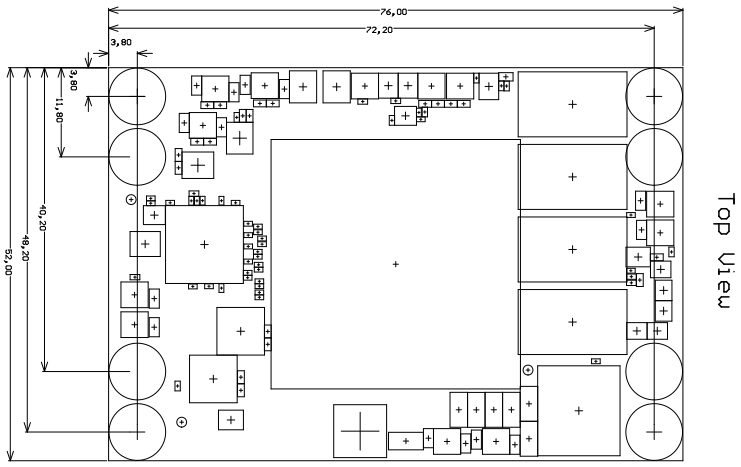
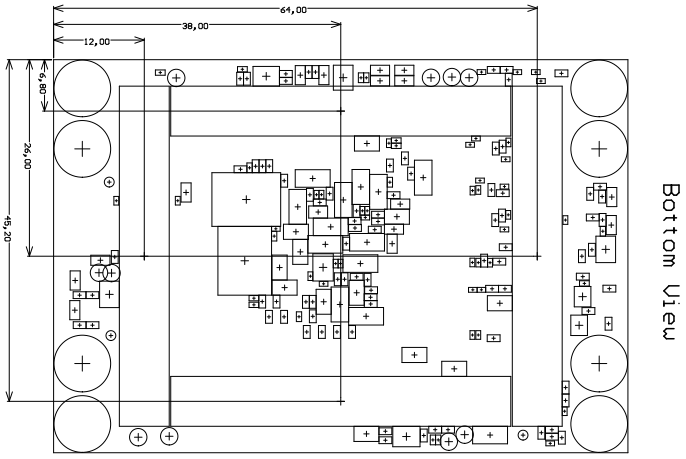
Download PDF version of this document.
Table of Contents
Overview
The Trenz Electronic TE0807 is an industrial-grade MPSoC SoM integrating an AMD Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC, up to 8 GBytes of DDR4 SDRAM via 64 bit wide data bus, max. 512 MByte Flash memory for configuration and operation, 20 Gigabit transceivers and powerful switch-mode power supplies for all on-board voltages. A large number of configurable I/Os are provided via rugged high-speed stacking connections. All this in a compact 5.2 x 7.6 cm form factor, at the competitive price.
Key Features
- MPSoC: ZYNQ UltraScale+ ZU7EV 900-pin package
- Memory
- 64 bit DDR4, 8 GByte maximum
- Dual SPI boot Flash in parallel, 512 MByte maximum - User I/Os
- 65 x PS MIOs, 48 x PL HD GPIOs, 156 x PL HP GPIOs (3 banks)
- Serial transceivers: 4 x GTR + 16 x GTH
- Transceiver clocks inputs and outputs
- PLL clock generator inputs and outputs - Si5345 - 10 output PLL
- All power supplies on board, single 3.3V power source required
- LPD, FPD, PL separately controlled power domains - Support for all boot modes (except NAND) and scenarios
- Support for any combination of PS connected peripherals
- Size: 52 x 76 mm, 3 mm mounting holes for skyline heat spreader
- B2B connectors: 4 x 160 pin
Additional assembly options are available for cost or performance optimization upon request.
Block Diagram
Main Components
- AMD ZYNQ UltraScale+ ZU7EV-1FBVB900 MPSoC, U1
- MPQ8633B 20 A PowerSoC DC-DC converter, U4
- TI TPS72018 LDO @1.8V, U6
- TI TPS74401 LDO @0.9V, U14
- TI TPS74401 LDO @1.2V, U28
- Clock, U5
- Quarz Crystal @50.000MHz, Y1
- Low-power programmable oscillator @ 25.000000 MHz (IN0 for U5), U25
- TI TPS74801 LDO @1.8V, U10
- TI TPS74801 LDO @0.9V, U8
- 8 Gbit (512Mx16) DDR4-2400 SDRAM, U12
- 8 Gbit (512Mx16) DDR4-2400 SDRAM, U9
- 8 Gbit (512Mx16) DDR4-2400 SDRAM, U2
- 8 Gbit (512Mx16) DDR4-2400 SDRAM, U3
- Ultra fine 0.50 mm pitch, Razor Beam™ LP Slim Terminal Strip with 160 contacts, J3
- Ultra fine 0.50 mm pitch, Razor Beam™ LP Slim Terminal Strip with 160 contacts, J1
- Ultra fine 0.50 mm pitch, Razor Beam™ LP Slim Terminal Strip with 160 contacts, J4
- Ultra fine 0.50 mm pitch, Razor Beam™ LP Slim Terminal Strip with 160 contacts, J2
- 1.8V, 512 Mbit QSPI flash memory ,U17
- 1.8V, 512 Mbit QSPI flash memory, U7
- TI TPS72018 LDO @1.8V, U27
Initial Delivery State
| Storage Device Name | Content | Notes |
|---|---|---|
SPI Flash OTP Area | Empty, not programmed | Except serial number programmed by flash vendor. |
SPI Flash Quad Enable bit | Programmed | - |
SPI Flash main array | Not programmed | - |
eFUSE USER | Not programmed | - |
eFUSE Security | Not programmed | - |
| Si5345A OTP NVM | Not programmed | - |
Table 1: Initial delivery state of programmable devices on the module
Boot Process
The boot device and mode of the Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC can be selected via 4 dedicated pins accessible on B2B connector J2:
| Boot Mode Pin | B2B Pin |
|---|---|
| PS_MODE0 | J2-109 |
| PS_MODE1 | J2-107 |
| PS_MODE2 | J2-105 |
| PS_MODE3 | J2-103 |
Table 2: Boot mode pins on B2B connector J2.
