Page History
| Page properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Template Revision 2.3 |
| HTML |
|---|
<!-- Template Revision 1.68 (HTML comments will be not displayed in the document, no need to remove them. For Template/Skeleton changes, increase Template Revision number. So we can check faster, if the TRM style is up to date). --> |
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
General Notes:
If some section is CPLD firmware dependent, make a note and if available link to the CPLD firmware description. It's in the TE shop download area in the corresponding module -> revision -> firmware folder.
--> |
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
General Notes:
Designate all graphics and pictures with a number and a description. For example "Figure 1: TE07xx-xx Block Diagram" or "Table 1: Initial delivery state". "Figure x" and "Table x" have to be formatted to bold.
--> |
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Link to the base folder of the module (remove de/ or en/ from the URL): for example:
https://shop.trenz-electronic.de/Download/?path=Trenz_Electronic/Modules_and_Module_Carriers/4x5/4x5_Carriers/TE0703/
--> |
...
| Scroll pdf ignore | |
|---|---|
Table of Contents
|
Overview
The Trenz Electronic TEF1001 FPGA board is a PCI Express form factor card (PCIe 2.0 or higher) integrating the Xilinx Kintex-7 XC7K160T, XC7K325T or XC7K410T FPGA SoC. The FPGA-board is designed for high system resources and intended for use in applications with high demands on system performance and throughput. To extent the board with standard DDR3 SDRAM memory module, there is a 204-pin SODIMM socket with 64bit databus width on the board present.
The board offers a HPC (High Pin Count) ANSI/VITA 57.1 compatible FMC interface connector for standard FPGA Mezzanine cards and modules. Other interface connectors found on-board include JTAG for accessing FPGA and on-board System Controller CPLD, and also connector with 5 high-speed I/O differential signaling pairs.
The TEF1001 FPGA board is intended to be used as add-on card in a PCIe 2.0 or higher capable host systems, it can not be used as a stand-alone device.
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Use short link the Wiki resource page: for example:
http://trenz.org/tef1001-info
List of available short links: https://wiki.trenz-electronic.de/display/CON/Redirects
--> |
| Scroll Only (inline) |
|---|
Refer to http://trenz.org/tef1001-info for the current online version of this manual and other available documentation.
|
Key Features
- Xilinx Kintex-7 XC7K160T, XC7K325T or XC7K410T FPGA SoC
- Large number of configurable I/Os are provided via rugged HPC FMC connector
- Dual ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore
- 1 GByte RAM (32-Bit wide DDR3)
- 32 MByte QSPI Flash memory
- 2 x Hi-Speed USB2 ULPI transceiver PHY
- 2 x Gigabit (10/100/1000 Mbps) Ethernet transceiver PHY
- 4 GByte eMMC (optional up to 64 GByte)
- 2 x MAC-address EEPROMs
- Optional 2x 64 MByte HyperFLASH or 2x 8 MByte HyperRAM (max 2x 32 MByte HyperRAM)
- Temperature compensated RTC (real-time clock)
- Si5338A programmable quad PLL clock generator for GTX transceiver clocks
- Plug-on module with 3 x 160-pin high-speed strips
- 16 GTX high-performance transceiver
- 2x GT transceiver clock inputs
- 254 FPGA I/O's (125 LVDS pairs)
- On-board high-efficiency switch-mode DC-DC converters
- System management
- eFUSE bit-stream encryption
- AES bit-stream encryption
- Evenly-spread supply pins for good signal integrity
- User LED
...
tables have all same width (web max 1200px and pdf full page(640px), flexible width or fix width on menu for single column can be used as before) -->
<style>
.wrapped{
width: 100% !important;
max-width: 1200px !important;
}
</style> |
| Page properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Important General Note:
|
| Page properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
----------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Page properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Note for Download Link of the Scroll ignore macro:
|
| Scroll Ignore |
|---|
| Scroll pdf ignore | |
|---|---|
Table of Contents
|
Overview
| Page properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Notes :
|
The Trenz Electronic TEF1001 FPGA board is a PCI Express form factor card integrating the Xilinx Kintex-7 XC7K160T, XC7K325T or XC7K410T FPGA SoC. The FPGA-board is designed for high system resources and intended for use in applications with high demands on system performance and throughput. To extent the board with standard DDR3 SDRAM memory module, there is a 204-pin SODIMM socket with 64bit databus width on the board present. Highspeed data transmission is enabled by the 4 lane PCIe Gen 2 interface.
The board offers a HPC (High Pin Count) ANSI/VITA 57.1 compatible FMC interface connector for standard FPGA Mezzanine cards and modules. Other interface connectors found on-board include JTAG for accessing FPGA and on-board System Controller CPLD.
The TEF1001 FPGA board is intended to be used as add-on card in a PCIe 2.0 or higher capable host system to meet the power supply requirements.
Refer to http://trenz.org/tef1001-info for the current online version of this manual and other available documentation.
Key Features
| Page properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Notes:
|
- Xilinx Kintex-7 XC7K160T, XC7K325T or XC7K410T FPGA SoC
- Large number of configurable I/Os are provided via HPC FMC connector
- 4 GTX high-performance transceiver
- 2x MGT transceiver clock inputs
- 160 FPGA I/O's (80 LVDS pairs)
- On-board high-efficiency switch-mode DC-DC converters
- Lattice MachXO2 LCMXO2-1200HC System Controller CPLD
- 10x User LEDs
- PCI Express x8 connector with 4 lane PCIe Gen 2 interface
- ANSI Vita 57.1 FMC High Pin Count (HPC) connector
- DDR3 SODIMM SDRAM with ECC socket with 64bit databus width
- 256Mbit (32MByte) Quad SPI Flash memory (for configuration and operation) accessible through:
- FPGA
- JTAG port (SPI indirect, bus width x4)
- FPGA configuration through:
- JTAG connector
- Quad SPI Flash memory
Clocking
Si5338 programmable quad PLL clock generator - 4 outputs for MGT and PL clocks
200MHz oscillator for DDR3 bank
- System management and power sequencing
Additional assembly options are available for cost or performance optimization upon request.
Block Diagram
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Block Diagram
| HTML |
|---|
<!--
Rules for all diagrams:
1. All diagrams are wrapped in the "Scroll Title" macro.
- The title has to be named with the diagrams name
- The anchor has the designation figure_x, whereby x is the number of the diagram
2. The Draw.IO diagram has to be inserted in the "Scroll Ignore" macro
- Border has to be switched off in the macro edit
- Toolbar has to be hidden in the macro edit
3. A PNG Export of the diagram has to be inserted in the "Scroll Only" macro, see Wiki page "Diagram Drawing Guidelines" how to do this step.
