
...
PCIe control line RESET_B
...
Internal signal assignment:
FEX_4_N <= PCIE_RSTB
...
Control Interface to clock synthesizer U9 (TI LMK04828B)
...
SPI (3 I/Os),
4 I/Os
...
CLK_SYNTH_SDIO, pin 75
CLK_SYNTH_SCK, pin 74
CLK_SYNTH_RESET, pin 54
CLK_SYNTH_CS, pin 53
CLK_SYNTH_SYNC, pin 52
LMK_STAT0, pin 62
LMK_STAT1, pin 63
...
U9, pin 20
U9, pin 19
U9, pin 5
U9, pin 18
U9, pin 6
U9, pin 31
U9, pin 48
...
Pull up to 3V3PCI.
Internal signal assignment:
LMK_SCK <= FEX_1_P
LMK_SDIO <= FEX_1_N
LMK_CS <= FEX_3_P
LMK_SYNC <= EX_3_N
LMK_RESET <= FEX_4_P
FEX_2_P => LMK_SDIO (FEX_2_N must be 0)
LMK_STAT0 and LMK_STAT1 signals are not used.
...
I2C (2 I/Os),
2 I/Os
...
LTM_SCL, pin 67
LTM_SDA, pin 66
LTM1_ALERT, pin 65
LTM2_ALERT, pin 64
...
U4, pin E6 and U3, pin E6
U4, pin D6 and U3, pin D6
U4, pin E5
U3, pin E5
...
3V3 pull-ups.
LTM I2C interface is also accessible trough header J10.
LTM1_Alert and LTM2_ALERT signals are not used.
...
EN_1V8, pin 58
PG_1V8, pin 59
EN_FMC_VADJ, pin 60
PG_FMC_VADJ, pin 61
EN_3V3, pin 51
PG_3V3, pin 57
...
U20, pin 27
U20, pin 28
U7, pin 27
U7, pin 28
U15, pin 27
U15, pin 28
...
Sequence of the supply voltages depend on the System Controller CPLD firmware.
EN_1V8, EN_3V3 and EN_FMC_VADJ will be set simultaneously at start-up.
PG signals will not be evaluated.
Table 12: Overview of the System Controller CPLD functions.
Clocking
The TEC0330 FPGA board has a sophisticated clock generation and conditioning system to meet the requirements of the Xilinx Virtex-7 GTH units with data transmission rates up to 13.1 Gb/s.
Clock sources
List of on-board and external reference clock signals of the TE0330 board:
...
CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN0_P,
CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN0_N (GND)
...
CLK0_P, CLK0_N
...
GBTCLK0_M2C_P,
GBTCLK0_M2C_N
...
GBTCLK1_M2C_P,
GBTCLK1_M2C_N
...
PCIE_CLK_P,
PCIE_CLK_N
...
100 MHz
(PCIe spec.)
...
Table 13: Clock generator sources overview.
| Page break |
|---|
Programmable Clock Generator
There is a Silicon Labs I2C programmable quad clock generator Si5338A (U13) on-board. It's output frequencies can be programmed by using the I2C-bus with address 0x70.
A 25 MHz (U14) oscillator is connected to pin 3 (IN3) and is used to generate the output clocks.
Once running, the frequency and other parameters can be changed by programming the device using the I2C bus connected between the FPGA (master) and clock generator (slave). Logic needs to be generated inside the FPGA module to utilize I²C-bus correctly.
...
IN1/IN2
...
CLKIN_5338_C_P, CLKIN_5338_C_N
...
Reference clock signal from clock synthesizer U9
(100 nF decoupling capacitors and 100Ω termination resistor)
...
IN3
...
Reference clock oscillator input, SiTime SiT8208AI (U14).
...
IN4/IN6
...
IN5
...
Not connected
...
CLK0 A/B
...
DDR3_CLK_P, DDR3_CLK_N
...
CLK1 A/B
...
MGTCLK_5338_C_P,
MGTCLK_5338_C_N
...
Reference clock signal to FPGA bank 115 MGT
(100 nF decoupling capacitors and 100Ω termination resistor)
...
CLK2 A/B
...
Input clock signal to clock synthesizer U9
(100 nF decoupling capacitors)
...
MGTCLK2_5338_C_P,
MGTCLK2_5338_C_N
...