Following boot modes are possible on the TE0808 UltraScale+ module by generating the corresponding 4-bit code by the pins PS_MODE0 ... PS_MODE3 (little-endian alignment):
| Boot Mode | Mode Pins [3:0] | MIO Location | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| JTAG | 0x0 | JTAG | Dedicated PS interface. |
| QSPI32 | 0x2 | MIO[12:0] | Configured on module with dual QSPI Flash Memory. 32-bit addressing. |
| SD0 | 0x3 | MIO[25:13] | Supports SD 2.0. |
| SD1 | 0x5 | MIO[51:38] | Supports SD 2.0. |
| eMMC_18 | 0x6 | MIO[22:13] | Supports eMMC 4.5 at 1.8V. |
| USB 0 | 0x7 | MIO[52:63] | Supports USB 2.0 and USB 3.0. |
| PJTAG_0 | 0x8 | MIO[29:26] | PS JTAG connection 0 option. |
| SD1-LS | 0xE | MIO[51:39] | Supports SD 3.0 with a required SD 3.0 compliant level shifter. |
Table 3: Selectable boot modes by dedicated boot mode pins
For functional details see ug1085 - Zynq UltraScale+ TRM (Boot Modes Section).
Signals, Interfaces and Pins
Board to Board (B2B) connectors
The TE0807 MPSoC SoM has four Board to Board (B2B) connectors with 160 contacts per connector.
Each connector has a specific arrangement of the signal pins, which are grouped together in categories related to their functionalities and to their belonging to particular units of the Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC like I/O banks, interfaces and Gigabit transceivers
or to the on-board peripherals.
Following table lists the I/O-bank signals, which are routed from the MPSoC's PL and PS banks as LVDS pairs or single ended I/O's to the B2B connectors.
| Bank | Type | B2B Connector | I/O Signal Count | Bank Voltage | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 47 | HD | J3 | 24 single-ended I/Os or 12 LVDS pairs | VCCO47 | VCCO max. 3.3V |
| 48 | HD | J3 | 24 single-ended I/Os or 12 LVDS pairs | VCCO48 | VCCO max. 3.3V |
| 64 | HP | J4 | 52 single-ended I/O's or 24 LVDS pairs | VCCO64 | VCCO max. 1.8V |
| 65 | HP | J4 | 52 single-ended I/Os or 24 LVDS pairs | VCCO65 | VCCO max. 1.8V |
| 66 | HP | J1 | 52 single-ended I/Os or 24 LVDS pairs | VCCO66 | VCCO max. 1.8V |
| 500 | MIO | J3 | 13 I/Os | PS_1V8 | User configurable I/Os on B2B |
| 501 | MIO | J3 | 26 I/Os | PS_1V8 | User configurable I/Os on B2B |
| 502 | MIO | J3 | 26 I/Os | PS_1V8 | User configurable I/Os on B2B |
Table 4: B2B connector pin-outs of available PL and PS banks of the TE0807-03 SoM.
All MIO banks are powered from on-module DC-DC power rail. All PL I/O Banks have separate VCCO pins in the B2B connectors, valid VCCO should be supplied from the baseboard.
For detailed information about the B2B pin-out, please refer to the Pin-out table.
The configuration of the I/O's MIO13 - MIO77 are depending on the base-board peripherals connected to these pins.
MGT Lanes
The AMD Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC device used on the TE0807 module has 20 high-speed data lanes (AMD GTH / GTR transceiver). All of them are wired directly to B2B connector. MGT (Multi Gigabit Transceiver) lane consists of one transmit and one receive (TX/RX) differential pairs, four signals total per one MGT lane. Following table lists lane number, MGT bank number, transceiver type, signal schematic name, board-to-board pin connection and FPGA pins connection:
| Bank | Type | Lane | Signal Name | B2B Pin | FPGA Pin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 224 | GTH | 0 |
|
|
|
| 1 |
|
|
| ||
| 2 |
|
|
| ||
| 3 |
|
|
| ||
| 225 | GTH | 0 |
|
|
|
| 1 |
|
|
| ||
| 2 |
|
|
| ||
| 3 |
|
|
| ||
| 226 | GTH | 0 |
|
|
|
| 1 |
|
|
| ||
| 2 |
|
|
| ||
| 3 |
|
|
| ||
| 227 | GTH | 0 |
|
|
|
| 1 |
|
|
| ||
| 2 |
|
|
| ||
| 3 |
|
|
| ||
| 505 | GTR | 0 |
|
|
|
| 1 |
|
|
| ||
| 2 |
|
|
| ||
| 3 |
|
|
|
Table 5: MGT lanes
There are 2 clock sources for the GTH and GTR transceivers. The clock inputs of the MGT transceivers are connected directly to the B2B connectors, so the clock can be provided by the carrier board. The second clock source is provided by the on-board clock generator Si5345A (U5). As there are no capacitive coupling of the data and clock lines that are connected to the B2B connectors, these may be required on the user’s PCB depending on the application.