The workaround with the additional PNG of the diagram is necessary until the bug of the Scroll PDF Exporter, which cuts diagram to two pages, is fixed.
IMPORTANT NOTE: In case of copy and paste the TRM skeleton to a new Wiki page, delete the Draw.IO diagrams and the PNGs, otherwise due to the linkage of the copied diagrams every change in the TRM Skeleton will effect also in the created TRM and vice versa!
See page "Diagram Drawing Guidelines" how to clone an existing diagram as suitable template for the new diagram!
--> |
...
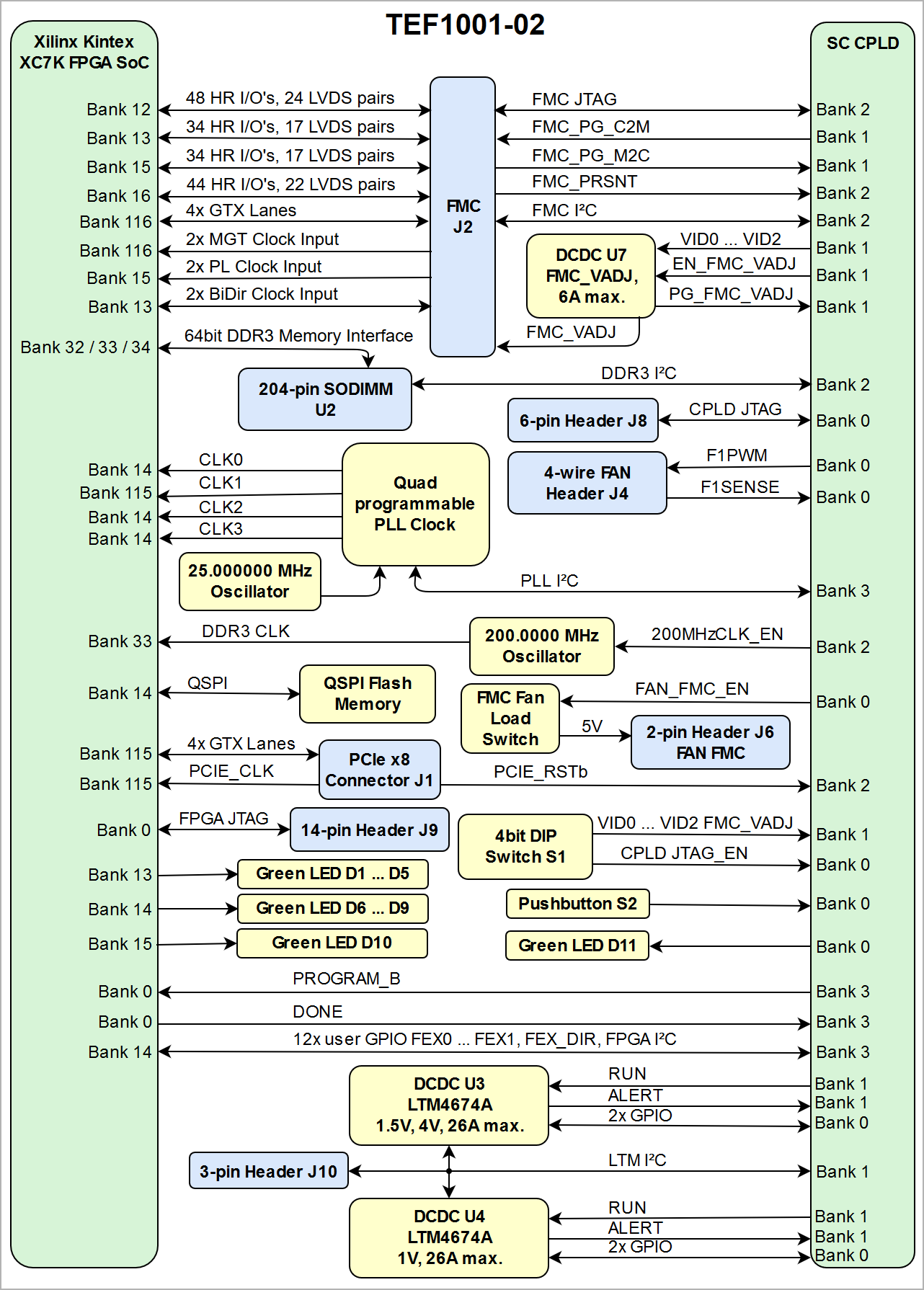
| anchor | Figure_1 |
|---|---|
| title | Figure 1: TEF1001-02 block diagram |
...