Reference clock signal to FPGA bank 118 MGT
(100 nF decoupling capacitors and 100Ω termination resistor)
Table 14: I/O pin description of programmable clock generator Si5338A.
| Page break |
|---|
Ultra low-noise high-performance clock synthesizer
The TEC0330 board utilizes an ultra low jitter clock synthesizer TI LMK04828B (U9) for conditioning and generating clean clock signals which are necessary for the GTH units of the Xilinx Virtex-7 FPGA module.
The clock synthesizer can be controlled and programmed by its SPI interface (SPI slave) and other control lines, which are routed to the FPGA module (SPI master) and by-passed trough the System Controller CPLD. See section 'System Controller CPLD' for more detailed information.
Logic needs to be generated inside the FPGA module to utilize SPI bus correctly.
...
SPI interface and control lines
...
CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN0_P,
CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN0_N
...
Input reference clock signal via SMA coaxial connector J3, connected to CLKin0* via serial decoupling capacitor 100nF.
CLKin0 to connected to GND via serial decoupling capacitor 100nF.
...
CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN1_P,
CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN1_N
...
CLK_SYNTH_DCLKOUT0_P,
CLK_SYNTH_DCLKOUT0_N
...
CLK_SYNTH_SDCLKOUT1_P,
CLK_SYNTH_SDCLKOUT1_N
...
CLKIN_5338_P,
CLKIN_5338_N
...
Reference clock signal to programmable quad clock generator Si5338A (U13)
(100 nF decoupling capacitors and 100Ω termination resistor)
...
CLK_SYNTH_DCLKOUT4_P,
CLK_SYNTH_DCLKOUT4_N
...
CLK_SYNTH_SDCLKOUT7_P,
CLK_SYNTH_SDCLKOUT7_N
...
CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN2_P,
CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN2_N
...
Reference clock signal to FPGA bank 18, pins J30/J31
(100 nF decoupling capacitors)
|
| ||||
| 1 | 115 | GTH |
|
|
|
| 2 | 115 | GTH |
|
|
|
| 3 | 115 | GTH |
|
|
|
| 4 | 114 | GTH |
|
|
|
| 5 | 114 | GTH |
|
|
|
| 6 | 114 | GTH |
|
|
|
| 7 | 114 | GTH |
|
|
|
Table 9: FPGA to PCIe connector MGT lanes overview.
| Page break |
|---|
Following table lists reference clock sources of the MGT banks.
| Clock Signal | MGT Bank | Source | FPGA Pin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGTCLK_5338_P | 115 | U13, CLK1A | MGTREFCLK0P_115, AB6 | On-board Si5338A. |
| MGTCLK_5338_N | 115 | U13, CLK1B | MGTREFCLK0N_115, AB5 | On-board Si5338A. |
| PCIE_CLK_P | 115 | J1-A13, REFCLK+ | MGTREFCLK1P_115, AD6 | External clock from PCIe slot. |
| PCIE_CLK_N | 115 | J1-A14, REFCLK- | MGTREFCLK1N_115, AD6 | External clock from PCIe slot. |
| CLK_SYNTH_DCLKOUT4_P | 116 | U9, DCLKout4 | MGTREFCLK0P_116, T6 | On-board LMK04828B. |
| CLK_SYNTH_DCLKOUT4_N | 116 | U9, DCLKout4* | MGTREFCLK0N_116, T6 | On-board LMK04828B. |
| GBTCLK0_M2C_P | 117 | J2-D4 | MGTREFCLK0P_117, M6 | External clock from FMC connector. |
| GBTCLK0_M2C_N | 117 | J2-D5 | MGTREFCLK0N_117, M5 | External clock from FMC connector. |
| GBTCLK1_M2C_P | 117 | J2-B20 | MGTREFCLK1P_117, P6 | External clock from FMC connector. |
| GBTCLK1_M2C_N | 117 | J2-B21 | MGTREFCLK1N_117, P5 | External clock from FMC connector. |
| CLK_SYNTH_SDCLKOUT7_P | 118 | U9, DCLKout7 | MGTREFCLK0P_118,F6 | On-board LMK04828B. |
| CLK_SYNTH_SDCLKOUT7_N | 118 | U9, DCLKout7* | MGTREFCLK0N_118,F5 | On-board LMK04828B. |
| MGTCLK2_5338_P | 118 | U13, CLK3A | MGTREFCLK1P_118, H6 | On-board Si5338A. |
| MGTCLK2_5338_N | 118 | U13, CLK3B | MGTREFCLK1N_118, H5 | On-board Si5338A. |
Table 10: MGT banks reference clock sources.