| Clock signal | Bank | Source | FPGA Pin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B224_CLK0_P | 224 | B2B, J3-62 | MGTREFCLK0P_224, R8 | Supplied by the carrier board |
| B224_CLK0_N | 224 | B2B, J3-60 | MGTREFCLK0N_224, R7 | Supplied by the carrier board |
| B224_CLK1_P | 224 | U5, CLK4_P | MGTREFCLK1P_224, N8 | On-board Si5345A |
| B224_CLK1_N | 224 | U5, CLK4_N | MGTREFCLK1N_224, N7 | On-board Si5345A |
| B225_CLK0_P | 225 | B2B, J3-67 | MGTREFCLK0P_225, L8 | Supplied by the carrier board |
| B225_CLK0_N | 225 | B2B, J3-65 | MGTREFCLK0N_225, L7 | Supplied by the carrier board |
| B225_CLK1_P | 225 | U5, CLK3_P | MGTREFCLK1P_225, J8 | On-board Si5345A |
| B225_CLK1_N | 225 | U5, CLK3_N | MGTREFCLK1N_225, J7 | On-board Si5345A |
| B226_CLK0_P | 226 | U5, CLK2_P | MGTREFCLK0P_226, H10 | On-board Si5345A |
| B226_CLK0_N | 226 | U5, CLK2_N | MGTREFCLK0N_226, H9 | On-board Si5345A |
| B226_CLK1_P | 226 | B2B, J3-61 | MGTREFCLK1P_226, F10 | Supplied by the carrier board |
| B226_CLK1_N | 226 | B2B, J3-59 | MGTREFCLK1N_226, F9 | Supplied by the carrier board |
| B227_CLK0_P | 227 | U5, CLK1_P | MGTREFCLK0P_227, D10 | On-board Si5345A |
| B227_CLK0_N | 227 | U5, CLK1_N | MGTREFCLK0N_227, D9 | On-board Si5345A |
| B227_CLK1_P | 227 | B2B, J2-22 | MGTREFCLK1P_227, B10 | Supplied by the carrier board |
| B227_CLK1_N | 227 | B2B, J2-24 | MGTREFCLK1N_227, B9 | Supplied by the carrier board |
| B505_CLK0_P | 505 | B2B, J2-10 | PS_MGTREFCLK0P_505, M23 | Supplied by the carrier board |
| B505_CLK0_N | 505 | B2B, J2-12 | PS_MGTREFCLK0N_505, M24 | Supplied by the carrier board |
| B505_CLK1_P | 505 | B2B, J2-16 | PS_MGTREFCLK1P_505, L25 | Supplied by the carrier board |
| B505_CLK1_N | 505 | B2B, J2-18 | PS_MGTREFCLK1N_505, L26 | Supplied by the carrier board |
| B505_CLK2_P | 505 | U5, CLK5_P | PS_MGTREFCLK2P_505, K23 | On-board Si5345A |
| B505_CLK2_N | 505 | U5, CLK5_N | PS_MGTREFCLK2N_505, K24 | On-board Si5345A |
| B505_CLK3_P | 505 | U5, CLK6_P | PS_MGTREFCLK3P_505, H23 | On-board Si5345A |
| B505_CLK3_N | 505 | U5, CLK6_N | PS_MGTREFCLK3N_505, H24 | On-board Si5345A |
Table 6: MGT reference clock sources
JTAG Interface
JTAG access is provided through the MPSoC's PS configuration bank 503 with bank voltage PS_1V8.
| JTAG Signal | B2B Connector Pin |
|---|---|
| TCK | J2-120 |
| TDI | J2-122 |
| TDO | J2-124 |
| TMS | J2-126 |
Table 7: B2B connector pin-out of JTAG interface.
Configuration Bank Control Signals
The AMD Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC's PS configuration bank 503 control signal pins are accessible through B2B connector J2.
For further information about the particular control signals and how to use and evaluate them, refer to the AMD Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC TRM and UltraScale Architecture Configuration - User Guide.
| Signal | B2B Connector Pin | Function |
|---|---|---|
| DONE | J2-116 | PL configuration completed. |
| PROG_B | J2-100 | PL configuration reset signal. |
| INIT_B | J2-98 | PS is initialized after a power-on reset. |
| SRST_B | J2-96 | System reset. |
| MODE0 ... MODE3 | J2-109/J2-107/J2-105/J2-103 | 4-bit boot mode pins. For further information about the boot modes refer to the AMD Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC TRM section 'Boot and Configuration'. |
| ERR_STATUS / ERR_OUT | J2-86 / J2-88 | ERR_OUT signal is asserted for accidental loss of power, an error, or an exception in the MPSoC's Platform Management Unit (PMU). ERR_STATUS indicates a secure lock-down state. |
| PUDC_B | J2-127 | Pull-up during configuration (pulled-up to PL_1V8). |
Table 8: B2B connector pin-out of MPSoC's PS configuration bank.