| Scroll Only |
|---|
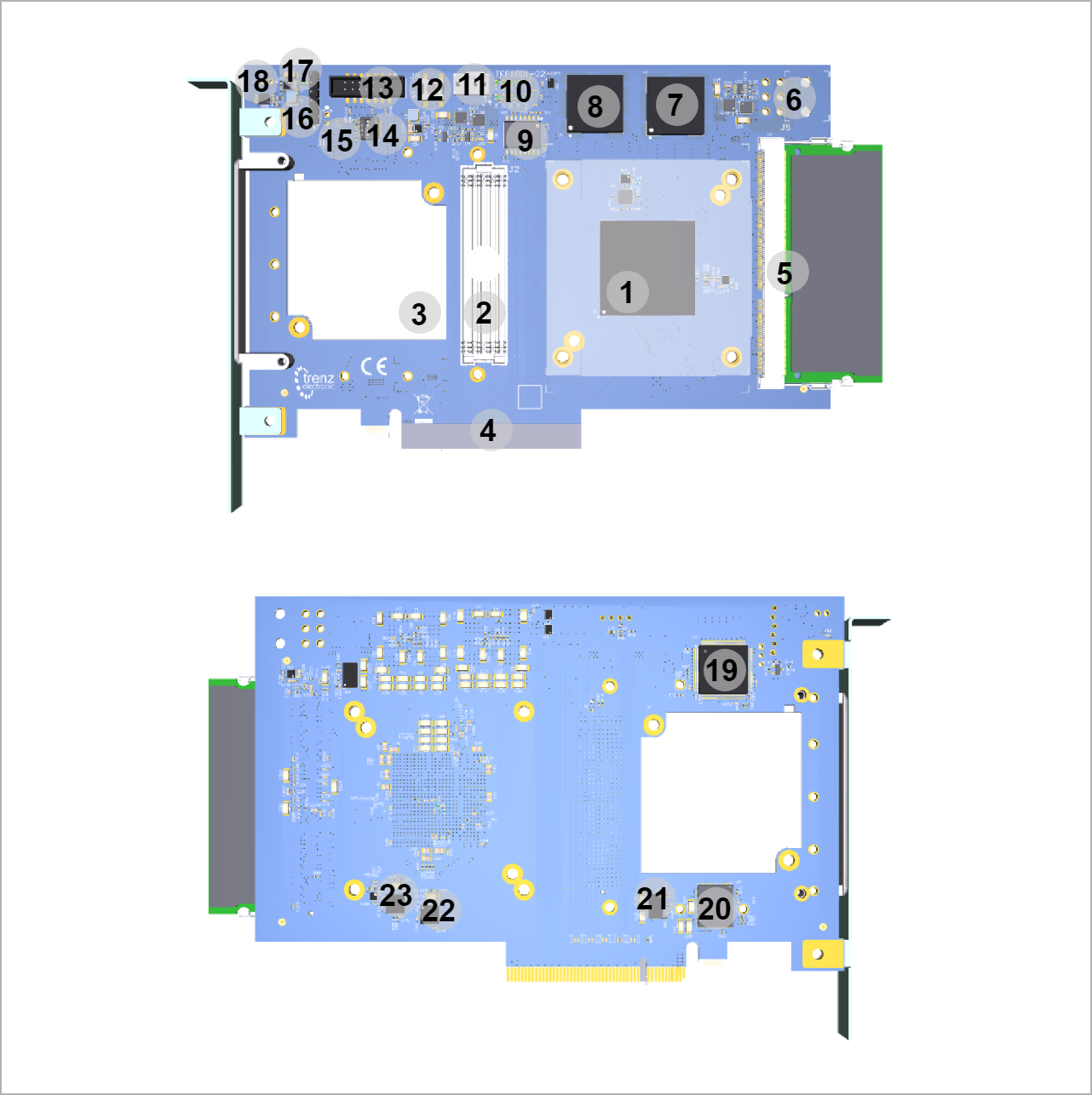
Main Components
| Scroll Title | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Main Components
| Page properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Notes :
|
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
- Xilinx Kintex XC7K-2FBG676I FPGA SoC, U6
- Xilinx Kintex XC7K-2FBG676I FPGA SoC, U6
- ANSI/VITA 57.1 compliant FMC HPC connector, J2
- Cooling fan 5VDC M1 (45X5MM, 0.7W, 1.06CFM), M1
- PCIe x8 connector, J1
- SO-DIMM socket, U2
- 6-pin 12V power connector, J5
- Step-down DC-DC converter @1.5V and @4V (LT LTM4676A), U3
- Step-down DC-DC converter @1.0V (LT LTM4676A), U4
- 256 Mbit Quad SPI Flash Memory (Micron N25Q256A), U12
- 10x Green user LEDs, D1 ... D10
- 4-wire PWM fan connector, J4
- User button, S2
- FPGA JTAG connector, J9
- sd
- sd
- sd
- sd
- s
- sd
- sd
- s
- sd
- sd
- s
- s
- sd
- sd
- sd
- sd
- FPGA JTAG connector, J9
- User button, S2
- SO-DIMM socket, U2
- Xilinx Virtex-7 XC7VX330T-2FFG1157C FPGA, U1
- ANSI/VITA 57.1 compliant FMC HPC connector, J2
- SMA coaxial connector for external clock input, J3
- System Controller CPLD JTAG connector, J8
- I2C connector for LT LTM4676 step-down DC-DC regulator, J10
- IDC header for access to 5 x high-speed data lanes (LVDS pairs), J7
- Cooling fan 5VDC M1 (45X5MM, 0.7W, 1.06CFM), M1
- PCIe x8 connector, J1
- DDR3 SODIMM 204-pin socket, U24-wire PWM fan connector, J4
- 6-pin 12V power connector, J5
- Reference clock generator @10.0 MHz (P5146) , U11
- Step-down DC-DC converter @1.5V and @4V (LT LTM4676A), U3
- Step-down DC-DC converter @1.0V (LT LTM4676A), U4LDO DC-DC regulator @3.3V (LMK_3V3) (TI TPS74901RGWR), U21
- 256 Mbit Quad SPI Flash Memory (Micron N25Q256A), U12
- Cooling fan 5VDC M1 (45X5MM, 0.7W, 1.06CFM)
- System Controller CPLD (Lattice Semiconductor LCMXO2-1200HC), U5
- Ultra low jitter clock synthesizer (TI LMK04828B), U9
- Step-down DC-DC regulator @1.0V (LT LTM4676), U4
- Step-down DC-DC regulator @1.5V (VCC1V5) (LT LTM4676, U3
- I2C Programmable quad clock generator (Silicon Labs Si5338A), U13
- 4A PowerSoC DC-DC converter @1.8V (Altera EN6347QI, U20
- LDO DC-DC regulator @1.0V (MGTAVCC_FPGA) (TI TPS74401RGW), U18
- 10x Green user LEDs connected to FPGA, D1 ... D10
- 4-wire PWM fan connector, J4
- User button, S2
- FPGA JTAG connector, J9
- 4bit DIP switch, S1
- I²C header for LTM4676A DC-DC converter, J10
- System Controller CPLD JTAG header, J8
- 1x Green LED connected to SC CPLD, D11
- 2-pin 5V FAN header, J6
- System Controller CPLD (Lattice Semiconductor LCMXO2-1200HC), U5
- 6A PowerSoC DC-DC converter @FMC_VADJ (Altera EN5365QI), U7
- 4A PowerSoC DC-DC converter @3.3V (3V3FMC) (Altera EN6347QI), U15
- LDO converter LDO DC-DC regulator @1.2V (MGTAVTT_FPGA) (TI TPS74401RGW), U174A PowerSoC DC-DC converter @3.3V (3V3FMC) (Altera EN6347QI)
- , U15LDO converter @1.0V (MGTAVCC_FPGA) (TI TPS74401RGW), U18
- 4A PowerSoC DC-DC converter @1.8V (FMC_VADJ) (Altera EN6347QI), U7
Initial Delivery State
...