| Page break |
|---|
JTAG Interfaces
There are three JTAG interfaces available on the TEC0330 board:
| JTAG Interface | Signal Schematic Name | JTAG Connector Pin | Connected to |
|---|---|---|---|
CPLD JTAG VCCIO: 3V3PCI Connector: J8 | CPLD_JTAG_TMS | J8-1 | SC CPLD, bank 0, pin 90 |
| CPLD_JTAG_TDI | J8-2 | SC CPLD, bank 0, pin 94 | |
| CPLD_JTAG_TDO | J8-3 | SC CPLD, bank 0, pin 95 | |
| CPLD_JTAG_TCK | J8-4 | SC CPLD, bank 0, pin 91 | |
FPGA JTAG VCCIO: 1V8 Connector: J9 | FPGA_JTAG_TMS | J9-4 | FPGA, bank 0, pin N9 |
| FPGA_JTAG_TMS | J9-6 | FPGA, bank 0, pin M8 | |
| FPGA_JTAG_TCK | J9-8 | FPGA, bank 0, pin N8 | |
| FPGA_JTAG_TDI | J9-10 | FPGA, bank 0, pin L8 | |
FMC JTAG VCCIO: 3.3VPCI Connector: J2 | FMC_TRST | J2-D34 | SC CPLD, bank 2, pin 36 |
| FMC_TRST | J2-D29 | SC CPLD, bank 2, pin 27 | |
| FMC_TCK | J2-D33 | SC CPLD, bank 2, pin 28 | |
| FMC_TMS | J2-D30 | SC CPLD, bank 2, pin 31 | |
| FMC_TDO | J2-D31 | SC CPLD, bank 2, pin 32 |
Table 11: JTAG interfaces on TEC0330 board.
On-board Peripherals
System Controller CPLD
The System Controller CPLD is the central system management unit that provides numerous interfaces between the on-board peripherals and to the FPGA module. The signals routed to the CPLD will be linked by the logic implemented in the CPLD firmware, which generates output signals to control the system, the on-board peripherals and the interfaces. So some interfaces between the on-board peripherals and to the FPGA module are by-passed, forwarded and controlled by the System Controller CPLD.
Other tasks of the System Controller CPLD are the monitoring of the power-on sequence, the proper programing of the FPGA module and to display its programming state.
| SC CPLD Bank | CPLD Bank's VCCIO |
|---|---|
| 0 | 3V3PCI |
| 1 | 3V3PCI |
| 2 | 3V3PCI |
| 3 | 1V8 |
Table 12: VCCIO voltages of CPLD banks.
Following table describes the interfaces and functionalities of the System Controller CPLD not described elsewhere in this TRM:
| CPLD Functionality | Interface | Designated CPLD Pins | Connected to | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2C interface between on-board peripherals and FPGA | I2C |
|
| VCCIO: 1V8, all with pull-up to 1V8. Following devices and connectors are linked to the FPGA_IIC I2C interface:
Note: FPGA_IIC_OE must kept high for I2C operation. For I2C slave device addresses refer to the component datasheets. |
User I/Os External LVDS pairs | 10 I/Os 5 x LVDS pairs |
|
| Can also be used for single-ended signaling. |
User I/Os Internal LVDS pairs | 13 I/Os 6 x LVDS pairs |
|
| VCCIO: 1V8 Can also be used for single-ended signaling. FPGA bank 18 has also reference clock input from FMC connector (CLK2, CLK3) and clock synthesizer U9 (FCLK). Internal signal assignment: FEX_DIR <= FMC_PRSNT_M2C_L |
| FPGA programming control and state | 2 I/Os |
|
| VCCIO: 1V8 |
| I2C interface to programmable quad clock generator | I2C |
|
| VCCIO: 1V8 Only PLL_SDA has 1V8 pull-up. |
| Fan PWM control J4 | 2 I/Os |
|
| Internal signal assignment:
|
| Button S2 | 1 I/O |
|
| Functionality depends on CPLD firmware, activating pin PROGRAM_B (active low) and LED1 in standard configuration. |
| LED1 | 1 I/O |
|
| Fast blinking, when FPGA is not programmed. Internal signal assignment:
|
PCIe control line RESET_B | 1 I/O |
|
| Internal signal assignment:
|
Control interface to clock synthesizer U9 (TI LMK04828B) | SPI (3 I/Os), 4 I/Os |
|
| Pull up to 3V3PCI.