Analog Input
The AMD Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC provides differential pairs for analog input values. The pins are exposed to B2B-connector J2.
| Signal | B2B Connector Pin | Function |
|---|---|---|
| V_P, V_N | J2-113, J2-115 | System Monitor |
| DX_P, DX_N | J2-119, J2-121 | Temperature-sensing diode pins |
Table 9: B2B connector pin-out of analog input pins
Quad SPI Interface
Quad SPI Flash memory ICs U7 and U17 are connected to the Zynq MPSoC PS QSPI0 interface via PS MIO bank 500, pins MIO0 ... MIO5 and MIO7 ... MIO12.
| MIO | Signal Name | U7 Pin | MIO | Signal Name | U17 Pin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | SPI Flash CLK | B2 | 7 | SPI Flash CS | C2 | |
| 1 | SPI Flash IO1 | D2 | 8 | SPI Flash IO0 | D3 | |
| 2 | SPI Flash IO2 | C4 | 9 | SPI Flash IO1 | D2 | |
| 3 | SPI Flash IO3 | D4 | 10 | SPI Flash IO2 | C4 | |
| 4 | SPI Flash IO0 | D3 | 11 | SPI Flash IO3 | D4 | |
| 5 | SPI Flash CS | C2 | 12 | SPI Flash CLK | B2 |
Table 10: PS MIO pin assignment of the Quad SPI Flash memory ICs.
Default PS MIO Mapping
| PS MIO | Function | Connected to |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | SPI0 | U7-B2, CLK |
| 1 | SPI0 | U7-D2, DO/IO1 |
| 2 | SPI0 | U7-C4, WP/IO2 |
| 3 | SPI0 | U7-D4, HOLD/IO3 |
| 4 | SPI0 | U7-D3, DI/IO0 |
| 5 | SPI0 | U7-C2, CS |
| 6 | N/A | Not connected |
| 7 | SPI1 | U17-C2, CS |
| 8 | SPI1 | U17-D3, DI/IO0 |
| 9 | SPI1 | U17-D2, DO/IO1 |
| 10 | SPI1 | U17-C4, WP/IO2 |
| 11 | SPI1 | U17-D4, HOLD/IO3 |
| 12 | SPI1 | U17-B2, CLK |
| 13 ... 77 | user dependent | B2B connector J2 |
Table 11: TE0807-03 PS MIO mapping
On-board Peripherals
Flash
The TE0807 SoM can be configured with max. 512 MByte Flash memory for configuration and operation.
| Name | IC | Designator | PS7 | MIO | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI Flash | MT25QU512ABB8E12-0SIT | U7 | QSPI0 | MIO0 ... MIO5 | dual parallel booting possible, 64 MByte memory per Flash IC at standard configuration |
| SPI Flash | MT25QU512ABB8E12-0SIT | U17 | QSPI0 | MIO7 ... MIO12 |
Table 12: Peripherals connected to the PS MIO pins.
DDR4 SDRAM
The TE0807-03 SoM is equipped with four DDR4 SDRAM chips with a total of up to 8 GByte memory. The SDRAM chips are connected to the Zynq MPSoC's PS DDR controller (bank 504) with a 64 bit wide data bus.
Refer to the AMD Zynq UltraScale+ datasheet DS925 for more information on whether the specific package of the Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC supports the maximum data transmission rate of 2400 MByte/s.
Programmable PLL Clock Generator
Following table illustrates on-board Si5345A programmable clock multiplier chip inputs and outputs:
| Input | Connected to | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| IN0 | On-board Oscillator (U25) | 25.000000 MHz | - |
| IN1 | B2B Connector pins J2-4, J2-6 (differential pair) | User | AC decoupling required on base |
| IN2 | B2B Connector pins J3-66, J3-68 (differential pair) | User | AC decoupling required on base |
| IN3 | OUT9 | User | Loop-back from OUT9 |
| XA/XB | Quartz (Y1) | 50.000 MHz | - |
| Output | Connected to | Frequency | Notes |
| OUT0 | B2B Connector pins J2-3, J2-1 (differential pair) | User | Default off |
| OUT1 | B227 CLK0 | User | Default off |
| OUT2 | B226 CLK0 | User | Default off |
| OUT3 | B225 CLK1 | User | Default off |
| OUT4 | B224 CLK1 | User | Default off |
| OUT5 | B505 CLK2 | User | Default off |
| OUT6 | B505 CLK3 | User | Default off |
| OUT7 | B2B Connector pins J2-7, J2-9 (differential pair) | User | Default off |
| OUT8 | B2B Connector pins J2-13, J2-15 (differential pair) | User | Default off |
| OUT9 | IN3 (Loop-back) | User | Default off |
Table 13: Programmable PLL clock generator input/output.
The Si5345A programmable clock generator's control interface pins are exposed to B2B connector J2. For further information refer to the Si5345A data sheet.
| Signal | B2B Connector Pin | Function |
|---|---|---|
| PLL_FINC | J2-81 | Frequency increment |
| PLL_LOLN | J2-85 | Loss of lock (active-low) |
| PLL_SEL0 / PLL_SEL1 | J2-93 / J2-87 | Manual input switching |
| PLL_FDEC | J2-94 | Frequency decrement |
| PLL_RST | J2-89 | Device reset (active-low) |
| PLL_SCL / PLL_SDA | J2-90 / J2-92 | I2C interface, external pull-ups needed for SCL / SDA lines I2C address in current configuration: 1101001b. |
Table 14: B2B connector pin-out of Si5345A programmable clock generator.