24AA025E48 EEPROM's
...
User content not programmed
...
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
...
|
...
Table 1: Initial delivery state of programmable devices on the module
Boot Process
4 of the 7 boot mode strapping pins (MIO2 ... MIO8) of the Xilinx Zynq-7000 SoC device are hardware programmed on the board, 3 of them are set by the SC CPLD firmware. The boot strapping pins are evaluated by the Zynq device soon after the 'PS_POR' signal is deasserted to begin the boot process (see section "Boot Mode Pin Settings" of Xilinx manual UG585).
The TE0782 board is programmed in the SC CPLD firmware to boot initially from the on-board QSPI Flash memory U38. See section Bootmode in the TE0782 SC CPLD reference Wiki page.
The JTAG interface of the module is provided for storing the data to the QSPI Flash memory through the Zynq-7000 device.
Signals, Interfaces and Pins
Board to Board (B2B) I/Os
Zynq-7000 SoC's I/O banks signals connected to the B2B connectors:
...
B2B Connector
...
I/O Signal Count
...
10
...
HR
...
J3
...
44
...
User
...
11
...
HR
...
J3
...
40
...
User
...
HR
...
J2
...
40
...
User
...
13
...
HR
...
J2
...
40
...
User
...
33
...
HP
...
J1
...
48
...
User
...
Control Signals
To get started with TEF1001 board, some basic control signals are essential and are described in the following table:
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Signals, Interfaces and Pins
| Page properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Notes:
|
FMC HPC Connector
I/O signals and interfaces connected to the FPGA SoCs I/O bank and FMC connector J2:
| Scroll Title | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
For detailed information about the pin out, please refer to the Pin-out Tables.
FMC connector J2 MGT Lanes:
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
FMC connector J2 reference clock sources:
| Scroll Title | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
FMC connector J2 VCC/VCCIO:
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
FMC connector J2 Cooling Fan:
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PCI Express Interface
The TEF1001 FPGA board is a PCI Express card designed to fit into systems with PCI Express x8 slots and has a data transmission capability which meets PCIe Gen. 2 with 4 GTX lanes routed to the PCIe interface.
Following table lists lane number, MGT
Table 2: General overview of board to board I/O signals
For detailed information about the pin-out, please refer to the Pin-out table.
MGT Lanes
The Xilinx Zynq-7000 SoC used on the TE0782 module has 16 MGT transceiver lanes. All of them are wired directly to B2B connectors J1 and J3. MGT (Multi Gigabit Transceiver) lane consists of one transmit and one receive (TX/RX) differential pairs, four signals total per one MGT lane with data transmission rates up to 12.5Gb/s per lane (Xilinx GTX transceiver). Following table lists lane number, FPGA bank number, transceiver type, signal schematic name, board-to-board pin connection connector and FPGA pins connection:
...
- MGT_RX0_P
- MGT_RX0_N
- MGT_TX0_P
- MGT_TX0_N
...
- J3-32
- J3-30
- J3-31
- J3-29
...
- MGTXRXP0_109
- MGTXRXN0_109
- MGTXTXP0_109
- MGTXTXN0_109
...
- MGT_RX1_P
- MGT_RX1_N
- MGT_TX1_P
- MGT_TX1_N
...
- J3-28
- J3-26
- J3-27
- J3-25
...
- MGTXRXP1_109
- MGTXRXN1_109
- MGTXTXP1_109
- MGTXTXN1_109
...
- MGT_RX2_P
- MGT_RX2_N
- MGT_TX2_P
- MGT_TX2_N
...
- J3-24
- J3-22
- J3-23
- J3-21
...
- MGTXRXP2_109
- MGTXRXN2_109
- MGTXTXP2_109
- MGTXTXN2_109
...
- MGT_RX3_P
- MGT_RX3_N
- MGT_TX3_P
- MGT_TX3_N
...
- J3-20
- J3-18
- J3-19
- J3-17
...
- MGTXRXP3_109
- MGTXRXN3_109
- MGTXTXP3_109
- MGTXTXN3_109
...
- MGT_RX4_P
- MGT_RX4_N
- MGT_TX4_P
- MGT_TX4_N
...
- J3-16
- J3-14
- J3-15
- J3-13
...
- MGTXRXP0_110
- MGTXRXN0_110
- MGTXTXP0_110
- MGTXTXN0_110
...
- MGT_RX5_P
- MGT_RX5_N
- MGT_TX5_P
- MGT_TX5_N
...
- J3-12
- J3-10
- J3-11
- J3-9
...
- MGTXRXP1_110
- MGTXRXN1_110
- MGTXTXP1_110
- MGTXTXN1_110
...
- MGT_RX6_P
- MGT_RX6_N
- MGT_TX6_P
- MGT_TX6_N
...
- J3-8
- J3-6
- J3-7
- J3-5
...
- MGTXRXP2_110
- MGTXRXN2_110
- MGTXTXP2_110
- MGTXTXN2_110
...
- MGT_RX7_P
- MGT_RX7_N
- MGT_TX7_P
- MGT_TX7_N
...
- J3-4
- J3-2
- J3-3
- J3-1
...
- MGTXRXP3_110
- MGTXRXN3_110
- MGTXTXP3_110
- MGTXTXN3_110
...
- MGT_RX8_P
- MGT_RX8_N
- MGT_TX8_P
- MGT_TX8_N
...
- J1-1
- J1-3
- J1-2
- J1-4
...
- MGTXRXP0_111
- MGTXRXN0_111
- MGTXTXP0_111
- MGTXTXN0_111
...
- MGT_RX9_P
- MGT_RX9_N
- MGT_TX9_P
- MGT_TX9_N
...
- J1-5
- J1-7
- J1-6
- J1-8
...
- MGTXRXP1_111
- MGTXRXN1_111
- MGTXTXP1_111
- MGTXTXN1_111
...
- MGT_RX10_P
- MGT_RX10_N
- MGT_TX10_P
- MGT_TX10_N
...
- J1-9
- J1-11
- J1-10
- J1-12
...
- MGTXRXP2_111
- MGTXRXN2_111
- MGTXTXP2_111
- MGTXTXN2_111
...
- MGT_RX11_P
- MGT_RX11_N
- MGT_TX11_P
- MGT_TX11_N
...
- J1-13
- J1-15
- J1-14
- J1-16
...