|
| Control Interface to DC-DC converters U3 and U4 (both LTM4676) | I2C (2 I/Os), 2 I/Os |
|
| 3V3 pull-ups. LTM I2C interface is also accessible trough header J10. LTM1_ALERT and LTM2_ALERT signals are not used. |
| Power-on sequence and monitoring | 6 I/Os |
|
| Sequence of the supply voltages depend on the System Controller CPLD firmware. EN_1V8, EN_3V3 and EN_FMC_VADJ will be set simultaneously at start-up. PG signals will not be evaluated. |
Table 13: Overview of the System Controller CPLD functions.
SO-DIMM Socket for DDR3 SDRAM
The TEC0330 board supports additional DDR3 SO-DIMM via 204-pin socket U2. The DDR3 memory interface is routed to the FPGA banks 34, 35 and 36.
The reference clock signal for the DDR3 interface is generated by the quad programmable clock generator U13 and is applied to the FPGA bank 35.
There is also a I2C interface between the System Controller CPLD and the DDR3 SDRAM memory:
| Interface Signals Schematic Name | System Controller CPLD Pin | DDR3 Memory Interface Pin |
|---|---|---|
| DDR3_SDA | Bank 2, pin 48 | Pin 200 (3V3PCI pull-up) |
| DDR3_SCL | Bank 2, pin 49 | Pin 202 (3V3PCI pull-up) |
Table 14: I2C-interface between SC CPLD and DDR3 SDRAM memory.
Quad SPI Flash Memory
An 256 Mbit (32 MByte) Quad SPI Flash Memory (Micron N25Q256A, U12) is provided for FPGA configuration file storage. After configuration process completes the remaining free memory can be used for application data storage. All four SPI data lines are connected to the FPGA allowing x1, x2 or x4 data bus widths to be used. The maximum data transfer rate depends on the bus width and clock frequency. The memory can be accessed indirectly by the FPGA JTAG port (J9) by implementing the functional logic for this purpose inside the FPGA.
Clock sources
The TEC0330 FPGA board has a sophisticated clock generation and conditioning system to meet the requirements of the Xilinx Virtex-7 GTH units with data transmission rates up to 13.1 Gb/s.
List of on-board and external reference clock signals of the TE0330 board:
| Clock Source | Schematic Name | Frequency | Clock Destination |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMA coaxial connector, J3 | CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN0_P, CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN0_N (GND) | User | Clock synthesizer U9, pins 37/38 |
| RAKON P5146LF oscillator, U11 | - | 10.0 MHz | Clock synthesizer U9, pins 43/44 |
| SiTime SiT8208 oscillator, U14 | CLK_25MHz | 25.0 MHz | Programmable quad clock generator U13, pin 3 |
| FMC connector J2, pins H4/H5 | CLK0_P, CLK0_N | User | FPGA bank 17, pins R28/R29 |
| FMC connector J2, pins G2/G3 | CLK1_P, CLK1_N | User | FPGA bank 17, pins P29/P30 |
| FMC connector J2, pins K4/K5 | CLK2_P, CLK2_N | User | FPGA bank 18, pins G30/G31 |
| FMC connector J2, pins J2/J3 | CLK3_P, CLK3_N | User | FPGA bank 18, pins H29/H30 |
| FMC connector J2, pins D4/D5 | GBTCLK0_M2C_P, GBTCLK0_M2C_N | User | FPGA bank 117, pins M6/M5 |
| FMC connector J2, pins B20/B21 | GBTCLK1_M2C_P, GBTCLK1_M2C_N | User | FPGA bank 117, pins P6/P5 |
| PCIe interface J1, pins A13/A14 | PCIE_CLK_P, PCIE_CLK_N | 100 MHz (PCIe spec.) | FPGA bank 115, pins AD6/AD5 |
Table 15: Clock generator sources overview.
| Page break |
|---|
Programmable Clock Generator
There is a Silicon Labs I2C programmable quad clock generator Si5338A (U13) on-board. It's output frequencies are programmable via FPGA I2C interface using slave device address 0x70 (corresponding I2C logic has to be implemented in FPGA design).