Si5345 OTP ROM is not programmed by default at delivery, so it is customers responsibility to either configure Si5345 during FSBL or then use SiLabs programmer and program the OTP ROM with customer fixed clock setup.
Si5345 OTP can only be programmed two times, as different user configurations may required different setup TE0807 is normally shipped with blank OTP.
For more information refer to Si5345 at SiLabs.
Oscillators
The TE0807-04 SoM is equipped with two on-board oscillators to provide the Zynq's MPSoC's PS configuration bank 503 with reference clock signals.
| Clock | Signal Schematic Name | Frequency | Connected to Bank 503 Pin |
|---|---|---|---|
| MEMS Oscillator, U32 | PS_CLK | 33.333333 MHz | Bank 503 Pin P20 |
| Quartz crystal, Y2 | XTALI / XTALO | 32.768 kHz | Bank 503 Pin R22/R23 |
| Quartz crystal, Y1 | XAXB_P / XAXB_N | 50.000 MHz | PLL U5, Pin XA/XB |
Table 15: On-board osciallators
MAC Address EEPROMs
There is one Microchip 24AA025E48 serial EEPROMs (U11) present containing a globally unique 48-bit node address, which are compatible with EUI-48(TM) specification. The device are organized as two blocks of 128 x 8 Kbit memory. One of the blocks stores the 48-bit node address and is write protected, the other block is available for application use. The MAC address EEPROM accessible over I2C bus on B2B connector J2-92 (PLL_SDA) / J2-90 (PLL_SCL).
On-board LEDs
LED | Color | Connected to | Description and Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | Red | DONE signal (PS Configuration Bank 503) | This LED goes ON when power has been applied to the module and stays ON until MPSoC's programmable logic is configured properly. |
Table 16: LED's description.
Power and Power-On Sequence
Power Consumption
The maximum power consumption of a module mainly depends on the design which is running on the FPGA.
AMD provide a power estimator excel sheets to calculate power consumption. It's also possible to evaluate the power consumption of the developed design with Vivado. See also Trenz Electronic Wiki FAQ.
| Power Input Pin | Typical Current |
|---|---|
| DCDCIN | TBD* |
| LP_DCDC | TBD* |
| PL_DCIN | TBD* |
| PS_BATT | TBD* |
Table 17: Maximum current of power supplies. *to be determined soon with reference design setup.
Power supply with minimum current capability of 3A for system startup is recommended. For the lowest power consumption and highest efficiency of on board DC/DC regulators it is recommended to powering the module from one single 3.3V supply. Except 'PS_BATT', all input power supplies have a nominal value of 3.3V. Although the input power supplies can be powered up in any order, it is recommended to power them up simultaneously.
The TE0807 module equipped with the AMD Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC delivers a heterogeneous multi-processing system with integrated programmable logic and independently operable elements and is designed to meet embedded system power management requirement by advanced power management features. This features allow to offset the power and heat constraints against overall performance and operational efficiency.
This features allowing highly flexible power management are achieved by establishing Power Domains for power isolation. The Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC has multiple power domains, whereby each power domain requires its own particular external DC-DC converters.
The Processing System contains three Power Domains:
- Battery Power Domain (BBRAM and RTC)
- Full-Power Domain (Application Processing Unit, DDR Controller, Graphics Processing Unit and High-Speed Connectivity)
- Low-Power Domain (Real-Time Processing Unit, Security and Configuration Unit, Platform Management Unit, System Monitor and General Connectivity)
The fourth Power Domain is for the Programmable Logic (PL). If individual Power Domain control is not required, power rails can be shared between domains.
On the TE0807 SoM, following power domains can be powered up individually with power rails available on the B2B connectors:
- Full-power domain, supplied by power rail DCDCIN
- Low-power domain, supplied by power rail LP_DCDC
- Programmable logic, supplied by power rail PL_DCIN
- Battery power domain, supplied by power rail PS_BATT
Each power domain has its own enable and power good signals. The power rail GT_DCDC is needed to generate the voltages for the Multi Gigabit Transceiver units of the Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC.
Power Distribution Dependencies
The power rails DCDCIN, LP_DCDC, PL_DCIN, PS_BATT have to be powered up on the assigned pins of the B2B connectors as listed on the section "Power Rails". Except 'PS_BATT' (see section "Recommended Operation Conditions"), all power-rails can be powered from 3.3V power sources (also share the same source, if power domain control is not required).
There are following dependencies how the initial voltages of the power rails on the B2B connectors are distributed to the on-board DC-DC converters, which power up further DC-DC converters and the particular on-board voltages:
See also AMD datasheet DS925 for additional information. User should also check related base board documentation when intending base board design for TE0807 module.
Power-On Sequence
The TE0807 SoM meets the recommended criteria to power up the AMD Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC properly by keeping a specific sequence of enabling the on-board DC-DC converters dedicated to the particular Power Domains and powering up the on-board voltages.
The on-board voltages of the TE0807 SoM will be powered-up in order of a determined sequence by activating the above-mentioned power rails and the Enable-Signals of the DC-DC converters. The on-board voltages will be powered up at three steps.