- MGTXRXP3_111
- MGTXRXN3_111
- MGTXTXP3_111
- MGTXTXN3_111
...
- MGT_RX12_P
- MGT_RX12_N
- MGT_TX12_P
- MGT_TX12_N
...
- J1-17
- J1-19
- J1-18
- J1-20
...
- MGTXRXP0_112
- MGTXRXN0_112
- MGTXTXP0_112
- MGTXTXN0_112
...
- MGT_RX13_P
- MGT_RX13_N
- MGT_TX13_P
- MGT_TX13_N
...
- J1-21
- J1-23
- J1-22
- J1-24
...
- MGTXRXP1_112
- MGTXRXN1_112
- MGTXTXP1_112
- MGTXTXN1_112
...
- MGT_RX14_P
- MGT_RX14_N
- MGT_TX14_P
- MGT_TX14_N
...
- J1-25
- J1-27
- J1-26
- J1-28
...
- MGTXRXP2_112
- MGTXRXN2_112
- MGTXTXP2_112
- MGTXTXN2_112
...
- MGT_RX15_P
- MGT_RX15_N
- MGT_TX15_P
- MGT_TX15_N
...
- J1-29
- J1-31
- J1-30
- J1-32
...
- MGTXRXP3_112
- MGTXRXN3_112
- MGTXTXP3_112
- MGTXTXN3_112
Table 3: MGT lanes
There are 2 clock sources for the GTX transceivers. MGT_CLK1 and MGT_CLK4 are connected directly to B2B connector J3 and J1, so the clock can be provided by the carrier board. Clocks MGT_CLK0, MGT_CLK3, MGT_CLK5 and MGT_CLK6 are provided by the on-board clock generator (U2). As there are no capacitive coupling of the data and clock lines that are connected to the connectors, these may be required on the user’s PCB depending on the application.
...
Table 4: MGT reference clock sources
JTAG Interface
JTAG access to the Xilinx Zynq-7000 is provided through B2B connector J3.
...
JTAG Signal
...
B2B Connector Pin
...
Table 5: Zynq JTAG interface signals
JTAG access to the LCMXO2-1200HC System Controller CPLD U14 is provided through B2B connector J3.
...
JTAG Signal
...
B2B Connector Pin
...
Pin J3-136 'JTAGENB' of B2B connector J3 is used to access the JTAG interface of the SC CPLD. Set high to program the System Controller CPLD via JTAG interaface.
System Controller CPLD I/O Pins
Special purpose pins are connected to System Controller CPLD and have following default configuration:
...
Bootmode Pins
currently configured in SC CPLD firmare to boot from QSPI Flash
...
reset USB2 PHYs
U4 and U8
...
Table 7: System Controller CPLD special purpose pins.
See also TE0782 CPLD reference Wiki page.
Default PS MIO Mapping
...
Table 8: Zynq PS MIO mapping
Gigabit Ethernet
...
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
JTAG Connectors
There are two JTAG connectors J8 and J9 available on the TEF1001 board:
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
FAN Connectors
The TEF1001 board offers one FAN connector for cooling the FPGA device and one built-in FAN for the FMC modules.
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
On-board Peripherals
| Page properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Notes :
|
System Controller CPLD
The System Controller CPLD (U5) is provided by Lattice Semiconductor LCMXO2-256HC (MachXO2 Product Family). The SC-CPLD is the central system management unit where essential control signals are logically linked by the implemented logic in CPLD firmware, which generates output signals to control the system, the on-board peripherals and the interfaces. Interfaces like JTAG and I2C between the on-board peripherals and to the FPGA module are by-passed, forwarded and controlled by the System Controller CPLD.
Other tasks of the System Controller CPLD are the monitoring of the power-on sequence and to display the programming state of the FPGA module.
For detailed function of the pins and signals, the internal signal assignment and the implemented logic, look to the Wiki reference page of the board's SC CPLD or into its bitstream file.. Table below lists the SC CPLD I/O pins with their default configuration:
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
DDR3 SDRAM ECC SO-DIMM Socket
The TEF1001 board supports additional DDR3 ECC SO-DIMM via 204-pin socket U2. The DDR3 memory interface has a 64bit wide databus and is routed to the FPGA banks 32, 33 and 34.
The reference clock signal for the DDR3 interface is generated by the 200.0000MHz MEMS oscillator U1 and is applied to the FPGA bank 33.
There is also a I2C interface between the System Controller CPLD U5 and the DDR3 ECC SO-DIMM memory socket U2.
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Info |
|---|
It is important to use SO-DIMMs which provide ECC functionality. SO-DIMMs without ECC are not compatible with this board. |
Quad SPI Flash Memory
A 256 Mbit (32 MByte) Quad SPI Flash Memory (Micron N25Q256A, U12) is provided for FPGA configuration file storage. After configuration process completes the remaining free memory can be used for application data storage. All four SPI data lines are connected to the FPGA allowing x1, x2 or x4 data bus widths to be used. The maximum data transfer rate depends on the bus width and clock frequency. The memory can be accessed indirectly by the FPGA JTAG port (J9) by implementing the functional logic for this purpose inside the FPGA.
Quad SPI Flash memory interface is connected to the FPGA bank 14, QSPI clock is provided by FPGA config bank 0.
| Scroll Title | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Note |
|---|
SPI Flash QE (Quad Enable) bit must be set to high or FPGA is unable to load its configuration from flash during power-on. By default this bit is set to high at the manufacturing plant. |
Programmable Clock Generator
There is a Silicon Labs I2C programmable quad PLL clock generator on-board (Si5338A, U13) to generate various reference clocks for the module.
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Oscillators
The FPGA module has following reference clocking sources provided by on-board oscillators and FMC connector J2:
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
On-board LEDs
| Scroll Title | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Configuration DIP-switch
There is one 4-bit DIP-witches S1 present on the TEB0911 board to configure options and set parameters. The following section describes the functionalities of the particular switches.
Table below describes the functionalities of the switches of DIP-switches S3 and S4 at their each positions:
| Scroll Title | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Push Buttons
There is one push buttons available to the user connected to the SC CPLD U5:
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Power and Power-On Sequence
Power Consumption
The maximum power consumption of a module mainly depends on the design running on the FPGA.
Xilinx provide a power estimator excel sheets to calculate power consumption. It's also possible to evaluate the power consumption of the developed design with Vivado. See also Trenz Electronic Wiki FAQ.
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
* TBD - To Be Determined soon with reference design setup.