A 25 MHz (U14) oscillator is connected to pin 3 (IN3) and is used to generate the output clocks.
| Si5338A (U13) Input | Signal Schematic Name | Notes |
|---|---|---|
IN1/IN2 | CLKIN_5338_C_P, CLKIN_5338_C_N | Reference clock signal from clock synthesizer U9 (100 nF decoupling capacitors and 100Ω termination resistor). |
IN3 | Reference clock oscillator input, SiTime SiT8208AI (U14). | 25.0 MHz fixed frequency. |
IN4/IN6 | Connected to the GND. | LSB (pin 'IN4') of the default I²C-adress 0x70 is zero. |
IN5 | Not connected | - |
| Si5338A (U13) Output | Signal Schematic Name | Notes |
CLK0 A/B | DDR3_CLK_P, DDR3_CLK_N | DDR3-RAM reference clock signal to FPGA bank 35. |
CLK1 A/B | MGTCLK_5338_C_P, MGTCLK_5338_C_N | Reference clock signal to FPGA bank 115 MGT (100 nF decoupling capacitors and 100Ω termination resistor). |
CLK2 A/B | LMK_CLK_P, LMK_CLK_N | Input clock signal to clock synthesizer U9 (100 nF decoupling capacitors). |
| CLK3 A/B | MGTCLK2_5338_C_P, MGTCLK2_5338_C_N | Reference clock signal to FPGA bank 118 MGT (100 nF decoupling capacitors and 100Ω termination resistor). |
Table 16: I/O pin description of programmable clock generator Si5338A.
| Page break |
|---|
Ultra low-noise high-performance clock synthesizer
The TEC0330 board utilizes an ultra low jitter clock synthesizer TI LMK04828B (U9) for conditioning and generating clean clock signals which are necessary for the GTH units of the Xilinx Virtex-7 FPGA module.
The clock synthesizer can be controlled and programmed by its SPI interface (SPI slave) and other control lines, which are routed to the FPGA module (SPI master) and by-passed trough the System Controller CPLD. See section 'System Controller CPLD' for more detailed information.
Logic needs to be generated inside the FPGA module to utilize SPI bus correctly.
| LMK04828B (U9) input | signal schematic name | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Status_LD1, Status_LD2 | LMK_STAT0, LMK_STAT1 | Connected to System Controller CPLD, not implemented in current CPLD firmware. |
SPI interface and control lines | see section 'System controller CPLD' | The clock synthesizer IC is accessible to the FPGA via the SPI interface and control lines, which are routed through the System Controller CPLD. |
| CLKin0, CLKin0* | CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN0_P, CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN0_N | Input reference clock signal via SMA coaxial connector J3, connected to CLKin0* via serial decoupling capacitor 100nF. CLKin0 to connected to GND via serial decoupling capacitor 100nF. |
| CLKin1, CLKin1* | CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN1_P, CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN1_N | Input reference clock signal from programmable quad clock generator Si5338A (U13) via serial decoupling capacitor 100nF. |
| OSCin, OSCin* | - | Signal from reference clock oscillator RAKON P51446LF, fixed to 10.0 MHz. |
| LMK04828B (U9) output | signal schematic name | Note |
| DCLKout0, DCLKout0* | CLK_SYNTH_DCLKOUT0_P, CLK_SYNTH_DCLKOUT0_N | Reference clock signal to FPGA bank 15 pins AD29/AE29. |
| SDCLKout1, SDCLKout1* | CLK_SYNTH_SDCLKOUT1_P, CLK_SYNTH_SDCLKOUT1_N | Reference clock signal to FPGA bank 15 pins AE31/AF31. |
| DCLKout2, DCLKout2* | CLKIN_5338_P, CLKIN_5338_N | Reference clock signal to programmable quad clock generator Si5338A (U13) (100 nF decoupling capacitors and 100Ω termination resistor). |
| DCLKout4, DCLKout4* | CLK_SYNTH_DCLKOUT4_P, CLK_SYNTH_DCLKOUT4_N | Reference clock signal to FPGA MGT bank 115, pins T6/T5. |
| SDCLKout7, SDCLKout7* | CLK_SYNTH_SDCLKOUT7_P, CLK_SYNTH_SDCLKOUT7_N | Reference clock signal to FPGA MGT bank 118, pins F6/F5. |
| OSCout0, OSCout0* | CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN2_P, CLK_SYNTH_CLKIN2_N | Reference clock signal to FPGA bank 18, pins J30/J31 (100 nF decoupling capacitors). |
Table 17: Pin description of clock synthesizer TI LMK04828B
Table 15: Pin description of clock synthesizer TI LMK04828B.