- Low-Power Domain (LPD) and on-board Si5345A programmable clock generator supply voltage
- Programmable Logic (PL) and Full-Power Domain (FPD)
- GTH, PS GTR transceiver and DDR memory
Hence, those three power instances will be powered up consecutively and the Power-Good-Signals of the previous instance has to be asserted.
Following diagram describes the sequence of enabling the three power instances utilizing the DC-DC converter control signals (Enable, Power-Good), which will power-up in descending order as listed in the blocks of the diagram.
Operation Conditions of the DC-DC Converter Control Signals
The control signals have to be asserted on the B2B connector J2, whereby some of the Power-Good signals need external pull-up resistors.
| Enable-Signal | B2B Connector Pin | Max. Voltage | Note | Power-Good-Signal | B2B Connector Pin | Pull-up Resistor | Note | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN_LPD | J2-108 | 6.5V | MPM3834CGPA data sheet | LP_GOOD | J2-106 | 4K7, pulled up to LP_DCDC | - | |
| EN_FPD | J2-102 | DCDCIN | NC7S08P5X data sheet | PG_FPD | J2-110 | 4K7, pulled up to DCDCIN | - | |
| EN_PL | J2-101 | PL_DCIN | left floating for logic high (drive to GND for logic low) | PG_PL | J2-104 | 10K, pulled up to PL_DCIN | - | |
| EN_DDR | J2-112 | DCDCIN | NC7S08P5X data sheet | PG_DDR | J2-114 | 4K7, pulled up to DCDCIN | - | |
| EN_PSGT | J2-84 | DCDCIN | NC7S08P5X data sheet | PG_PSGT | J2-82 | External pull-up needed (max. 5.5V), max. sink current 1 mA | TPS74801 data sheet | |
| EN_GT_R | J2-95 | GT_DCDC | NC7S08P5X data sheet | PG_GT_R | J2-91 | External pull-up needed (max. 5.5V), max. sink current 1 mA | TPS74401 data sheet | |
| EN_PLL_PWR | J2-77 | 6.5V | MPM3834CGPA data sheet | PG_PLL_1V8 | J2-80 | 10K, pulled up to GT_DCDC | TPS82085SIL data sheet |
Table 18: Recommended operation conditions of DC-DC converter control signals.
Core voltages and main supply voltages have to reach stable state and their "Power Good"-signals have to be asserted before other voltages like bank's I/O voltages (VCCOx) can be powered up.
It is important that all PS and PL I/Os are tri-stated at power-on until the "Power Good"-signals are high, meaning that all on-module voltages have become stable and module is properly powered up.
See AMD datasheet DS925 for additional information. User should also check related base board documentation when intending base board design for TE0807 SoM.
Voltage Monitor Circuit
The voltages LP_DCDC and LP_0V85 are monitored by the voltage monitor circuit U41, which generates the POR_B reset signal at power-on. A manual reset is also possible by driving the MR-pin (J2-83) to GND. Leave this pin unconnected or connect to VDD (LP_DCDC) when unused.
Power Rails
Power Rail Name | B2B J1 Pins | B2B J2 Pins | B2B J3 Pins | B2B J4 Pins | Directions | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL_DCIN | 151, 153, 155, 157, 159 | - | - | - | Input | - |
| DCDCIN | - | 154, 156, 158, 160, | - | - | Input | - |
| LP_DCDC | - | 138, 140, 142, 144 | - | - | Input | - |
| PS_BATT | - | 125 | - | - | Input | - |
| GT_DCDC | - | - | 157, 158, 159, 160 | - | Input | - |
| PLL_3V3 | - | - | 152 | - | Input | U5 (programmable PLL) 3.3V nominal input |
| SI_PLL_1V8 | - | - | 151 | - | Output | Internal voltage level 1.8V nominal output |
| PS_1V8 | - | 99 | 147, 148 | - | Output | Internal voltage level |
| PL_1V8 | 91, 121 | - | - | - | Output | Internal voltage level |
| DDR_1V2 | - | 135 | - | - | Output | Internal voltage level |
| VCCO47 | - | - | 43, 44 | - | Input | - |
| VCCO48 | - | - | 15, 16 | - | Input | - |
| VCCO64 | - | - | - | 58, 106 | Input | - |
| VCCO65 | - | - | - | 69, 105 | Input | - |
| VCCO66 | 90, 120 | - | - | - | Input | - |
Table 19: TE0807-03 power rails
Bank Voltages
| Bank | Type | Schematic Name | Voltage | Reference Input Voltage | Voltage Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 47 | HD | VCCO47 | user | - | 1.2V to 3.3V |
| 48 | HD | VCCO48 | user | - | 1.2V to 3.3V |
| 64 | HP | VCCO64 | user | VREF_64, pin J4-88 | 1.2V to 1.8V |
| 65 | HP | VCCO65 | user | VREF_65, pin J4-15 | 1.2V to 1.8V |
| 66 | HP | VCCO66 | user | VREF_66, pin J1-108 | 1.2V to 1.8V |
| 500 | MIO | PS_1V8 | 1.8V | - | - |
| 501 | MIO | PS_1V8 | 1.8V | - | - |
| 502 | MIO | PS_1V8 | 1.8V | - | - |
| 503 | CONFIG | PS_1V8 | 1.8V | - | - |
Table 20: TE0807-03 I/O bank voltages
See AMD Zynq UltraScale+ datasheet DS925 for the voltage ranges allowed.