It is recommended to connect the ATX connector J5 to a 12V power supply source with minimum current capability of 6A to provide a sufficient power source to the board. Only one power source is needed at the same time, the system disconnects automatically PCIe power supply from PCIe edge connector J1 if the board is powered by the ATX connector J5.
| Warning |
|---|
| To avoid any damage to the module, check for stabilized on-board voltages should be carried out (i.e. power good and enable signals) before powering up any FPGA's I/O bank voltages VCCO_x. All I/Os should be tri-stated during power-on sequence. |
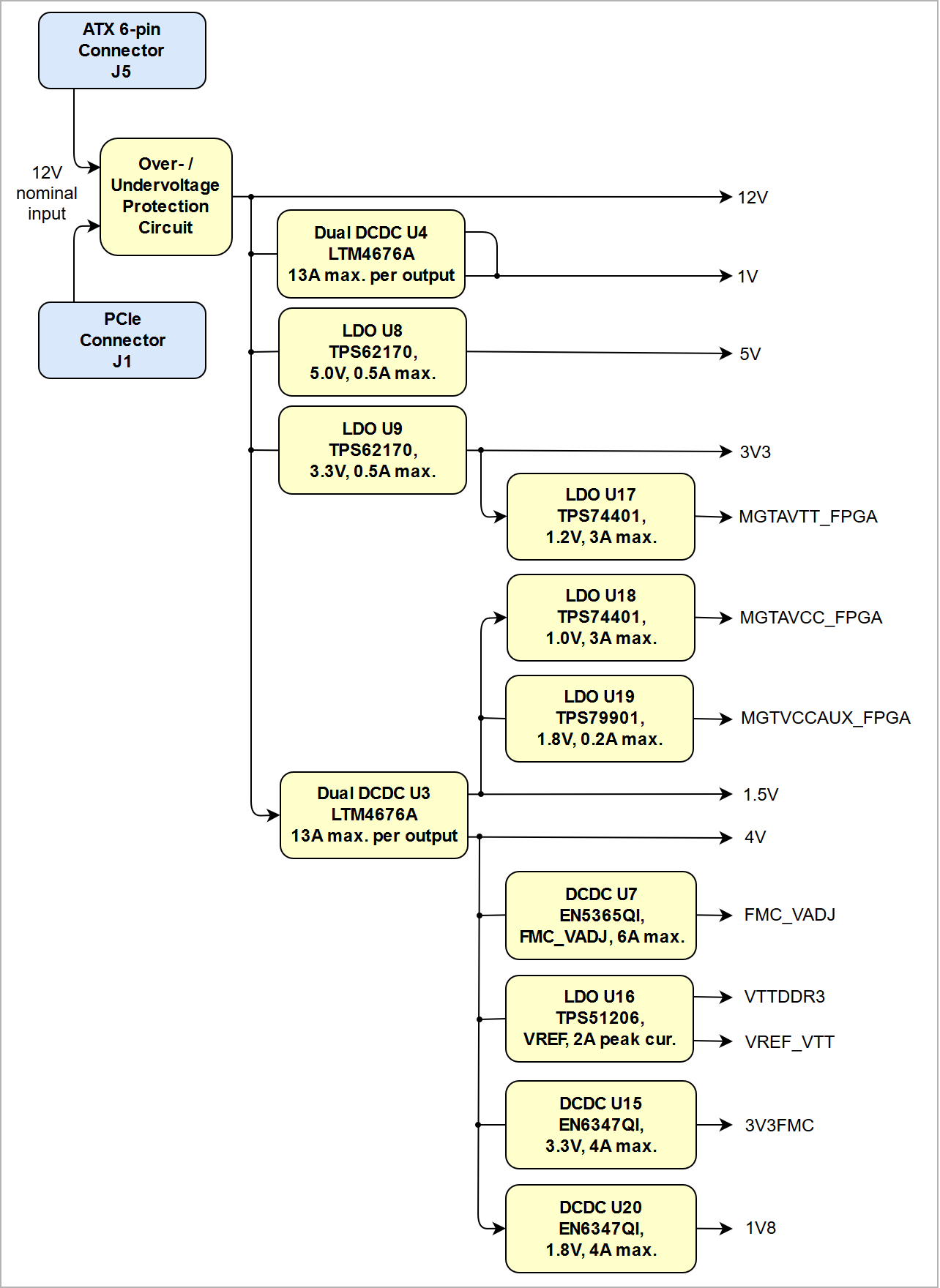
Power Distribution Dependencies
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
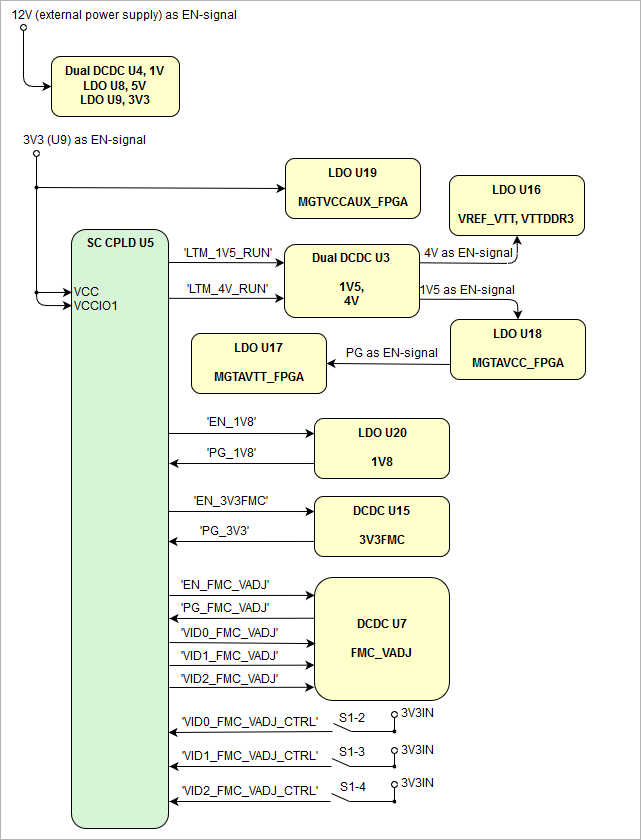
Power-On Sequence
The TEF1001 board meets the recommended criteria to power up the Xilinx FPGA properly by keeping a specific sequence of enabling the on-board DC-DC converters dedicated to the particular functional units of the FPGA chip and powering up the on-board voltages.