32 MByte Quad SPI Flash Memory
An 256 Mbit (32 MByte) Quad SPI Flash Memory (Micron N25Q256A, U12) is provided for FPGA configuration file storage. After configuration process completes the remaining free memory can be used for application data storage. All four SPI data lines are connected to the FPGA allowing x1, x2 or x4 data bus widths to be used. The maximum data transfer rate depends on the bus width and clock frequency. The memory can be accessed indirectly by the FPGA JTAG port (J9) by implementing the functional logic for this purpose inside the FPGA.
Power and Power-On Sequence
...
| Power Input | Typical Current |
|---|---|
| 12V (J5) | TBD |
| 3V3PCI (J1) | TBD |
Table 1618: Maximum current of Typical power suppliesconsumption.
TBD - To Be Determined.
| Page break |
|---|
Power-On Sequence
The on-board voltages of the TEC0330 FPGA board will be are powered up in order of a determined predefined sequence after the external voltages 12V on connector J5 and 3V3PCI on connector J1 are become available.
Core voltages and main supply voltages have to reach stable state and their "Power Good" - signals have to be asserted before other voltages like PL bank's I/O voltages can be powered up.
...
| Bank | Schematic Name | Voltage | Range | NoteNotes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1V8 | 1.8V | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | Config bank (fixed to 1.8V) / JTAG interface. |
| 14 | 1V8 | 1.8V | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | QSPI flash memory interface. |
| 15 | 1V8 | 1.8V | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | Reference clock input. |
| 16 | 1V8 | 1.8V | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | I2C interface of FPGA. |
| 17 | 1V8 | 1.8V | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | Reference clock input. |
| 18 | 1V8 | 1.8V | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | Reference clock input / I/O's to CPLD. |
| 34 | VCC1V5 | 1.5V | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | DDR3 memory interface. |
| 35 | VCC1V5 | 1.5V | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | DDR3 memory interface. |
| 36 | VCC1V5 | 1.5V | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | DDR3 memory interface. |
114 115 116 117 118 | MGTAVCC_FPGA MGTVCCAUX_FPGA MGTAVTT_FPGA | 1.0V 1.8V 1.2V | MGT bank supply voltage MGT bank auxiliary supply voltage MGT bank termination circuits voltage | MGT banks with Xilinx GTH transceiver units. |
| 19 | 1V8 | 1.8V | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | I/Os routed to FMC, usable as LVDS pairs. |
| 37 | 1V8 | 1.8V | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | I/Os routed to FMC, usable as LVDS pairs. |
| 38 | 1V8 | 1.8V | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | I/Os routed to FMC, usable as LVDS pairs. |
| 39 | VIO_B_FMC | user | HP: 1.2V to 1.8V | I/Os routed to FMC, usable as LVDS pairs. |
Table 1719: Range of FPGAs bank voltages.
...
| Connector / Pin | Voltage | Direction | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| J4, pin 2 | 12V (filtered) | Output | 4-wire PWM fan connector supply voltage |
| J6, pin 2 | 5V (filtered) | Output | Cooling fan M1 supply voltage |
| J8, pin 6 | 3V3PCI | Output | VCCIO CPLD JTAG |
| J9, pin 2 | 1V8 | Output | VCCIO FPGA JTAG |
| J2, pin C35 / C37 | 12V | Output | VCCIO FMC |
| J2, pin D32 | 3V3PCI | Output | VCCIO FMC |
| J2, pin D36 / D38 / D39 / D40 | 3V3FMC | Output | VCCIO FMC |
| J2, pin H1 | VREF_A_M2C | Input | VREF voltage for bank 37 / 38 |
| J2, pin K1 | VREF_B_M2C | Input | VREF voltage for bank 39 |
| J2, pin J39 / J40 | VIO_B_FMC | Input | PL I/O voltage bank 39 (VCCO) |
| J2, pin H40 / G39 / F40 / E39 | FMC_VADJ | Output | VCCIO FMC (fixed to 1.8V) |
| J1, pin A10 / A11 / B8 | 3V3PCI | Input | PCIe interface supply voltage |
| J5, pin 1 / 2 / 3 | 12V | Input | Main power supply connector |
Table 1820: Power rails and corresponding connectors of the FPGA board.