Board to Board Connectors
- 4x REF-192552-02 (160-pins)
- ST5 Mates with SS5
5.2 x 7.6 cm UltraSoM+ carrier use four Samtec Razor Beam LP Socket Strip (SS5) on the top side.
- 4x REF192552-01 (160-pins)
- SS5 Mates with ST5
Features
- Board-to-Board Connector 160-pins, 80 contacts per row
- Ultrafine .0197" (0.50 mm) pitch
- Narrow body design saves space on board
- Lead style -03.5
- Samtec 28+ Gbps Solution
- Mates with: ST5
- Insulator Material: Liquid Crystal Polymer, schwarz
- Operating Temperature Range: -55°C bis +125°C
- Lead-Free Solderable: Yes
- RoHS Konform: Yes
Connector Stacking height
When using the standard type on baseboard and module, the mating height is 5 mm.
Other mating heights are possible by using connectors with a different height:
| Order number | REF number | Samtec Number | Type | Contribution to stacking height | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27219 | REF192552-01 | SS5-80-3.50-L-D-K-TR | Baseboard connector | 3.5mm | Standard connector used on carrier |
| 27018 | REF-189545-02 | SS5-80-3.00-L-D-K-TR | Baseboard connector | 3 mm | Assembly option on request |
| 27220 | REF-192552-02 | ST5-80-1.50-L-D-P-TR | Module connector | 1.5 mm | Standard connector used on modules |
| 27017 | REF-189545-01 | ST5-80-1.00-L-D-P-TR | Module connector | 1 mm | Assembly option on request |
The module can be manufactured using other connectors upon request.
Current Rating
Current rating of Samtec Razor Beam LP Terminal/Socket Strip ST5/SS5 B2B connectors is 1.5 A per pin (1 pin powered per row).
Connector Speed Ratings
The connector speed rating depends on the stacking height:
Stacking height | Speed rating |
|---|---|
| 4 mm, Single-Ended | 13GHz/26Gbps |
| 4 mm, Differential | 13.5GHz/27Gbps |
| 5 mm, Single-Ended | 13.5GHz/27Gbps |
| 5 mm, Differential | 20GHz/40 Gbps |
The SS5/ST5 series board-to-board spacing is currently available in 4mm (0.157"), 4.5mm (0.177") and 5mm (0.197") stack heights.
The data in the reports is applicable only to the 4mm and 5mm board-to-board mated connector stack height.
Manufacturer Documentation
Variants Currently In Production
| Trenz shop TE0807 overview page | |
|---|---|
| English page | German page |
Technical Specifications
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter | Min | Max | Unit | Notes / Reference Document |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL_DCIN | -0.3 | 4.5 | V | MPQ8633B data sheet |
| DCDCIN | -0.3 | 6.5 | V | MPM3834CGPA data sheet |
| LP_DCDC | -0.3 | 4 | V | TPS3106K33DBVR data sheet |
| GT_DCDC | -0.3 | 6 | V | TPS74401RGW data sheet |
| PS_BATT | -0.5 | 2 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet |
| PLL_3V3 | -0.5 | 3.8 | V | Si5345/44/42 data sheet |
| VCCO for HD I/O banks | -0.5 | 3.4 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet |
| VCCO for HP I/O banks | -0.5 | 2 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet |
| I/O input voltage for HD I/O banks | -0.55 | VCCO + 0.55 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet |
| I/O input voltage for HP I/O banks | -0.55 | VCCO + 0.55 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet |
| PS I/O input voltage (MIO pins) | -0.5 | VCCO_PSIO + 0.55 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet, VCCO_PSIO 1.8V nominally |
| PS GTR reference clocks absolute input voltage | -0.5 | 1.1 | V | AMD document DS925 |
| PS GTR absolute input voltage | -0.5 | 1.1 | V | AMD document DS925 |
| MGT clock absolute input voltage | -0.5 | 1.3 | V | AMD document DS925 |
MGT Receiver (RXP/RXN) and transmitter | -0.5 | 1.2 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet |
Voltage on input pins of | -0.5 | VCC + 0.5 | V | NC7S08P5X data sheet, see schematic for VCC |
Voltage on input pins (nMR) of | -0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V | TPS3106 data sheet, |
| "Enable"-signals on TPS82085SIL (EN_PLL_PWR, EN_LPD) | -0.3 | 7 | V | TPS82085SIL data sheet |
Storage temperature (ambient) | -40 | 100 | °C | ROHM Semiconductor SML-P11 Series data sheet |
Table 21: Module absolute maximum ratings
Recommended Operating Conditions
| Parameter | Min | Max | Unit | Notes / Reference Document |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL_DCIN | 3.3 | 3.399 | V | |
| DCDCIN | 3.3 | 3.465 | V | |
| LP_DCDC | 3.3 | 3.399 | V | |
| GT_DCDC | 3.3 | 3.399 | V | |
| PS_BATT | 1.2 | 1.5 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet |
| PLL_3V3 | 3.3 | 3.47 | V | Si5345/44/42 data sheet 3.3V typical |
| VCCO for HD I/O banks | 1.14 | 3.4 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet |
| VCCO for HP I/O banks | 0.95 | 1.9 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet |
| I/O input voltage for HD I/O banks. | -0.2 | VCCO + 0.2 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet |
| I/O input voltage for HP I/O banks | -0.2 | VCCO + 0.2 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet |
| PS I/O input voltage (MIO pins) | -0.2 | VCCO_PSIO + 0.2 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet, VCCO_PSIO 1.8V nominally |
| PL bank reference voltage VREF pin | -0.5 | 2 | V | AMD DS925 data sheet |
| Voltage on input pins of NC7S08P5X 2-Input AND Gate | 0 | VCC | V | NC7S08P5X data sheet, |
Voltage on input pin 'MR' of | 0 | VDD | V | TPS3106 data sheet, |
Table 22: Recommended operating conditions
Module operating temperature range depends also on customer design and cooling solution. Please contact us for options.