Some of the voltages are handled by the System Controller CPLD using "Power good"-signals from the voltage regulators:
Following diagram clarifies the sequence of enabling the particular on-board voltages, which will power-up in descending order as listed in the blocks of the diagram:
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Bank Voltages
| Scroll Title | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Power Rails
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Technical Specifications
Absolute Maximum Ratings
| Scroll Title | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Note |
|---|
| Assembly variants for higher storage temperature range are available on request. |
Recommended Operating Conditions
| Scroll Title | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ETH1 PHY connection:
...
Table 9: General overview of the Gigabit Ethernet1 PHY signals
ETH2 PHY connection:
...
-
...
Table 10: General overview of the Gigabit Ethernet2 PHY signals
USB Interface
The TE0782 is equipped with two USB PHY's USB3320 from Microchip (U4 (USB0) and U8 (USB1)). The ULPI interface of USB0 is connected to the Zynq PS USB0, ULPI interface of USB1 to Zynq PS USB1. The I/O Voltage is fixed at 1.8V.
The reference clock input of both PHY's is supplied from an on board 52MHz oscillator (U7).
USB0 PHY connection:
...
Table 11: General overview of the USB0 PHY signals
USB1 PHY connection:
...
Table 12: General overview of the USB1 PHY signals
I2C Interface
The on-board I2C components are connected to bank 35 pins L15 (I2C_SDA) and L14 (I2C_SCL).
I2C addresses for on-board components:
...
Table 13: Address table of the I2C bus slave devices
Pin Definitions
Pins with names ending with _VRN and _VRP are connected to Zynq PL HP bank special purpose pins VRN/VRP and can be routed to DCI calibration resistors on the baseboard. Otherwise they are usable as general purpose I/Os.
Bank 35 has 100 ohm DCI calibration resistors installed, it is also possible to "borrow" the DCI calibration from bank 35 for banks 34 and 33. For more detailed information about the DCI check Xilinx documentation.
On-board Peripherals
System Controller CPLD
The System Controller CPLD (U14) is provided by Lattice Semiconductor LCMXO2-1200HC (MachXO2 product family). It is the central system management unit with module specific firmware installed to monitor and control various signals of the FPGA, on-board peripherals, I/O interfaces and module as a whole.
See also TE0782 CPLD reference Wiki page.
eMMC Flash Memory
eMMC Flash memory device (U15) is connected to the Zynq PS MIO bank 500 pins MIO10..MIO15. eMMC chips MTFC4GMVEA-4M IT (Flash NAND-IC 2x 16 Gbit) is used with 4 GByte of memory density.
DDR3L Memory
By default TE0782-02 module has two 16-bit wide IM (Intelligent Memory) IM4G16D3FABG-125I DDR3L SDRAM (DDR3-1600 Speedgrade) chips (U10, U19) arranged into 32-bit wide memory bus providing total of 1 GBytes of on-board RAM.
Quad SPI Flash Memory
Two quad SPI compatible serial bus flash memory for FPGA configuration file storage is provided by Spansion S25FL256SAGBHI20 (U38) with 256 Mbit (32 MByte) memory density. After configuration completes the remaining free memory can be used for application data storage. All four SPI data lines are connected to the FPGA allowing x1, x2 or x4 data bus widths to be used. The maximum data transfer rate depends on the bus width and clock frequency.
Gigabit Ethernet PHYs
On-board Gigabit Ethernet PHYs (U18, U20) are provided by Marvell Alaska 88E1512. The Ethernet PHYs' RGMII interfaces are connected to the Zynq's PS MIO bank 501 and to PL bank 9. I/O voltage is fixed at 1.8V for HSTL signaling. The reference clock input of both PHYs is supplied from an on-board 25.000000 MHz oscillator (U11).
High-speed USB ULPI PHYs
Hi-speed USB ULPI PHYs (U4. U8) are provided with USB3320 from Microchip. The ULPI interfaces are connected to the Zynq PS USB0 and USB1 via MIO28..51, bank 501 (see also section USB interface). The I/O voltage is fixed at 1.8V and PHY reference clock input is supplied from the on-board 52.000000 MHz oscillator (U7).
MAC Address EEPROMs
Two Microchip 24AA025E48 serial EEPROMs (U22, U24) contain globally unique 48-bit node address, which are compatible with EUI-48(TM) specification. The devices are organized as two blocks of 128 x 8 Kbit memory. One of the blocks stores the 48-bit node address and is write protected, the other block is available for application use. The MAC address EEPROMS areaccessible over I2C bus (see also section I²C interface).
Configuration EEPROM
The TE0782 board contains one EEPROM (U26) for configuration and general user purposes. The EEPROMs is provided by Microchip 24LC128-I/ST with 128 KBit memory density, the EEPROM is areaccessible over I2C bus (see also section I²C interface).
Programmable Clock Generator
There is a Silicon Labs I2C programmable clock generator Si5338A (U2) chip on-board. It's output frequencies can be programmed using the I2C bus address 0x70 or 0x71. Default address is 0x70, IN4/I2C_LSB pin must be set to high for address 0x71.
A 25.000000 MHz oscillator (U3) is connected to the pin IN3 and is used to generate the output clocks. The output voltage of the oscillator is provided by the 1.8V power rail, thus making output frequency available as soon as 1.8V is present. All 4 of the Si5338 clock outputs are connected to the MGT banks of the Zynq device. It is possible to use the clocks connected to the GTR bank in the user's logic design. This is achieved by instantiating a IBUFDSGTE buffer in the design.
Once running, the frequency and other parameters can be changed by programming the device using the I2C bus connected between the FPGA (master) and clock generator (slave). For this, proper I2C bus logic has to be implemented in FPGA.
...
External clock signal supply from B2B connector J3, pins J3-38 / J3-40
...
IN3
...
25.000000 MHz
...
Fixed input clock signal from reference clock generator SiT8008BI-73-18S-25.000000E (U3)
...
IN5
...
-
...
Not connected
...
IN6
...
-
...
-
...
reference clock 0 of Bank 112 GTX
...
CLK1 A/B
...
reference clock 1 of Bank 111 GTX
...
CLK2 A/B
...
-
...
reference clock 0 of Bank 110 GTX
...
Table 14: General overview of the on-board quad clock generator I/O signals
Oscillators
The module has following reference clock signals provided by on-board oscillators and external source from carrier board:
...