...
| Parameter | Min | Max | Units | Notes | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
12V power supply voltage | 11.4 | 12.6 | V | 12V ± 5 % | ANSI/VITA 57.1 FPGA Mezzanine Card (FMC) standard |
| PL I/O voltage for HP banks | -0.55 | VCCO_X + 0.55 | V | - | Xilinx datasheet DS183 |
| GTH transceivers | -0.5 | 1.26 | V | - | Xilinx datasheet DS183 |
| Voltage on System Controller CPLD pins | -0.3 | 3.6 | V | - | MachXO2 family datasheet |
| Storage temperature | -55 | +125 | °C | - | MachXO2 family datasheet |
Table 1921: Absolute maximum ratings.
...
| Parameter | Min | Max | Units | Notes | Reference Document |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V power supply voltage | 11.4 | 12.6 | V | 12V ± 5 % | ANSI/VITA 57.1 FPGA Mezzanine Card (FMC) standard |
| PL I/O voltage for HP banks | -0.2 | VCCO_X + 0.2 | V | - | Xilinx datasheet DS183 |
| GTH transceivers | (*) | (*) | - | - | Xilinx datasheet DS183 |
| Voltage on System Controller CPLD pins | 3.135 | 3.6 | V | - | MachXO2 family datasheet |
Table 2022: Recommended operation conditions.
...
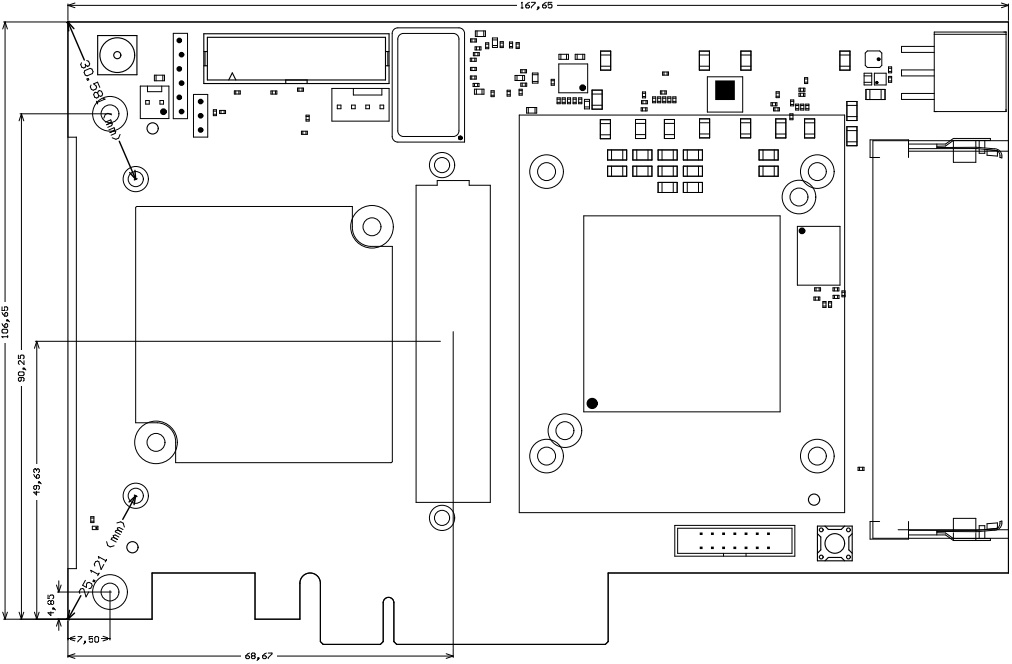
All dimensions are given in millimeters.
Figure 4: Physical dimensions of the TEC0330-03 board.
...
156 g - Plain board.
Revision History
Hardware Revision History
| Date | Revision | Notes | PCN | Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 03 | First production release | - | - |
| 2015-11-05 | 02 | Prototype | - | - |
| - | 01 | Prototype | - | - |
Table 2123: Hardware revision history.
Hardware revision number is printed on the PCB board together with the model number separated by the dash.
Figure 5: TE0330 board hardware revision number.
Document Change History
| Date | Revision | Contributors | Description | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan Kumann |
| |||||||||
2017-08-30 | v.15 | Jan Kumann |
| ||||||||
| 2017-03-15 | v.3 | Ali Naseri | Initial TRM release. |
Table 2224: Document change history.
...