Physical Dimensions
Module size: 52 mm × 76 mm. Please download the assembly diagram for exact numbers
Mating height with standard connectors: 5 mm
PCB thickness: 1.7 mm
Highest part on PCB: approx. 3mm. Please download the step model for exact numbers
All dimensions are given in millimeters.
Revision History
Hardware Revision History
| Date | Revision | Notes | PCN Link | Documentation Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024-07-01 | 04 | current available module revision | PCN-20240514 TE0807-03 to TE0807-04 Hardware Revision Change | TE0807-04 |
| 2020-06-05 | 03 | current available module revision | PCN-20200511 | TE0807-03 |
| - | 02 | current available module revision | - | TE0807-02 |
| - | 01 | first production release | - | TE0807-01 |
Table 23: Hardware revision history table
Document Change History
Date | Revision | Contributors | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
2023-07-12 | v.29 | Markus Kirberg |
|
2021-09-07 |
| ||
| 2021-06-10 | v.27 | John Hartfiel |
|
| 2021-05-17 | v.26 | John Hartfiel |
|
| 2021-05-03 | v.25 | Martin Rohrmüller |
|
2021-03-11 | v.24 | Antti Lukats |
|
2019-06-14 | v.22 | John Hartfiel |
|
2018-08-07 | v.20 | Ali Naseri |
|
Table 24: Document change history
Disclaimer
Data Privacy
Please also note our data protection declaration at https://www.trenz-electronic.de/en/Data-protection-Privacy
Document Warranty
The material contained in this document is provided “as is” and is subject to being changed at any time without notice. Trenz Electronic does not warrant the accuracy and completeness of the materials in this document. Further, to the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, Trenz Electronic disclaims all warranties, either express or implied, with regard to this document and any information contained herein, including but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose or non infringement of intellectual property. Trenz Electronic shall not be liable for errors or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, use, or performance of this document or of any information contained herein.
Limitation of Liability
In no event will Trenz Electronic, its suppliers, or other third parties mentioned in this document be liable for any damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, those resulting from lost profits, lost data or business interruption) arising out of the use, inability to use, or the results of use of this document, any documents linked to this document, or the materials or information contained at any or all such documents. If your use of the materials or information from this document results in the need for servicing, repair or correction of equipment or data, you assume all costs thereof.
Copyright Notice
No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means (including electronic storage and retrieval or translation into a foreign language) without prior agreement and written consent from Trenz Electronic.
Technology Licenses
The hardware / firmware / software described in this document are furnished under a license and may be used /modified / copied only in accordance with the terms of such license.
Environmental Protection
To confront directly with the responsibility toward the environment, the global community and eventually also oneself. Such a resolution should be integral part not only of everybody's life. Also enterprises shall be conscious of their social responsibility and contribute to the preservation of our common living space. That is why Trenz Electronic invests in the protection of our Environment.
REACH, RoHS and WEEE
REACH
Trenz Electronic is a manufacturer and a distributor of electronic products. It is therefore a so called downstream user in the sense of REACH. The products we supply to you are solely non-chemical products (goods). Moreover and under normal and reasonably foreseeable circumstances of application, the goods supplied to you shall not release any substance. For that, Trenz Electronic is obliged to neither register nor to provide safety data sheet. According to present knowledge and to best of our knowledge, no SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) on the Candidate List are contained in our products. Furthermore, we will immediately and unsolicited inform our customers in compliance with REACH - Article 33 if any substance present in our goods (above a concentration of 0,1 % weight by weight) will be classified as SVHC by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA).
RoHS
Trenz Electronic GmbH herewith declares that all its products are developed, manufactured and distributed RoHS compliant.
WEEE
Information for users within the European Union in accordance with Directive 2002/96/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 January 2003 on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE).
Users of electrical and electronic equipment in private households are required not to dispose of waste electrical and electronic equipment as unsorted municipal waste and to collect such waste electrical and electronic equipment separately. By the 13 August 2005, Member States shall have ensured that systems are set up allowing final holders and distributors to return waste electrical and electronic equipment at least free of charge. Member States shall ensure the availability and accessibility of the necessary collection facilities. Separate collection is the precondition to ensure specific treatment and recycling of waste electrical and electronic equipment and is necessary to achieve the chosen level of protection of human health and the environment in the European Union. Consumers have to actively contribute to the success of such collection and the return of waste electrical and electronic equipment. Presence of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment results in potential effects on the environment and human health. The symbol consisting of the crossed-out wheeled bin indicates separate collection for waste electrical and electronic equipment.
Trenz Electronic is registered under WEEE-Reg.-Nr. DE97922676.