Table 15: Reference clock signals
On-board LEDs
...
Table 16: On-board LEDs
Power and Power-on Sequence
Power Supply
Power supply with minimum current capability of 4A for system startup is recommended.
Power Consumption
...
* TBD - To Be Determined soon with reference design setup.
| Warning |
|---|
| To avoid any damage to the module, check for stabilized on-board voltages should be carried out (i.e. power good and enable signals) before powering up any Zynq's I/O bank voltages VCCO_x. All I/Os should be tri-stated during power-on sequence. |
Power Distribution Dependencies
The Trenz TE0782 SoM is equipped with two quad DC-DC voltage regulators to generate required on-board voltage levels 1V, 3.3V, 1.8V, 1.2V_MGT, 1V_MGT. Additional voltage regulators are used to generate voltages 1.5V, VTT, VTTREF and 1.8V_MGT.
The power supply voltage 'C3.3V' of System Controller CPLD of the SoM have to be externally supplied with 3.3V nominal.
There are following dependencies how the initial voltages of the power rails on the B2B connectors are distributed to the on-board DC-DC converters, which power up further DC-DC converters and the particular on-board voltages:
...
| anchor | Figure_3 |
|---|---|
| title | Figure 3: TE0782-02 Power Distribution Diagram |
...
Power-On Sequence
Power-on sequence is handled by the System Controller CPLD using "Power good"-signals from the voltage regulators:
...
| anchor | Figure_4 |
|---|---|
| title | Figure 4: TE0782-02 Power-on Sequence Diagram |
...
111, 112, 123, 124, 135 136
169, 170, 171, 172
...
Table 18: Module power rails
Bank Voltages
...
See Xilinx Zynq-7000 datasheet DS191 for the voltage ranges allowed.
Board to Board Connectors
The TE0782 SoM has three 160-pin double-row ASP-122952-01 Samtec connectors on the bottom side which mate with ASP-122953-01 Samtec connectors on the baseboard. Mating height is 5 mm.
Variants Currently In Production
...
Technical Specifications
Absolute Maximum Ratings
...
Parameter
...
Units
...
Notes
...
VIN supply voltage
...
-0.3
...
15
...
V
...
Voltage on SC CPLD pins
...
-0.5
...
V
...
Storage temperature
...
-40
...
+85
...
°C
...
Table 20: Module absolute maximum ratings
Recommended Operating Conditions
...
|
...
|
1) Temperature range may vary depending on assembly options
2) The operating temperature range of the FPGA soC and on-board peripherals are junction and also ambient operating temperature ranges
Board operating temperature range depends also on customer design and cooling solution. Please contact us for options.
| Note |
|---|
| Please check also Xilinx datasheet DS182 for complete list of absolute maximum and recommended operating ratings. |
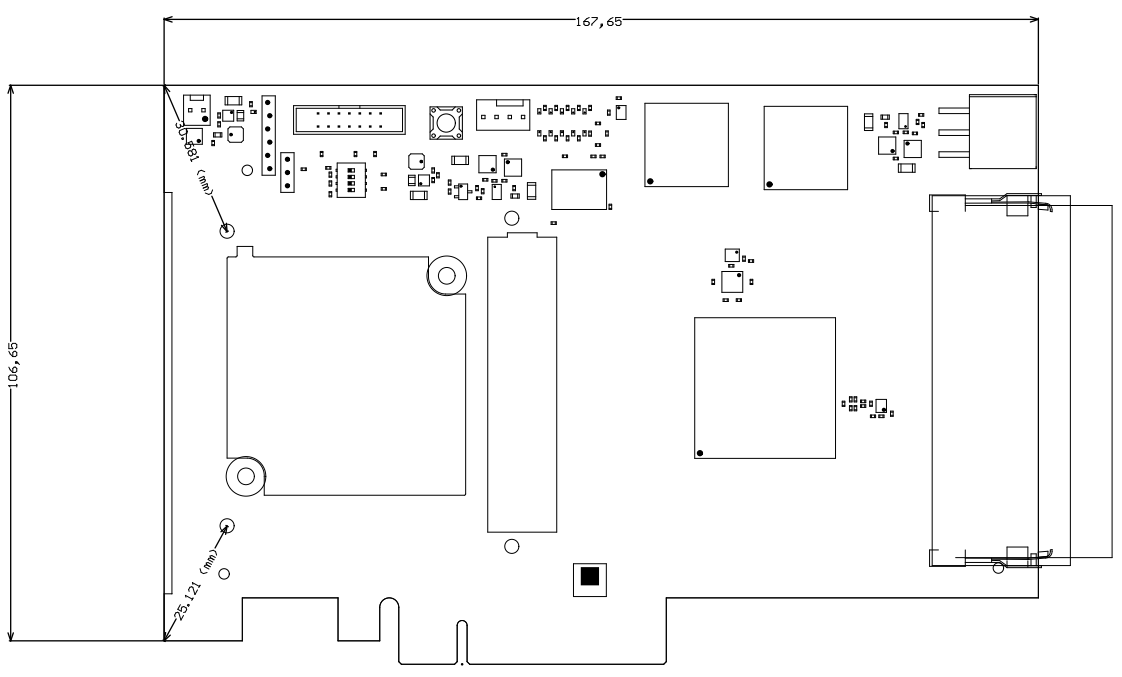
Physical Dimensions
| Scroll Title | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Variants Currently In Production
| Page properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
|
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
Revision History
Hardware Revision History
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
Table 21: Recommended operating conditions
Module operating temperature range depends also on customer design and cooling solution. Please contact us for options.
| Note |
|---|
| See Xilinx datasheet DS191 for more information about absolute maximum and recommended operating ratings for the Zynq-7000 chips. |
Physical Dimensions
Module size: 85 mm × 85 mm. Please download the assembly diagram for exact numbers.
Mating height with standard connectors: 5 mm
PCB thickness: 1.7 mm
All dimensions are shown in millimeters.
...
| anchor | Figure_5 |
|---|---|
| title | Figure 5: Module physical dimensions drawing |
Revision History
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
...
|
...
|
...
|
| Scroll Title | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Document Change History
| |
Hardware revision number can be found on the PCB board together with the module model number separated by the dash.
Document Change History
| Page properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| ||||
| HTML | ||||
<!--
Generate new entry:
1.add new row below first
2.Copy "Page Information
|
| Scroll Title | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
Disclaimer
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|